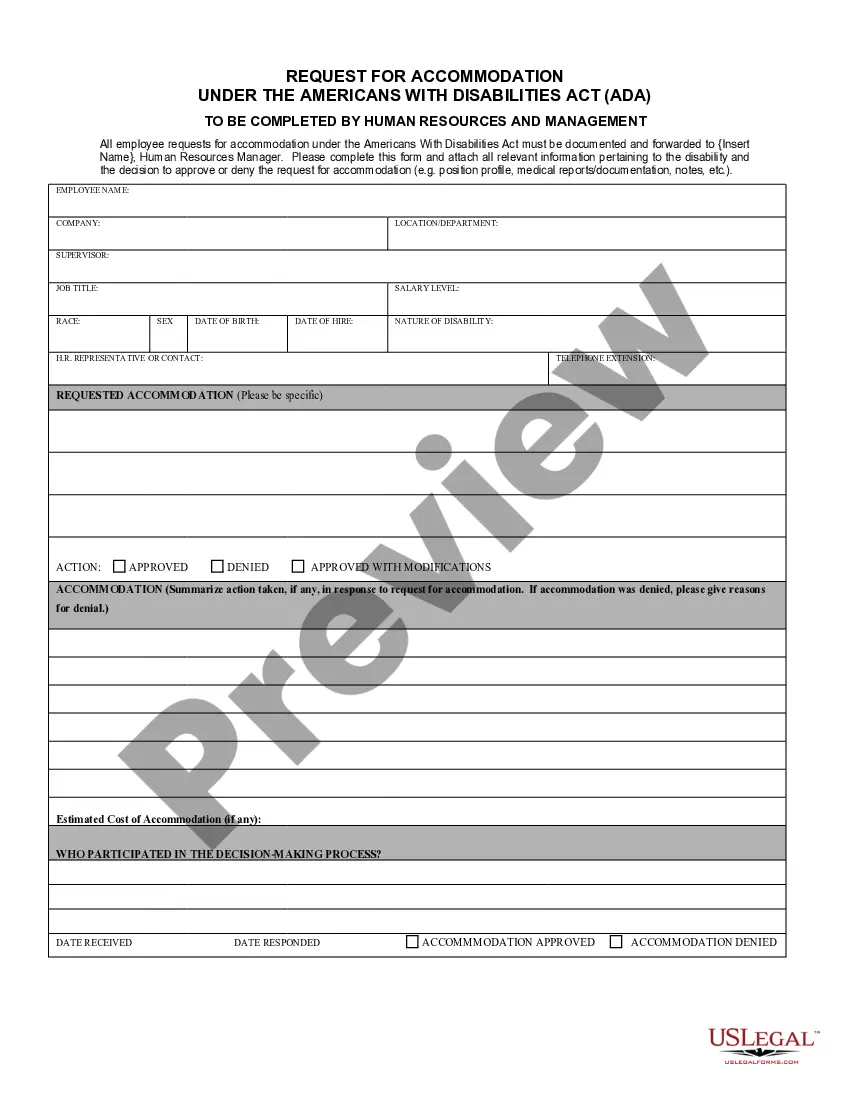
Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA: A Comprehensive Guide Introduction: The Georgia Request for Accommodation under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a formal procedure through which individuals with disabilities in Georgia can seek reasonable accommodations in various areas of life. The ADA is a federal law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities and ensures equal access to employment, public services, transportation, and more. This detailed description aims to provide valuable information about the Georgia Request for Accommodation process, its significance, and the various types of accommodations available. Key Keywords: Georgia Request for Accommodation, ADA, Americans with Disabilities Act, reasonable accommodations, discrimination, disabilities, equal access. Types of Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA: 1. Employment Accommodations: Under the ADA, individuals with disabilities are protected from employment discrimination and can request reasonable accommodations to perform their job duties effectively. These accommodations can include modifications to the work environment, equipment, flexible schedules, or even changes in job tasks, all aimed at enabling equal opportunities and access to employment. 2. Public Services Accommodations: Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA also extends to public services provided by state and local government entities. Individuals with disabilities can request modifications, accommodations, or auxiliary aids that ensure equal participation in programs, activities, or events organized by government entities, such as accessible housing, transportation, education, or recreational facilities. 3. Housing Accommodations: Individuals with disabilities in Georgia can seek accommodations under the ADA to ensure accessible and reasonable housing options within the state. These accommodations can involve modifications to living spaces, installation of ramps, elevators, or wider doorways, and removal of architectural barriers that impede accessibility. 4. Transportation Accommodations: Georgia individuals with disabilities can request transportation accommodations to ensure equal access to public transportation services. These accommodations may include accessible vehicles, wheelchair lifts, audio announcements, or other modifications that enable individuals with disabilities to use public transportation systems independently and safely. 5. Education Accommodations: Students with disabilities in Georgia are entitled to reasonable accommodations under the ADA to ensure equal access to educational opportunities. These accommodations can include academic adjustments, modified testing procedures, provision of assistive technologies, accessible classrooms, or other necessary modifications to facilitate learning in an inclusive environment. Conclusion: The Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA provides a powerful framework for individuals with disabilities to seek necessary accommodations and ensure equal access to various aspects of life. By understanding the different types of accommodations available, individuals can navigate this process more effectively and exercise their rights under the ADA, promoting inclusivity and equal opportunities for all.
Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA
Description
How to fill out Georgia Request For Accommodation Under The ADA?
Choosing the right lawful record design can be quite a have difficulties. Obviously, there are plenty of templates available on the net, but how do you discover the lawful kind you want? Utilize the US Legal Forms internet site. The services gives 1000s of templates, including the Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA, that you can use for organization and personal requirements. Each of the kinds are checked by experts and meet up with federal and state needs.
When you are previously authorized, log in for your profile and click on the Down load key to find the Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA. Use your profile to appear throughout the lawful kinds you may have purchased earlier. Check out the My Forms tab of your respective profile and obtain yet another version from the record you want.
When you are a whole new end user of US Legal Forms, here are straightforward recommendations that you should comply with:
- Initial, make sure you have selected the correct kind to your town/region. You can examine the form using the Preview key and browse the form explanation to make certain this is the right one for you.
- In case the kind does not meet up with your needs, utilize the Seach area to find the right kind.
- Once you are certain that the form is proper, go through the Acquire now key to find the kind.
- Select the pricing program you want and enter the required details. Create your profile and pay money for an order with your PayPal profile or Visa or Mastercard.
- Pick the document file format and down load the lawful record design for your product.
- Comprehensive, revise and printing and sign the received Georgia Request for Accommodation under the ADA.
US Legal Forms is the most significant collection of lawful kinds for which you will find various record templates. Utilize the service to down load professionally-made paperwork that comply with state needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
REASONABLE ACCOMMODATION RELATED TO THE BENEFITS AND PRIVILEGES OF EMPLOYMENT. The ADA requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations so that employees with disabilities can enjoy the "benefits and privileges of employment" equal to those enjoyed by similarly-situated employees without disabilities.
Wheelchair use:Installing a ramp to make a workplace wheelchair-accessible.Modifying a restroom so a worker with disabilities can use it.Changing the layout of cubicles to provide enough room for a wheelchair to pass.Providing a raised or adjustable desk so that a wheelchair can be used in place of a chair.
Examples of reasonable accommodations include making existing facilities accessible; job restructuring; part-time or modified work schedules; acquiring or modifying equipment; changing tests, training materials, or policies; providing qualified readers or interpreters; and reassignment to a vacant position.
An individual meets the Americans with Disabilities with Act definition act of disability that would qualify them for reasonable accommodations if they have a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities (sometimes referred to in the regulations as an actual disability)
Under Title I of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), a reasonable accommodation is a modification or adjustment to a job, the work environment, or the way things are usually done during the hiring process.
4. What accommodations are not considered reasonable? Reasonable accommodation does not include removing essential job functions, creating new jobs, and providing personal need items such as eye glasses and mobility aids.
The ADA does not name all of the impairments that are covered, but common examples of disabilities include wheelchair confinement, blindness, deafness, learning disabilities, and certain kinds of mental illness.
Examples of accommodations include:sign language interpreters for students who are deaf;computer text-to-speech computer-based systems for students with visual impairments or Dyslexia;extended time for students with fine motor limitations, visual impairments, or learning disabilities;More items...?
A reasonable accommodation is any change to the application or hiring process, to the job, to the way the job is done, or the work environment that allows a person with a disability who is qualified for the job to perform the essential functions of that job and enjoy equal employment opportunities.
For example, a request for reasonable accommodation is a right under Title I and therefore a protected activity. A protected activity can also include opposing a practice the individual thinks is unlawful discrimination under Title I.