Title: Florida Contract — Sale of Goods: A Comprehensive Overview and Types of Contracts Introduction: Florida Contract — Sale of Goods refers to a legal agreement between parties involved in the buying and selling of goods within the state of Florida, governed by specific laws and regulations. This detailed description will explore the essential elements and key features of a Florida Contract — Sale of Goods, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and the different types of contracts that exist within this realm. I. Essential Elements of a Florida Contract — Sale of Goods: 1. Offer and Acceptance: A valid contract requires a clear offer by one party and an unequivocal acceptance by the other. 2. Mutual Agreement: Both parties must reach a common understanding of the terms and conditions of the contract, demonstrating their intention to be bound by its provisions. 3. Consideration: Contracts must involve a valuable exchange, whereby each party provides something of value in return for the goods being sold. 4. Capacity and Legality: Both parties must have the legal capacity and authority to enter into a contract, and the agreement should not violate any state or federal laws. 5. Goods Description: The contract should include a detailed description of the goods being sold, including specifications, quantity, quality, and any specific terms related to the purchase. II. Different Types of Florida Contracts — Sale of Goods: 1. Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Contracts: UCC is a standardized set of laws adopted by most states, including Florida, governing commercial transactions, including the sale of goods. Under UCC, contracts for the sale of goods over $500 are required to be in writing. 2. Installment Contracts: Installment contracts are used when the sale of goods involves multiple payments over time. It allows for the buyer to receive and use the goods while making payments in installments until the full purchase price is paid. 3. Conditional Sales Contracts: Conditional sales contracts include specific conditions or contingencies that must be met before the buyer takes full ownership of the goods. These conditions may involve payment deadlines, inspections, or any other agreed-upon terms. 4. Consignment Contracts: In a consignment contract, the seller (consignor) delivers goods to another party (consignee) for sale. The consignee only receives compensation if the goods are sold, and any unsold goods are usually returned to the consignor. 5. Auction Contracts: Auction contracts govern the sale of goods through public bidding. These contracts outline the terms of the auction, including starting bids, bidding increments, and any applicable commissions or fees. Conclusion: Understanding the intricacies of a Florida Contract — Sale of Goods is crucial for individuals and businesses engaging in commercial transactions within the state. By adhering to the essential elements and familiarizing oneself with the different types of contracts, parties can ensure clarity, mutual protection, and the smooth execution of sales agreements. It is advisable to seek legal advice or reference official guidelines to navigate the complexities of Florida Contract — Sale of Goods effectively.
Florida Contract - Sale of Goods
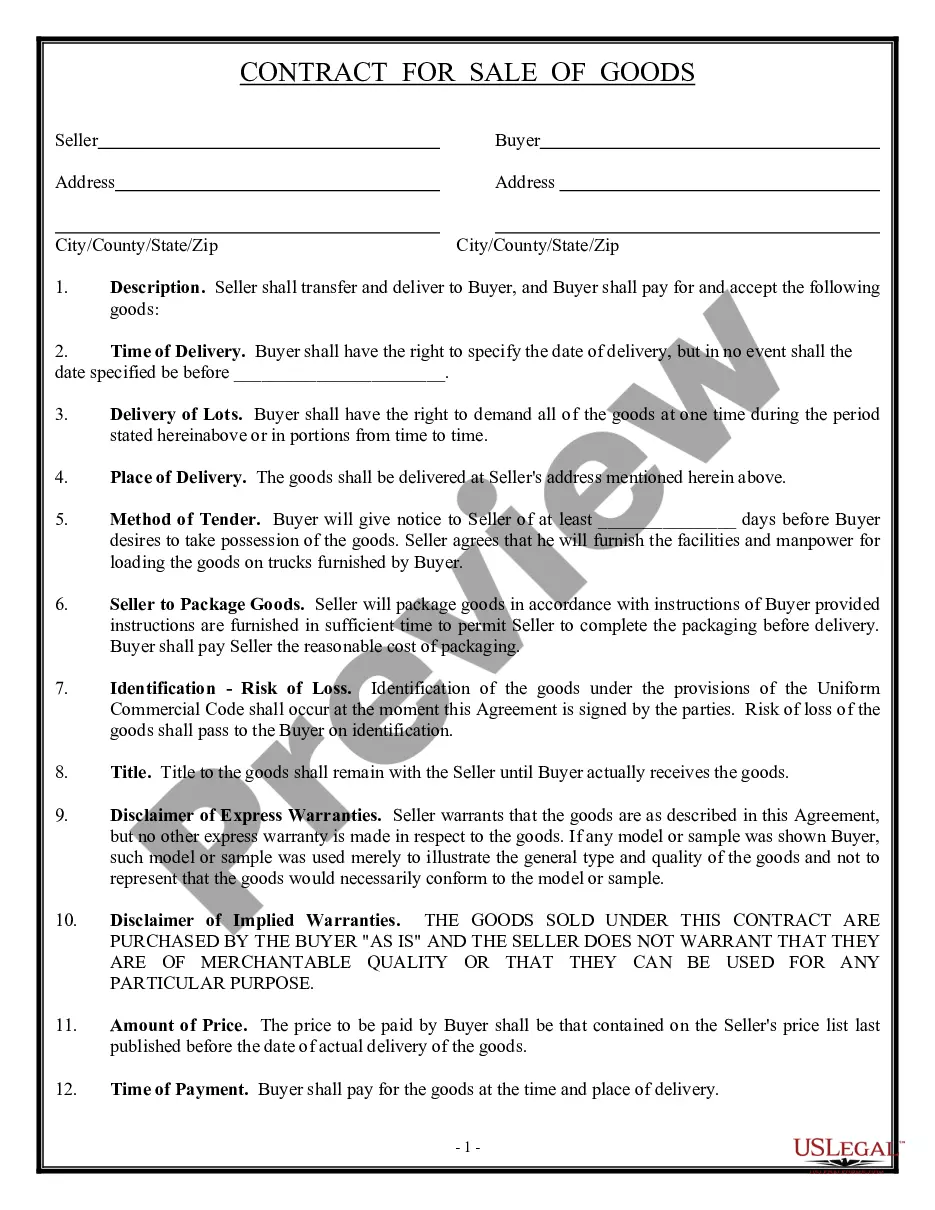
Description
How to fill out Florida Contract - Sale Of Goods?
US Legal Forms - one of the most significant libraries of authorized varieties in the United States - offers a wide range of authorized record layouts you can acquire or printing. While using internet site, you will get 1000s of varieties for business and specific reasons, categorized by types, states, or keywords.You will find the newest variations of varieties such as the Florida Contract - Sale of Goods within minutes.
If you already have a registration, log in and acquire Florida Contract - Sale of Goods in the US Legal Forms collection. The Obtain option will show up on every form you perspective. You have accessibility to all earlier saved varieties inside the My Forms tab of your own bank account.
If you would like use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are easy directions to help you started off:
- Be sure to have picked out the proper form for your personal city/state. Go through the Preview option to review the form`s information. Browse the form outline to ensure that you have chosen the proper form.
- In case the form does not fit your demands, utilize the Research field towards the top of the monitor to find the the one that does.
- When you are satisfied with the form, verify your choice by clicking on the Acquire now option. Then, opt for the costs program you favor and offer your credentials to register to have an bank account.
- Approach the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal bank account to complete the transaction.
- Find the formatting and acquire the form on your gadget.
- Make modifications. Fill out, change and printing and signal the saved Florida Contract - Sale of Goods.
Every template you put into your money lacks an expiration time and it is your own permanently. So, if you wish to acquire or printing yet another duplicate, just go to the My Forms area and then click on the form you require.
Gain access to the Florida Contract - Sale of Goods with US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive collection of authorized record layouts. Use 1000s of expert and status-distinct layouts that meet up with your small business or specific demands and demands.