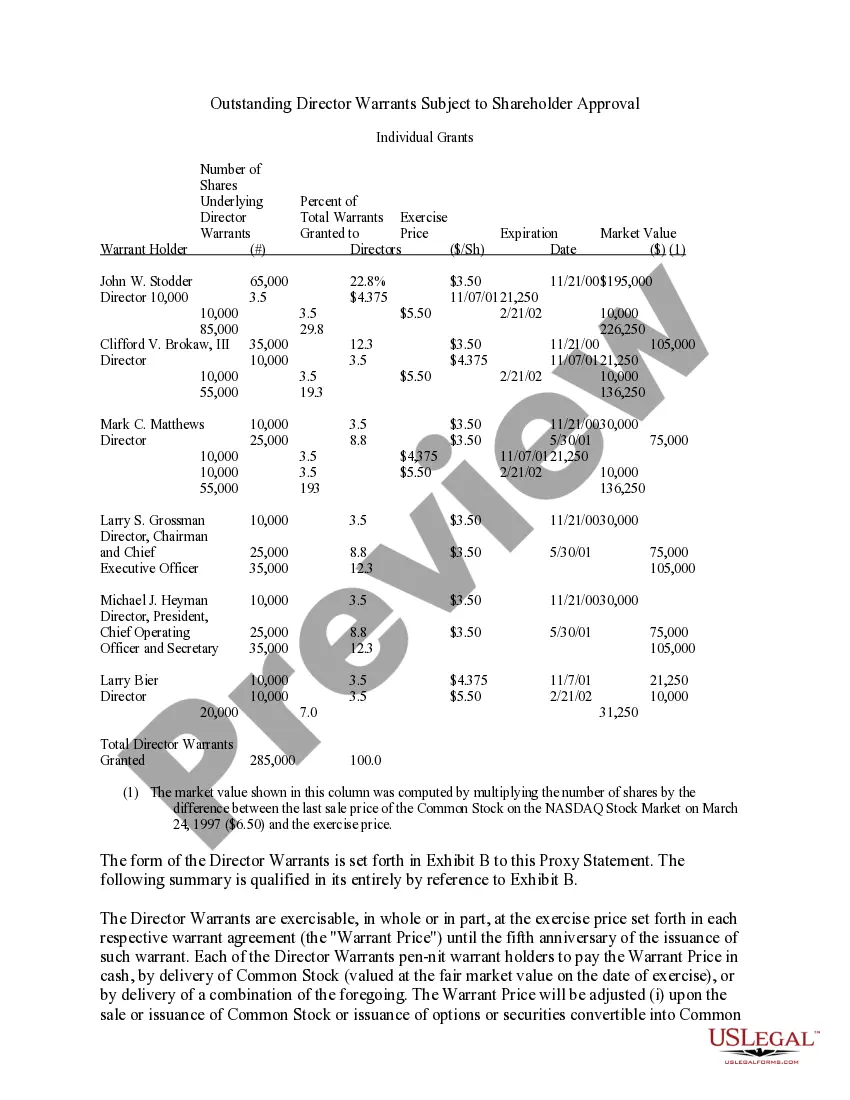
Delaware Approval of director warrants
Description
How to fill out Approval Of Director Warrants?
It is possible to commit hrs online attempting to find the lawful document web template that fits the state and federal specifications you need. US Legal Forms provides thousands of lawful forms which are reviewed by experts. You can easily obtain or print out the Delaware Approval of director warrants from our service.
If you currently have a US Legal Forms account, you may log in and then click the Down load option. Next, you may full, modify, print out, or indicator the Delaware Approval of director warrants. Each lawful document web template you get is the one you have forever. To obtain another backup of any purchased kind, check out the My Forms tab and then click the related option.
If you use the US Legal Forms site the first time, keep to the straightforward directions under:
- Initial, ensure that you have chosen the proper document web template to the state/city that you pick. Look at the kind information to ensure you have chosen the right kind. If available, make use of the Preview option to look with the document web template as well.
- If you would like discover another variation from the kind, make use of the Search area to get the web template that meets your needs and specifications.
- Once you have identified the web template you need, simply click Purchase now to proceed.
- Choose the pricing plan you need, enter your credentials, and register for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the deal. You should use your credit card or PayPal account to cover the lawful kind.
- Choose the file format from the document and obtain it in your device.
- Make modifications in your document if possible. It is possible to full, modify and indicator and print out Delaware Approval of director warrants.
Down load and print out thousands of document layouts utilizing the US Legal Forms web site, that provides the biggest selection of lawful forms. Use specialist and condition-certain layouts to tackle your organization or personal needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
(a) A written restriction or restrictions on the transfer or registration of transfer of a security of a corporation, or on the amount of the corporation's securities that may be owned by any person or group of persons, if permitted by this section and noted conspicuously on the certificate or certificates representing ...
Actions that Require Board Approval All issuances of securities (whether shares of stock, option grants, convertible promissory notes, warrants, etc.) Amendments to the articles/certificate of incorporation or bylaws.
Section 203 is an antitakeover statute in Delaware which provides that if a person or entity (an ?interested stockholder?) acquires 15% or more of the voting stock of a Delaware corporation (the ?target?) without prior approval of the target's board, then the interested stockholder may not engage in a business ...
Section 204 of the DGCL provides the procedure by which corporations may ratify a defective corporate act that is otherwise void or voidable due to a failure to properly authorize these acts, such as officer or director appointments or stock issuances.
Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, or DGCL, is a Delaware statute that prevents shareholders (along with their affiliates and associates) from engaging in a tender or exchange offer for a period of three years after buying more than 15 percent of the company's stock unless certain criteria are met.
(a) Subject to subsection (f) of this section, no defective corporate act or putative stock shall be void or voidable solely as a result of a failure of authorization if ratified as provided in this section or validated by the Court of Chancery in a proceeding brought under § 205 of this title.
Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, or DGCL, is a Delaware statute that prevents shareholders (along with their affiliates and associates) from engaging in a tender or exchange offer for a period of three years after buying more than 15 percent of the company's stock unless certain criteria are met.