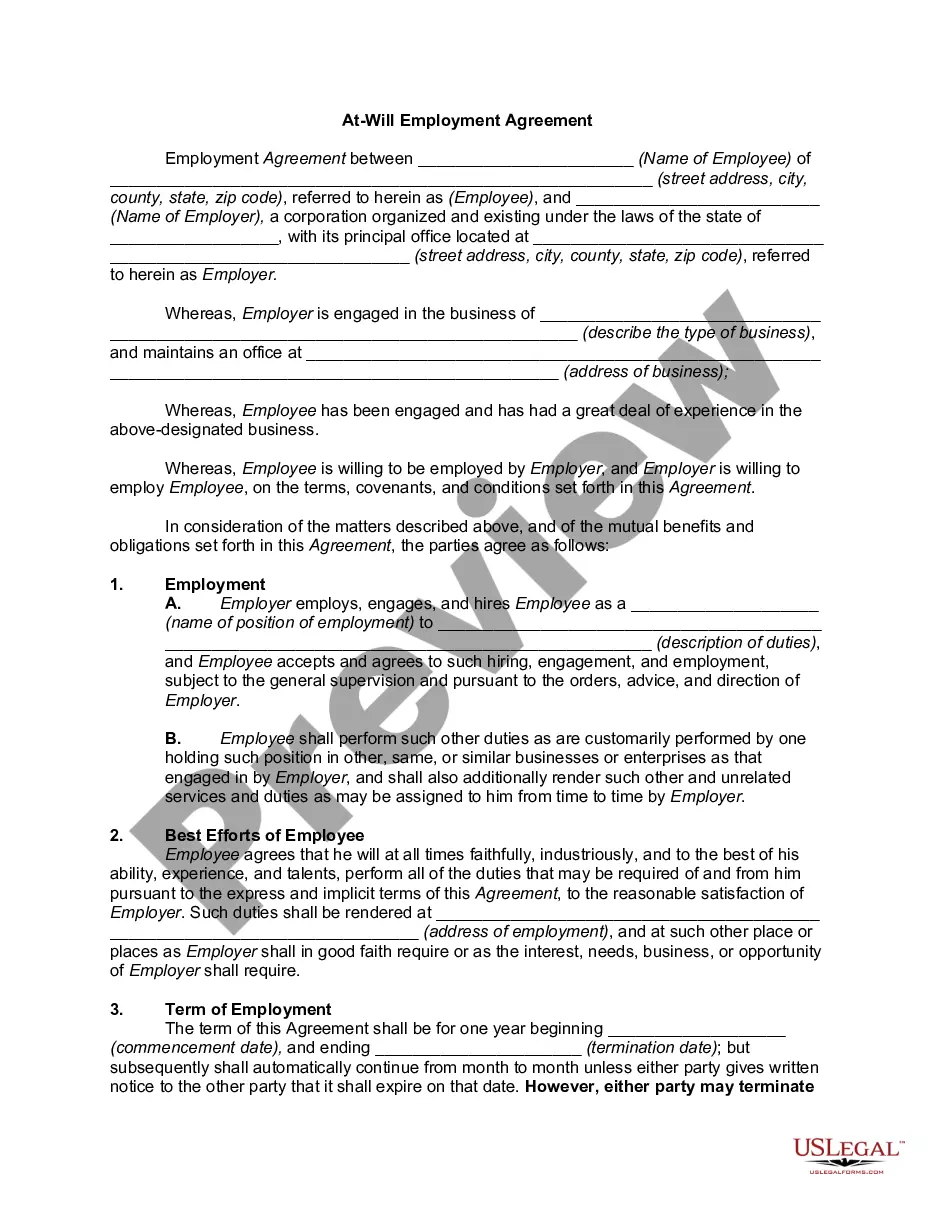
In most instances, an employment contract will not state its expiration date. In such a case, the contract may be terminated at any time by either party. If the employment contract does not have a definite duration, it is terminable at will. This is called employment at will. Under the employment at will doctrine, the employer has historically been allowed to terminate the contract at any time for any reason or for no reason. Some State Courts and some State Legislatures have changed this rule by limiting the power of the employer to discharge the employee without cause.
Georgia At Will Employment Agreement
Description
How to fill out At Will Employment Agreement?
If you desire to collect, acquire, or print valid document formats, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of legal templates accessible online.
Leverage the site's user-friendly and efficient search feature to locate the papers you require.
Numerous templates for commercial and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click the Purchase now button. Choose the payment plan you prefer and enter your details to register for an account.
Step 5. Process the transaction. You can use your Visa or MasterCard or PayPal account to complete the purchase.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to find the Georgia At Will Employment Agreement in just a few clicks.
- If you are currently a US Legal Forms member, Log In to your account and click the Download button to retrieve the Georgia At Will Employment Agreement.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded from the My documents tab in your account.
- If this is your first time using US Legal Forms, follow the instructions below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the template for your appropriate city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the form's details. Don't forget to read the information.
- Step 3. If you are unsatisfied with the form, use the Search bar at the top of the screen to find other variations of the legal form type.
Form popularity
FAQ
The possibility of career advancement and the freedom and flexibility to leave a position without reason or notice are the two primary benefits of employment-at-will. To take full advantage of these benefits, it's important to be open to outside opportunities that come your way.
Georgia is an employment-at-will state. This means that in the absence of an enforceable employment contract or violation of federal law or any anti-discrimination laws, employees in Georgia can be terminated at will.
The contract binds both you and the employee, so it limits your flexibility. This may pose a problem if you later decide that you don't like the contract terms or the needs of your business change.
At-will employment means you can quit or be fired for almost any reason. Right-to-work means you can work for a unionized employer without joining the union. The relevant laws vary from state to state and change over time.
Georgia also does not recognize a claim for wrongful termination, as Georgia is an employment-at-will state. This means that, in the absence of an enforceable employment contract or a violation of any anti-discrimination laws or federal statutes, employees in Georgia can be terminated at will.
A contract of employment is a legally binding agreement between you and your employer. A breach of that contract happens when either you or your employer breaks one of the terms, for example your employer doesn't pay your wages, or you don't work the agreed hours. Not all the terms of a contract are written down.
Both parties are getting something that they have agreed to (or exchange something of actual value for something of actual value) There must be mutual consent to enter into the agreement. Both parties agree to the basic terms of the contract.
Georgia Wrongful Termination Laws Georgia is an at-will employment state, meaning that an employee can be fired for any reason except an illegal one.
Georgia Wrongful Termination Laws Georgia is an at-will employment state, meaning that an employee can be fired for any reason except an illegal one.
In Georgia, most workers are usually regarded as employees "at will." This means that the employee works at the will of the employer and the employer can fire the worker at any time, for any reason (just about), and without any notice.