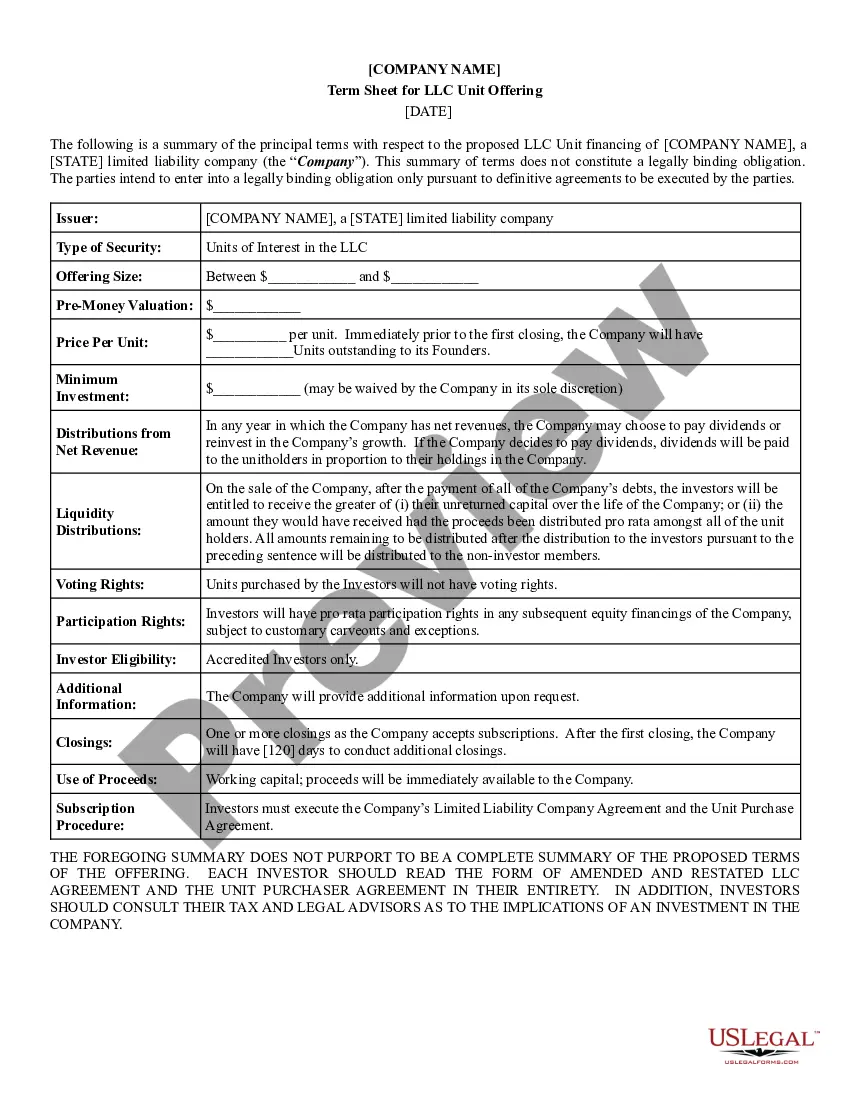
Georgia Year 2000 Services Agreement
Description
How to fill out Year 2000 Services Agreement?
US Legal Forms - one of the biggest libraries of authorized varieties in America - delivers an array of authorized record templates you are able to acquire or print out. Using the web site, you will get thousands of varieties for business and specific uses, sorted by classes, says, or keywords.You will find the latest variations of varieties such as the Georgia Year 2000 Services Agreement in seconds.
If you already possess a subscription, log in and acquire Georgia Year 2000 Services Agreement in the US Legal Forms collection. The Acquire option will appear on every single type you look at. You gain access to all formerly saved varieties within the My Forms tab of the account.
If you would like use US Legal Forms the first time, listed here are straightforward directions to help you started:
- Be sure to have picked out the best type to your town/county. Select the Preview option to examine the form`s content material. Browse the type description to ensure that you have selected the appropriate type.
- When the type does not fit your demands, make use of the Look for field on top of the screen to find the the one that does.
- In case you are pleased with the form, verify your choice by visiting the Buy now option. Then, opt for the costs plan you want and supply your qualifications to register for an account.
- Process the purchase. Use your charge card or PayPal account to perform the purchase.
- Pick the file format and acquire the form on the gadget.
- Make alterations. Load, change and print out and sign the saved Georgia Year 2000 Services Agreement.
Every single design you included in your money does not have an expiration day which is your own permanently. So, if you wish to acquire or print out yet another version, just visit the My Forms area and click about the type you want.
Obtain access to the Georgia Year 2000 Services Agreement with US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of authorized record templates. Use thousands of professional and state-distinct templates that meet your small business or specific requires and demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
They are processed through different offices. We recommend mailing the request. Normal processing takes one day, plus additional time for mailing, and costs $3. Expedited service is not available because processing only takes one day, plus additional time for mailing.
The primary cost to start an LLC in Georgia is the state registration fee of $100 ($110 for in person or mailed filings).
The GSCCCA is the only state agency authorized to issue apostilles for documents originating in the State of Georgia. Note: Notarized documents do not require additional county certification prior to obtaining the apostille.
The document must be notarized by a Georgia notary. The notary must date, sign and seal the document; all signatures and seals must be original. You must then obtain a notary certification from the clerk of superior court in the county in which the notary is commissioned.
An Apostille is a certificate that authenticates the origin of a public document. It is issued by a country that is party to the Apostille Convention to be used in another country which is also a party to the Convention. On , the Philippines became a party to the Apostille Convention.
You will need to: Hire a registered agent in the state. Reserve a business name. File Articles of Organization. Submit a Transmittal form. Apply for the appropriate Georgia business licenses and permits.
A converting LLC must pay filing fees to state agencies for filing the documents required for conversion. The Georgia Secretary of State charges $95.00 for the Certificate of Conversion and $100.00 for the Articles of Organization?which means the total filing fees in Georgia will be $195.00.
Georgia is the top job market in the U.S. for attracting young, well-educated workers, and home of the nation's top workforce training program. Financial Assistance. Businesses wishing to relocate have a wide range of grants and loans available via specialized public programs that foster business development.
To end a Georgia LLC, just file form CD-415, Certificate of Termination, with the Georgia Secretary of State, Corporations Division (SOS). The certificate of termination is available on the Georgia SOS website or your Northwest Registered Agent online account. You are not required to use SOS forms.
How long does it take to process an Apostille? Payment for DFA-OCA's Authentication service is : Php100.00 for regular processing (released after five working days) and Php200.00 for expedited processing (released after two working days).