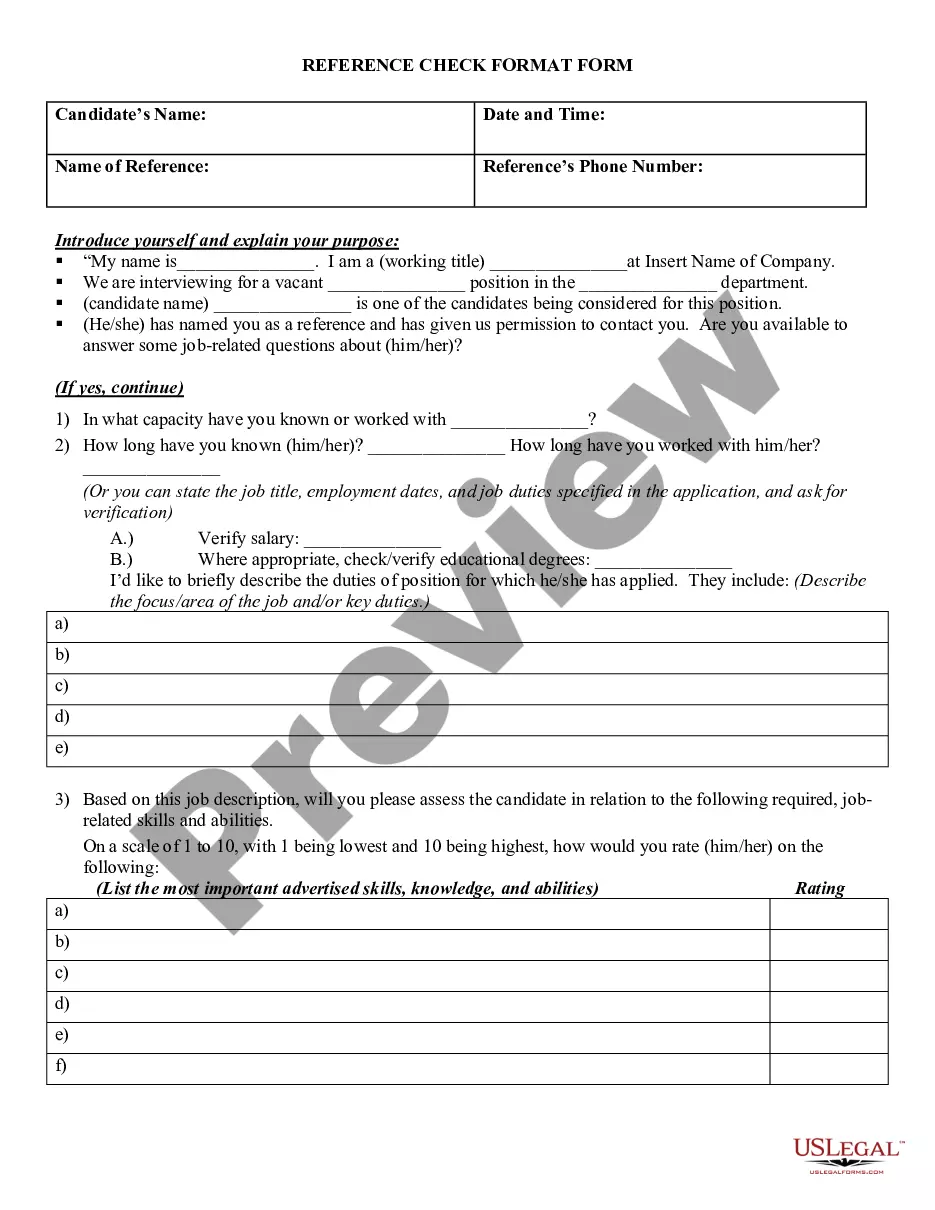
Delaware CHART FOR DETERMINING AMOUNT of WAGES SUBJECT TO 15% ATTACHMENT
Description
How to fill out Delaware CHART FOR DETERMINING AMOUNT Of WAGES SUBJECT TO 15% ATTACHMENT?
The greater number of papers you need to make - the more worried you feel. You can get thousands of Delaware Chart for Determining Amount of Wages Subject to Attachment / Garnishment 15% blanks on the internet, still, you don't know which of them to trust. Remove the headache to make detecting samples less complicated using US Legal Forms. Get accurately drafted forms that are published to satisfy state demands.
If you have a US Legal Forms subscription, log in to your profile, and you'll find the Download key on the Delaware Chart for Determining Amount of Wages Subject to Attachment / Garnishment 15%’s page.
If you have never used our service earlier, finish the registration process with the following instructions:
- Check if the Delaware Chart for Determining Amount of Wages Subject to Attachment / Garnishment 15% is valid in the state you live.
- Re-check your choice by reading through the description or by using the Preview functionality if they are available for the chosen file.
- Click on Buy Now to begin the registration procedure and choose a pricing program that meets your preferences.
- Provide the requested details to make your profile and pay for your order with the PayPal or bank card.
- Select a practical document structure and obtain your copy.
Find each document you get in the My Forms menu. Simply go there to produce a fresh version of the Delaware Chart for Determining Amount of Wages Subject to Attachment / Garnishment 15%. Even when using expertly drafted web templates, it is nevertheless vital that you think about asking the local attorney to double-check completed form to ensure that your document is correctly filled in. Do more for less with US Legal Forms!
Form popularity
FAQ
A.) The amount by which disposable earnings exceed 30 times the federal minimum hourly wage (currently $7.25 an hour), or. b.) 25 percent of disposable earnings (after federal, state, and local taxes and retirement contributions).
In Alberta, for instance, you keep the first $800 of your monthly net income, then creditors can garnish 50% of your monthly net income between $800 and $2400, and 100% of any net income above $2400. Then these exemption limits are increased by $200 for each dependent you support.
If you have a garnish imposed on your earnings, money will be taken from your gross income rather than your net income in order to satisfy your debt obligations.
If a judgment creditor is garnishing your wages, federal law provides that it can take no more than: 25% of your disposable income, or. the amount that your income exceeds 30 times the federal minimum wage, whichever is less.
(When it comes to wage garnishment, disposable income means anything left after the necessary deductions such as taxes and Social Security.) Either 25% or the amount by which your weekly income exceeds 30 times the federal minimum wage (currently $7.25 an hour), whichever is less.
2)What Happens When the Wage Garnishment is Paid? The wage garnishment continues until the debt is paid in full. Once the debt is paid, the creditor should notify the employer to stop deductions for the debt. It is difficult to stop a wage garnishment after it begins.
In most states, employers answer a writ of garnishment by filling out the paperwork attached to the judgment and returning it to the creditor or the creditor's attorney.
By federal law, in most cases only one creditor can lay claim to your wages at a single time. In essence, whichever creditor files for an order first gets to garnish your paycheck.In that case, another creditor's order can be put into effect up to the amount allowed by law to be taken out of each of your paychecks.
If you are served with a garnishment summons, do not ignore these documents because they do not directly involve a debt that you owe. Instead, you should immediately freeze any payments to the debtor, retain the necessary property, and provide the required written disclosure.