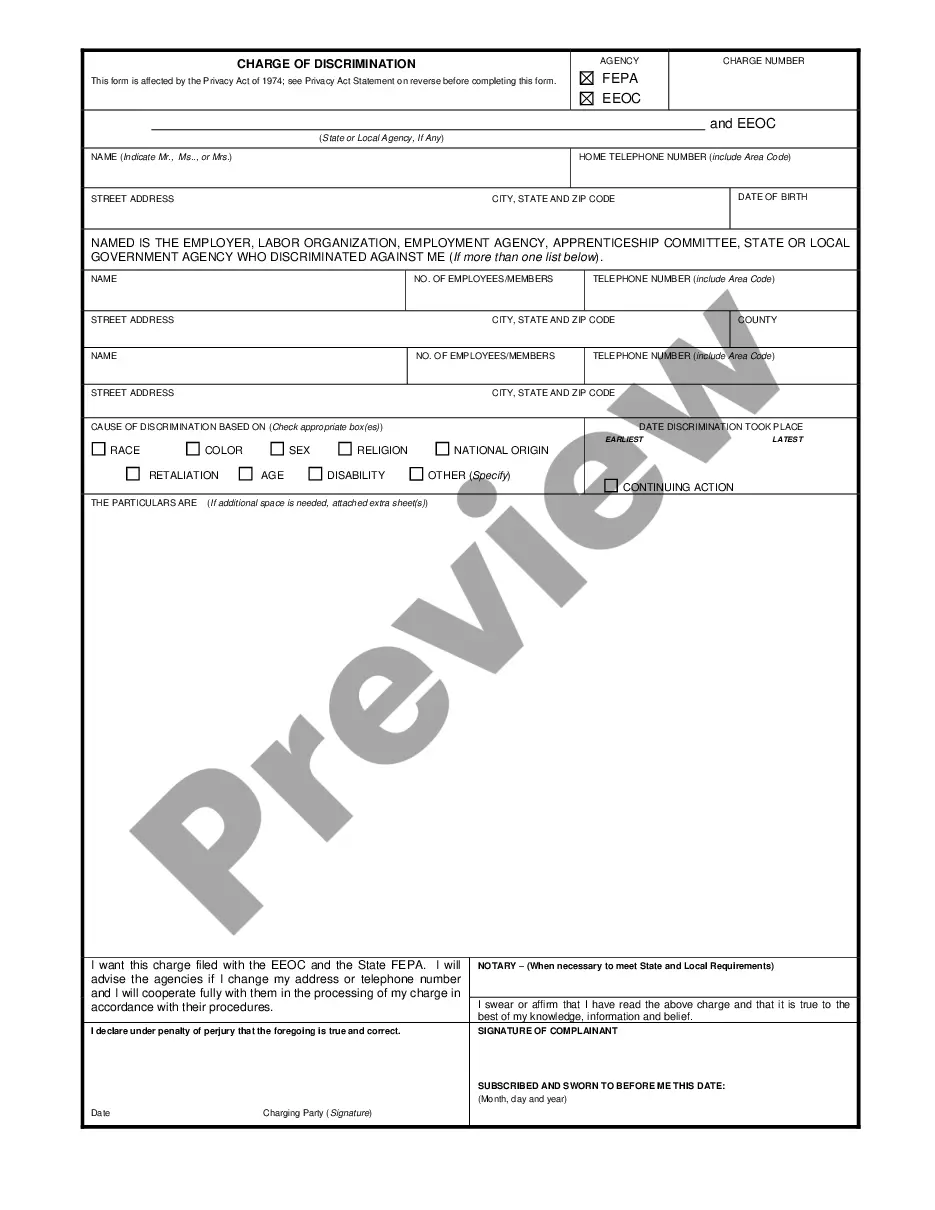
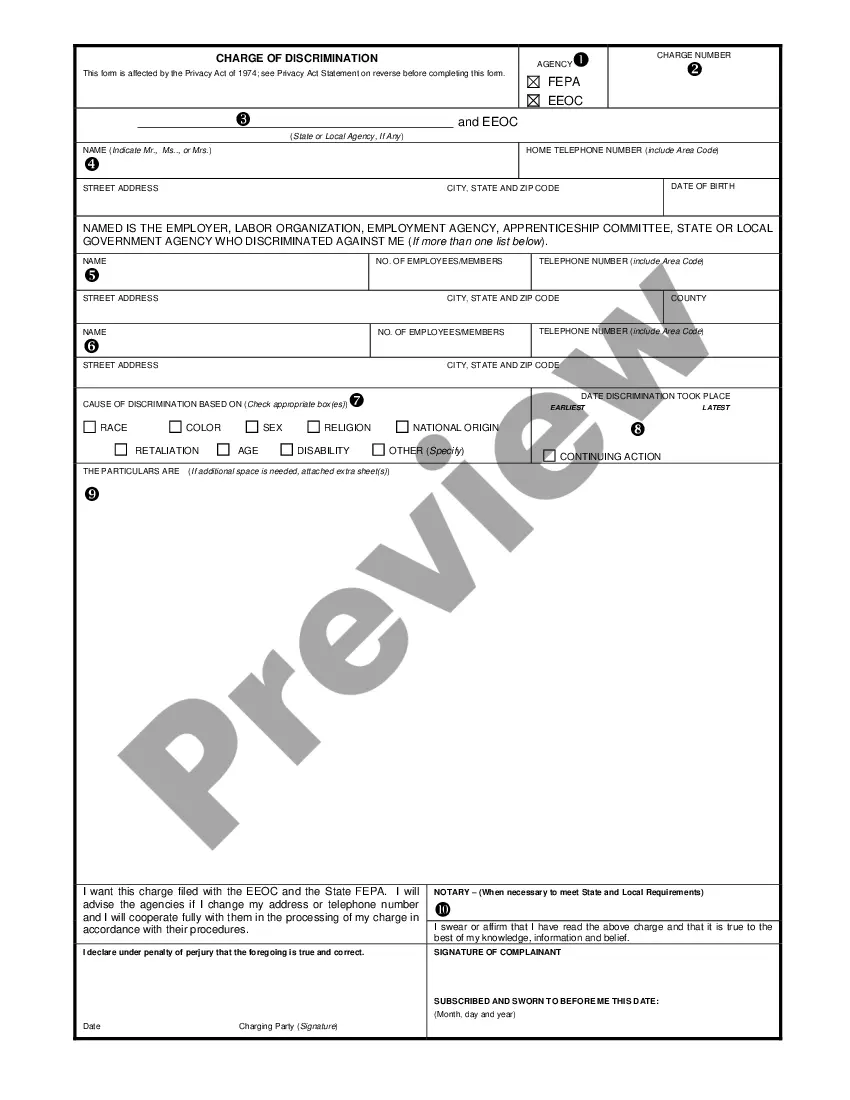
EEOC is the abbreviated form of Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. The EEOC commission is a federal agency which aims to end employment discrimination. The commission investigates various discriminations based on a person's color, race, nationality, sex, religion, age and disability.
Georgia Charge of Discrimination: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Complaint Process When faced with workplace discrimination issues in Georgia, employees can turn to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) for help. This article aims to provide a detailed description of the Georgia Charge of Discrimination, the legal process, and the different types of complaints that individuals can file with the EEOC. The Georgia Charge of Discrimination is a formal complaint filed by an employee or job applicant against an employer, alleging discriminatory practices in the workplace. Discrimination can occur based on various protected characteristics, such as race, color, national origin, sex, age, disability, religion, or genetic information. The EEOC is responsible for investigating these claims and enforcing federal laws that prohibit employment discrimination. Filing a Georgia Charge of Discrimination involves several essential steps. Firstly, the aggrieved party must submit a completed charge form, available on the EEOC's website. This form captures essential information such as the parties involved, the alleged discriminatory acts, and a concise description of the events. It is crucial to provide specific details and relevant facts when completing the form. In Georgia, there are two primary types of EEOC charges that individuals can file: 1. Individual Charges: These are complaints filed by an individual against their employer, alleging discrimination based on the protected characteristics mentioned above. The individual must typically file the charge within 180 days of the alleged discriminatory act, although this time frame can be extended under certain circumstances. 2. Class or Collective Action Charges: In some instances, multiple individuals may have faced similar discriminatory practices by the same employer. Such cases can be filed as class or collective action charges, where multiple aggrieved parties collectively challenge the discriminatory actions. These cases have the potential to impact a larger number of employees and may have more significant implications for the employer. Once the charge is submitted, the EEOC reviews the information provided and determines if it falls within their jurisdiction. If the charge meets the necessary criteria, the EEOC will then notify the employer, who must respond to the allegations within a given timeframe. The EEOC may then attempt to mediate a resolution between the parties, facilitating a settlement and avoiding formal litigation. If mediation fails or is not suitable, the EEOC will conduct an investigation into the allegations. This may involve requesting additional information from both parties, interviewing witnesses, and reviewing relevant documents. The investigation aims to gather evidence that supports or refutes the claims made in the complaint. After the investigation, the EEOC will make a determination on the merits of the charge. If they find evidence of discrimination, they will attempt to settle the matter amicably between the parties. If a settlement cannot be reached, the EEOC may choose to file a lawsuit on behalf of the aggrieved party or issue them a "Notice of Right to Sue," enabling them to pursue the matter in federal court. In summary, the Georgia Charge of Discrimination is a vital tool for individuals who believe they have faced discrimination in the workplace. By filing a charge with the EEOC, employees can seek justice and potentially secure remedies for the harm they suffered. Whether it's an individual charge or a class action, the EEOC plays a crucial role in enforcing federal anti-discrimination laws and striving for workplace equality in Georgia.