District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading
Description
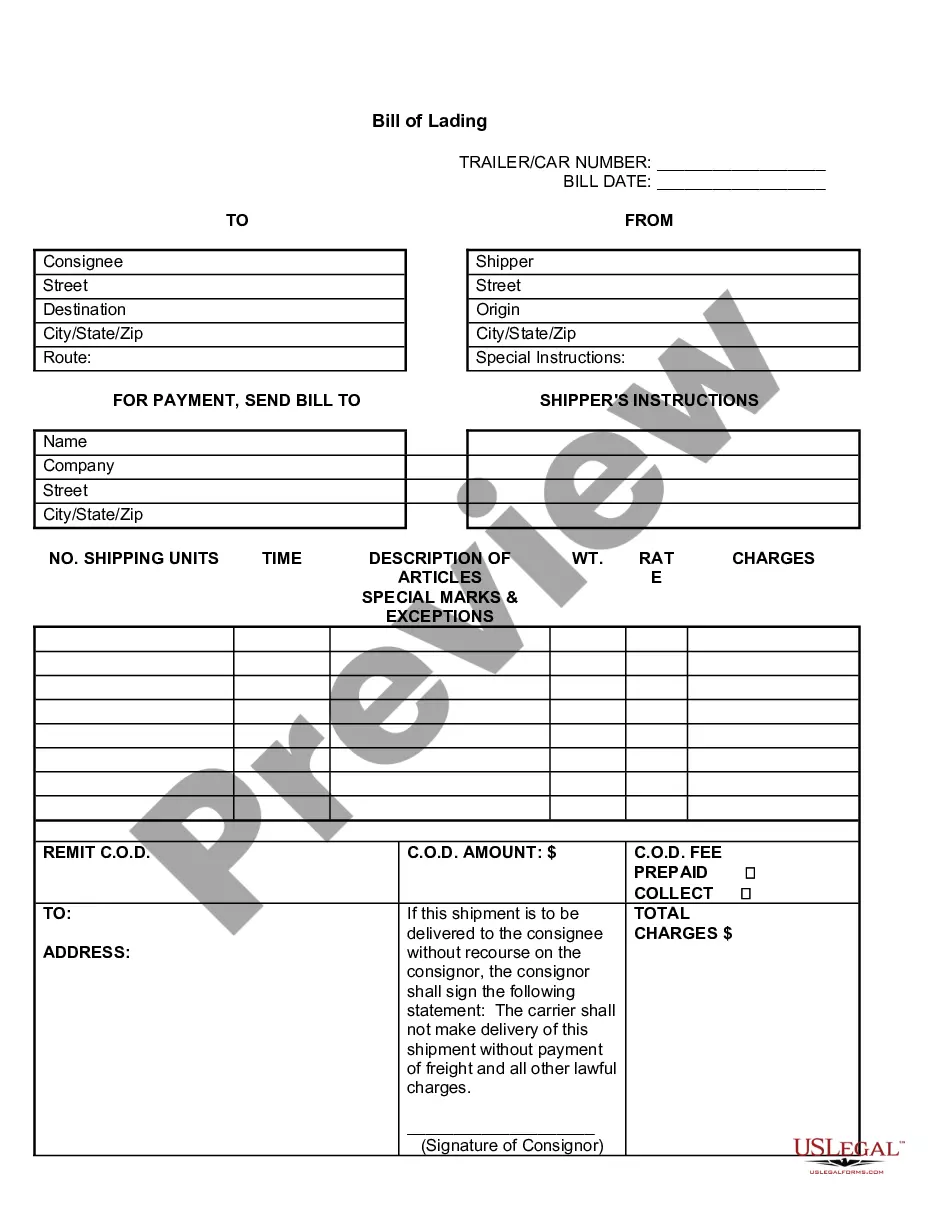
A bill of lading is a receipt given by a shipper of goods from the carrier, such as a trucking company, railroad, ship or air freighter, for shipment to a particular buyer. It is a contract protecting the shipper by guaranteeing payment and ensures the carrier that the recipient has proof of the right to the goods. The bill of lading is then sent to the buyer by the shipper upon payment for the goods, and constitutes proof that the recipient is entitled to the goods when received.
How to fill out Receipt For Bill Of Lading?
Selecting the most suitable authentic document template can be somewhat challenging.
Of course, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how can you find the authentic version you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. This service provides thousands of templates, including the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading, which can be employed for both business and personal purposes.
First, ensure you have selected the correct template for your city/state. You can review the document using the Preview option and check the document details to confirm it is the right one for you.
- All of the templates are reviewed by professionals and comply with federal and state regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to obtain the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading.
- Use your account to review the official templates you may have purchased previously.
- Navigate to the My documents section of your account and download another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, follow these simple instructions.
Form popularity
FAQ
A dock receipt is a document that is issued when goods are received at the dock and indicates that the items are in the custody of the carrier. In contrast, a bill of lading serves as a title document for the goods and outlines the terms of the shipment. Regarding the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading, understanding this distinction is essential for managing shipping logistics effectively, ensuring all parties are aware of their rights and responsibilities.
Payment upon receipt of bill of lading refers to a transaction arrangement where payment is made when the bill of lading is presented. This process ensures that the seller receives payment as soon as the goods are acknowledged by the buyer or their agent. The District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading plays a vital role in this arrangement by providing clear evidence of delivery, thus facilitating smoother transactions and reducing risks for both parties.
A bill of lading receipt is a formal document issued by a carrier to acknowledge the receipt of cargo for transportation. This document acts as a contract between the shipper and carrier, detailing the terms under which the goods will be transported. Within the framework of the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading, this receipt also serves as proof of ownership, allowing the holder to claim the goods upon delivery.
A received bill of lading represents a document that confirms the receipt of goods by a carrier. This document outlines the details of the shipment, including the type of goods, their quantity, and the intended destination. In the context of the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading, it serves as a crucial record for both shippers and carriers, ensuring transparency and accountability in the shipping process.
To fill out a District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading form, start by entering the shipper’s and consignee’s information. Next, include a description of the goods, the total weight, and any specific instructions for transport. You should also review all entries for accuracy before submitting the form, as this helps improve the efficiency of your shipment.
The four main contents of the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading are the shipper’s information, consignee’s details, cargo description, and terms of carriage. These components ensure that all parties are clear on the shipping arrangements and what is being transported. Properly documenting these elements helps mitigate disputes and ensures smoother logistics.
On a District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading, you will find several key components including the shipper and consignee’s names, a detailed list of items being shipped, their quantities, and the agreed freight charges. Additionally, it often contains terms of agreement that govern the transport of goods. This information collectively ensures accountability throughout the shipping process.
Essential data for the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading includes the shipper’s details, consignee information, item descriptions, quantity, and shipping route. Any necessary special handling instructions should also be documented. Accurate data entry is crucial as it facilitates efficient processing and delivery of goods.
A receipt for shipment bill of lading serves as proof that the carrier has received the cargo from the shipper. This document outlines the terms of the shipment and assures the consignee that their goods are in transit. It is an essential part of logistics and underpins the legal agreement between the shipper and carrier.
On the District of Columbia Receipt for Bill of Lading, you should circle the type of cargo, whether it is prepaid or collect, the shipping charges, and any special instructions for handling the shipment. Highlighting these four items helps ensure clarity and avoids confusion during transit. This attention to detail can significantly streamline shipping processes.