Delaware Bill of Lading
Description
How to fill out Bill Of Lading?
Selecting the appropriate authorized document format can pose a challenge. Obviously, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how can you obtain the authorized version you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. This service offers thousands of templates, including the Delaware Bill of Lading, suitable for both business and personal requirements. All templates are reviewed by experts and comply with federal and state regulations.
If you are already a member, Log In to your account and click the Acquire button to download the Delaware Bill of Lading. Use your account to review the authorized documents you have previously acquired. Visit the My documents tab in your account to download another copy of the document you need.
US Legal Forms is the largest repository of authorized documents where you can find various document templates. Utilize this service to obtain professionally crafted paperwork that adheres to state regulations.
- First, ensure that you have chosen the correct document for your city/state. You can preview the document with the Preview button and review the document outline to ensure it is suitable for you.
- If the document does not meet your requirements, use the Search field to find the proper document.
- Once you are confident that the document is correct, click the Acquire now button to purchase the document.
- Select the pricing plan you wish and provide the required information. Create your account and place your order using your PayPal account or credit card.
- Choose the file format and download the authorized document to your device.
- Complete, modify, print, and sign the downloaded Delaware Bill of Lading.
Form popularity
FAQ
When reviewing a Delaware Bill of Lading, you should circle the shipper's name, consignee's name, the description of goods, and the special instructions if any. Highlighting these items ensures clarity and helps prevent misunderstandings during the shipping process. Always double-check these details to ensure they match your shipment accurately.
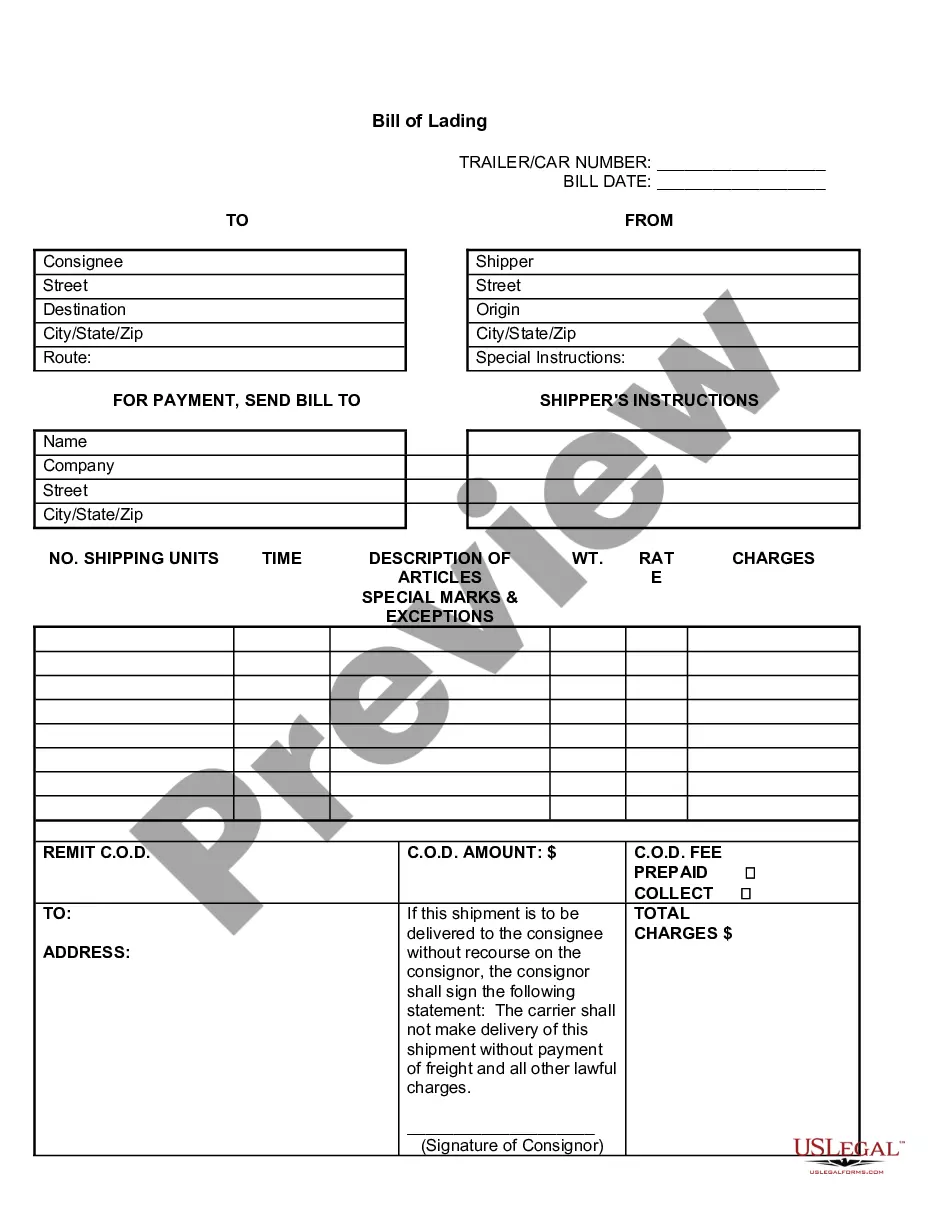
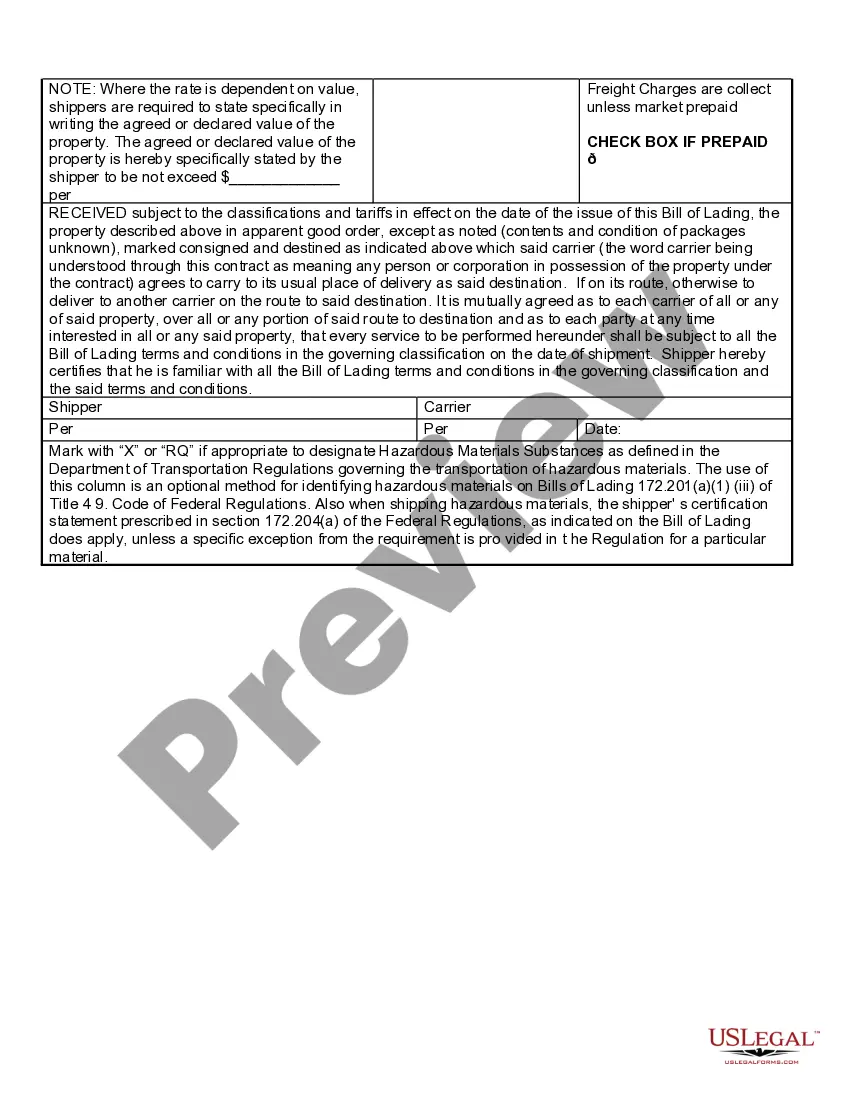
The legal requirements for a Delaware Bill of Lading include providing a clear identification of the parties involved, details of the transportation, and a binding signature from the carrier. Additionally, the bill must outline the terms and conditions of the shipment. Non-compliance can lead to disputes, so having accurate and complete information is essential.
Legally, a Delaware Bill of Lading must outline the terms of carriage and provide essential details like the date of shipment, the points of origin and destination, and the description of the goods. It acts as a receipt for the goods and signifies the carrier's responsibility. Therefore, including this information is crucial for compliance with shipping regulations.
A Delaware Bill of Lading must contain specific information to be legally valid. This includes the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, a description of the goods, the freight charges, and the signature of the carrier. Ensure that all details are accurate, as this document serves as a contract between the shipper and the carrier.
You can obtain a Delaware Bill of Lading from various sources. Many logistics companies, freight forwarders, and shipping services offer these documents. Additionally, you can visit uslegalforms, where you can easily access templates and forms to create your own Delaware Bill of Lading.
Delaware does not require corporations to have a physical principal office in the state, allowing for more flexibility in business operations. However, having a registered agent is mandatory to receive legal paperwork. This setup is particularly beneficial for those conducting business online or from multiple locations. Remember, if you're involved in shipping practices, the Delaware Bill of Lading will help maintain your shipping accountability.
Section 133 of the General Corporation Law pertains to notice of meetings and stipulates how corporations must deliver notices to shareholders regarding meetings. This section ensures that all shareholders are adequately informed and can participate in corporate governance. Familiarity with these regulations is vital for compliance and proper documentation, such as when using a Delaware Bill of Lading for business transactions.
A Delaware LLC is not required to maintain a physical office in Delaware, but it must designate a registered agent within the state. This agent will receive legal documents on behalf of the LLC. Many business owners find this beneficial as it allows them to operate remotely while still complying with state laws. Utilizing services like US Legal Forms can streamline the creation and management of necessary documents, including the Delaware Bill of Lading.
Section 228 of the Delaware corporate law relates to the voting rights of shareholders and allows for written consent without a formal meeting. This section enables quicker decision-making for corporations by allowing actions to be approved through written agreements instead of requiring a physical assembly. Understanding this can be critical for efficient governance. It also ties into maintaining proper documentation like the Delaware Bill of Lading for accountability.
Yes, you can register your business in Delaware regardless of your residency. Many entrepreneurs choose Delaware due to its favorable business laws and tax advantages. This makes it an attractive option for those looking to incorporate outside their home state. If you plan to use a Delaware Bill of Lading, establishing your business here can streamline shipping logistics.