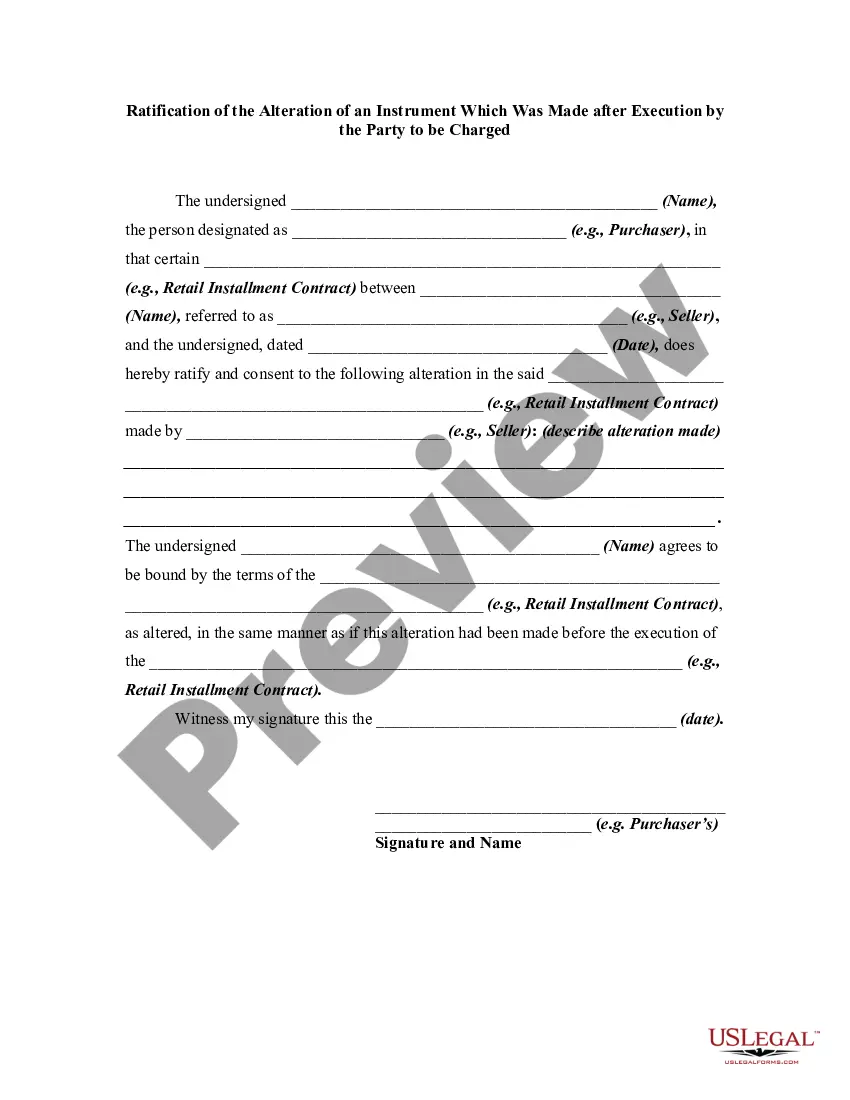
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought. If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Georgia Ratification, Alteration of an Instrument, Party to be Charged The Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a legal process that deals with the validation and acceptance of changes made to a document or contractual agreement after its execution. This process allows the party to be charged, or the party who signed the instrument, to confirm their agreement with the alterations made. In Georgia, there are different types of ratification that can occur for the alteration of an instrument. These types include: 1. Ratification by Express Agreement: This type of ratification occurs when the party to be charged explicitly agrees to the changes made to the instrument. It can be done through a written or verbal agreement, signaling their acceptance of the altered terms. 2. Implied Ratification: Implied ratification occurs when the party to be charged behaves or acts as though they accept the altered instrument. This can be shown through their continued participation in the agreement without raising any objections or by accepting benefits related to the altered instrument. 3. Statutory Ratification: In certain cases, the state of Georgia may have specific laws or statutes that provide for the ratification of alterations made to certain types of instruments. These statutes outline the procedure for ratifying the changes and ensure compliance with legal requirements. The purpose of the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is to maintain the integrity of contractual agreements and prevent fraudulent alterations. By requiring the party to be charged to explicitly confirm their acceptance of the changes, it protects the interests of all parties involved. Keywords: Georgia, Ratification, Alteration of an Instrument, Party to be Charged, legal process, validation, contractual agreement, changes, execution, express agreement, implied ratification, statutory ratification, integrity, fraudulent alterations.Georgia Ratification, Alteration of an Instrument, Party to be Charged The Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a legal process that deals with the validation and acceptance of changes made to a document or contractual agreement after its execution. This process allows the party to be charged, or the party who signed the instrument, to confirm their agreement with the alterations made. In Georgia, there are different types of ratification that can occur for the alteration of an instrument. These types include: 1. Ratification by Express Agreement: This type of ratification occurs when the party to be charged explicitly agrees to the changes made to the instrument. It can be done through a written or verbal agreement, signaling their acceptance of the altered terms. 2. Implied Ratification: Implied ratification occurs when the party to be charged behaves or acts as though they accept the altered instrument. This can be shown through their continued participation in the agreement without raising any objections or by accepting benefits related to the altered instrument. 3. Statutory Ratification: In certain cases, the state of Georgia may have specific laws or statutes that provide for the ratification of alterations made to certain types of instruments. These statutes outline the procedure for ratifying the changes and ensure compliance with legal requirements. The purpose of the Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is to maintain the integrity of contractual agreements and prevent fraudulent alterations. By requiring the party to be charged to explicitly confirm their acceptance of the changes, it protects the interests of all parties involved. Keywords: Georgia, Ratification, Alteration of an Instrument, Party to be Charged, legal process, validation, contractual agreement, changes, execution, express agreement, implied ratification, statutory ratification, integrity, fraudulent alterations.