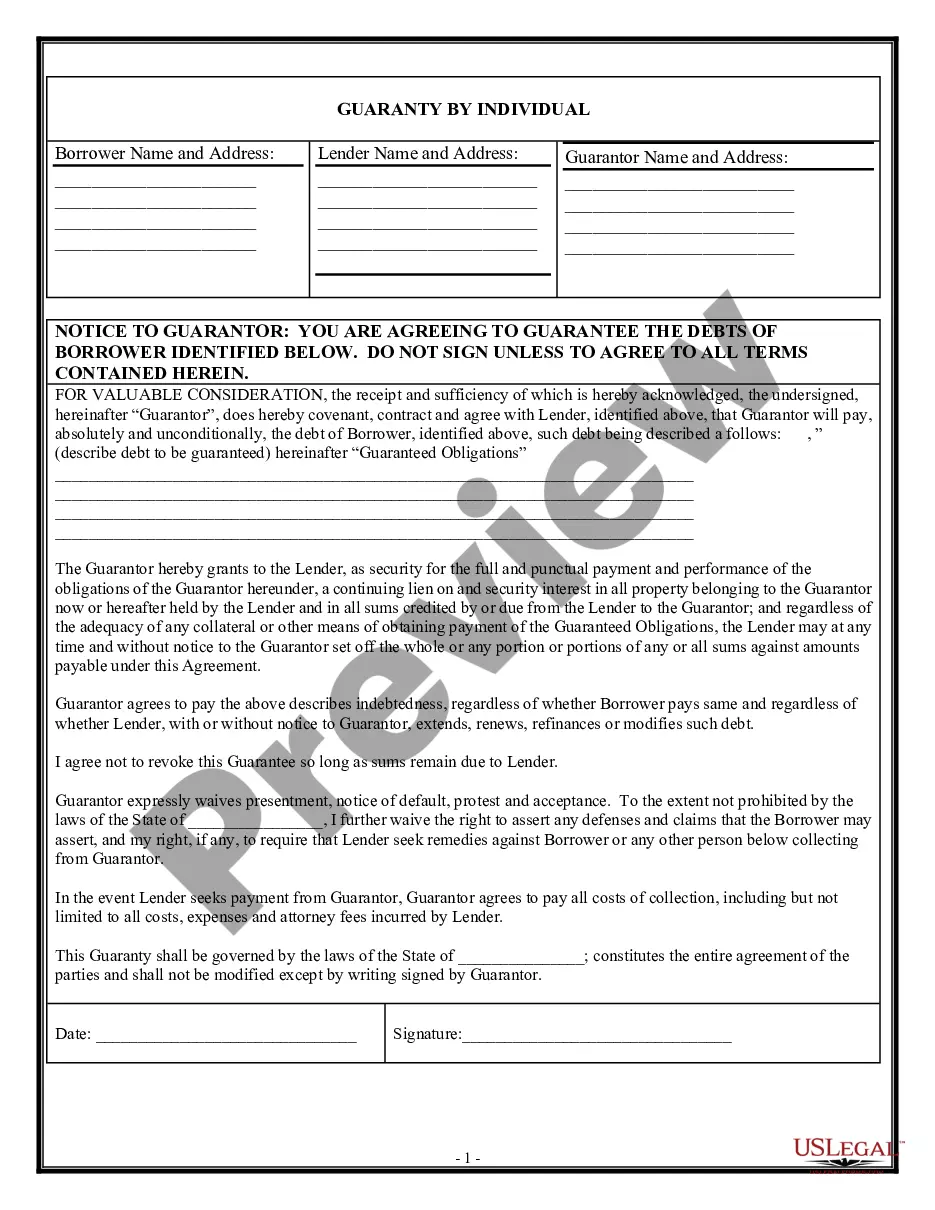
Delaware Clawback Guaranty
Description
How to fill out Clawback Guaranty?
US Legal Forms - one of the most significant libraries of legal varieties in the USA - provides an array of legal file templates you may down load or print out. Utilizing the internet site, you can get 1000s of varieties for organization and person reasons, categorized by groups, suggests, or keywords.You will discover the most recent models of varieties like the Delaware Clawback Guaranty within minutes.
If you already possess a monthly subscription, log in and down load Delaware Clawback Guaranty from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button can look on each type you see. You gain access to all earlier saved varieties inside the My Forms tab of the accounts.
If you want to use US Legal Forms for the first time, listed here are straightforward directions to get you started out:
- Be sure to have picked out the proper type for the city/state. Click on the Review button to analyze the form`s content material. Read the type explanation to actually have selected the right type.
- If the type doesn`t suit your demands, utilize the Lookup field towards the top of the display to get the one that does.
- In case you are content with the shape, affirm your option by clicking on the Buy now button. Then, opt for the rates plan you prefer and offer your credentials to register on an accounts.
- Method the deal. Use your credit card or PayPal accounts to complete the deal.
- Choose the structure and down load the shape in your system.
- Make changes. Complete, revise and print out and signal the saved Delaware Clawback Guaranty.
Each format you added to your bank account lacks an expiry time and is also yours for a long time. So, if you want to down load or print out an additional backup, just proceed to the My Forms area and then click around the type you require.
Get access to the Delaware Clawback Guaranty with US Legal Forms, probably the most extensive library of legal file templates. Use 1000s of expert and status-specific templates that meet your company or person demands and demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
Section 203 is an antitakeover statute in Delaware which provides that if a person or entity (an ?interested stockholder?) acquires 15% or more of the voting stock of a Delaware corporation (the ?target?) without prior approval of the target's board, then the interested stockholder may not engage in a business ...
§ 17-303. Liability to third parties. (a) A limited partner is not liable for the obligations of a limited partnership unless he or she is also a general partner or, in addition to the exercise of the rights and powers of a limited partner, he or she participates in the control of the business.
Corporations § 144. Interested directors; quorum. (3) The contract or transaction is fair as to the corporation as of the time it is authorized, approved or ratified, by the board of directors, a committee or the stockholders.
Under Delaware law, a shareholder has a to right to vote on any amendment to the corporation's governing documents, whether such class of shares is entitled to vote or not under the governing documents, for actions that would (i) increase or decrease the number of authorized shares of such class; (ii) increase or ...
Section 145 of the Delaware General Corporation Law (DGCL) allows corporations to protect present and former directors and officers from expenses incurred in connection with proceedings arising from actions taken in service to the company or at the company's direction.
Section 144(a) codified judicially acknowledged principles of corporate governance to provide a limited safe harbor for corporate boards to prevent director conflicts of interest from voiding corporate action.
Corporations § 144. Interested directors; quorum. (3) The contract or transaction is fair as to the corporation as of the time it is authorized, approved or ratified, by the board of directors, a committee or the stockholders.