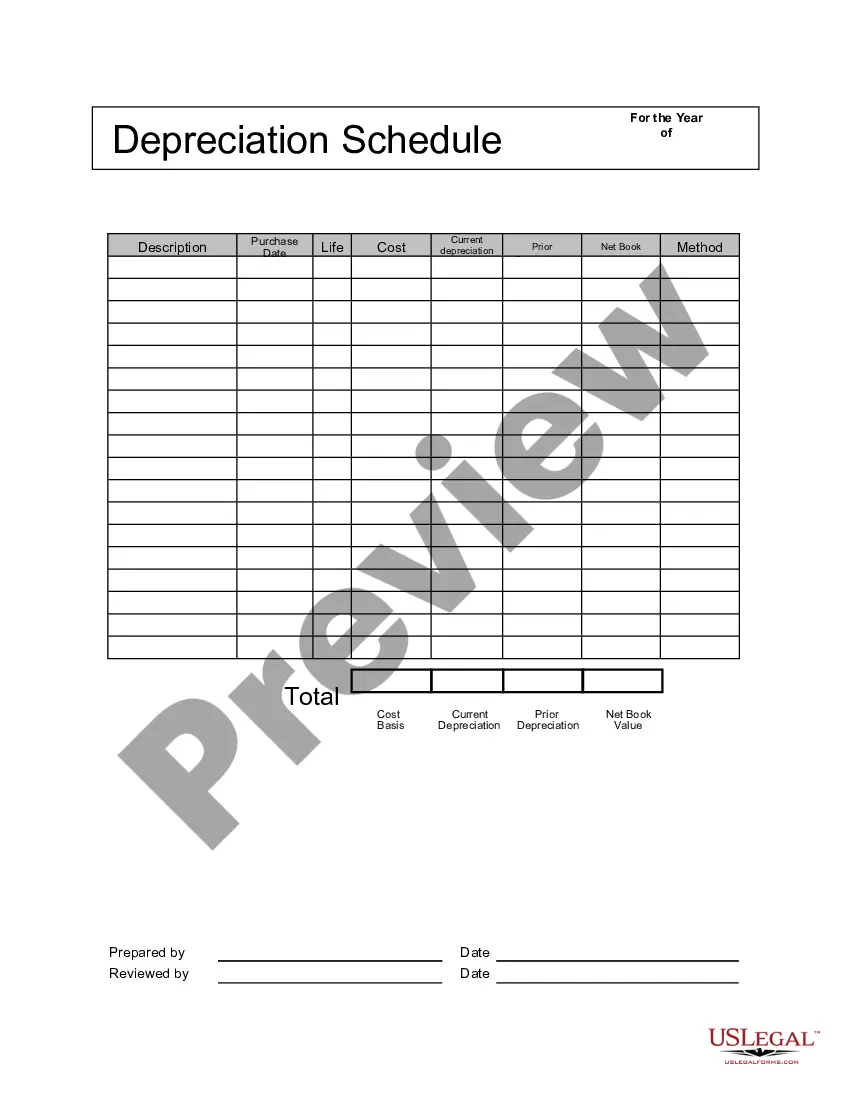
Georgia Depreciation Schedule
Description
How to fill out Depreciation Schedule?
You can invest several hours online seeking the authorized document template that aligns with the federal and state requirements you desire.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal forms that are verified by experts.
It is easy to download or print the Georgia Depreciation Schedule from their service.
If available, use the Preview button to browse through the document template as well.
- If you already have a US Legal Forms account, you can sign in and click on the Download button.
- Then, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Georgia Depreciation Schedule.
- Each legal document template you purchase is yours to keep for years.
- To obtain another copy of any purchased document, visit the My documents tab and click the corresponding button.
- If this is your first time using the US Legal Forms website, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, make sure you have selected the correct document template for the county/city of your choice.
- Review the document description to ensure you have chosen the appropriate form.
Form popularity
FAQ
This form is for a net operating loss carry-back adjustment by an individual or fiduciary that desires a refund of taxes afforded by carry-back of a net operating loss.
Regarding net operating losses, Georgia follows the new federal rule relating to no carryback and unlimited carryforward of net operating losses for losses incurred after 2017. Georgia also adopts the 80% limitation on the use of NOLs, with the state 80% limitation based on Georgia taxable net income.
Five states Colorado, Georgia, Hawaii, New York, and North Carolina have already decoupled their tax laws from these provisions to avoid having to give back revenue they have already collected; other states should do the same.
States that have adopted the new bonus depreciation rules:Alabama.Alaska.Colorado.Delaware.Illinois.Kansas.Louisiana.Michigan.More items...
For 2021, Georgia has adopted the increased I.R.C. Section 179 deduction of $1,050,000 as well as the $2,620,000 phaseout. Georgia has not, however, adopted the Section 179 deduction for certain real property (I.R.C. Sections 179(d)(1)(B)(ii)).
Federal depreciation should be added back to Georgia income by entering it on the other addition line of the return. Depreciation must then be computed for Georgia purposes on Georgia Form 4562 which should be attached to the Georgia return.
Decoupled states: Colorado, Hawaii, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, New York, North Carolina, and West Virginia.
States can avert this loss of revenue by "decoupling." Decoupling means protecting the relevant parts of their tax code from the changes in the federal tax code, in most cases by remaining linked to federal law as it existed prior to the change.
The State of Georgia will recognize your valid Federal extension and grant you a corresponding state extension. Make sure to attach a copy of Form 4868 (or the IRS confirmation letter if you e-filed your Federal extension) to your Georgia tax return when it's filed.
Regarding net operating losses, Georgia follows the new federal rule relating to no carryback and unlimited carryforward of net operating losses for losses incurred after 2017. Georgia also adopts the 80% limitation on the use of NOLs, with the state 80% limitation based on Georgia taxable net income.