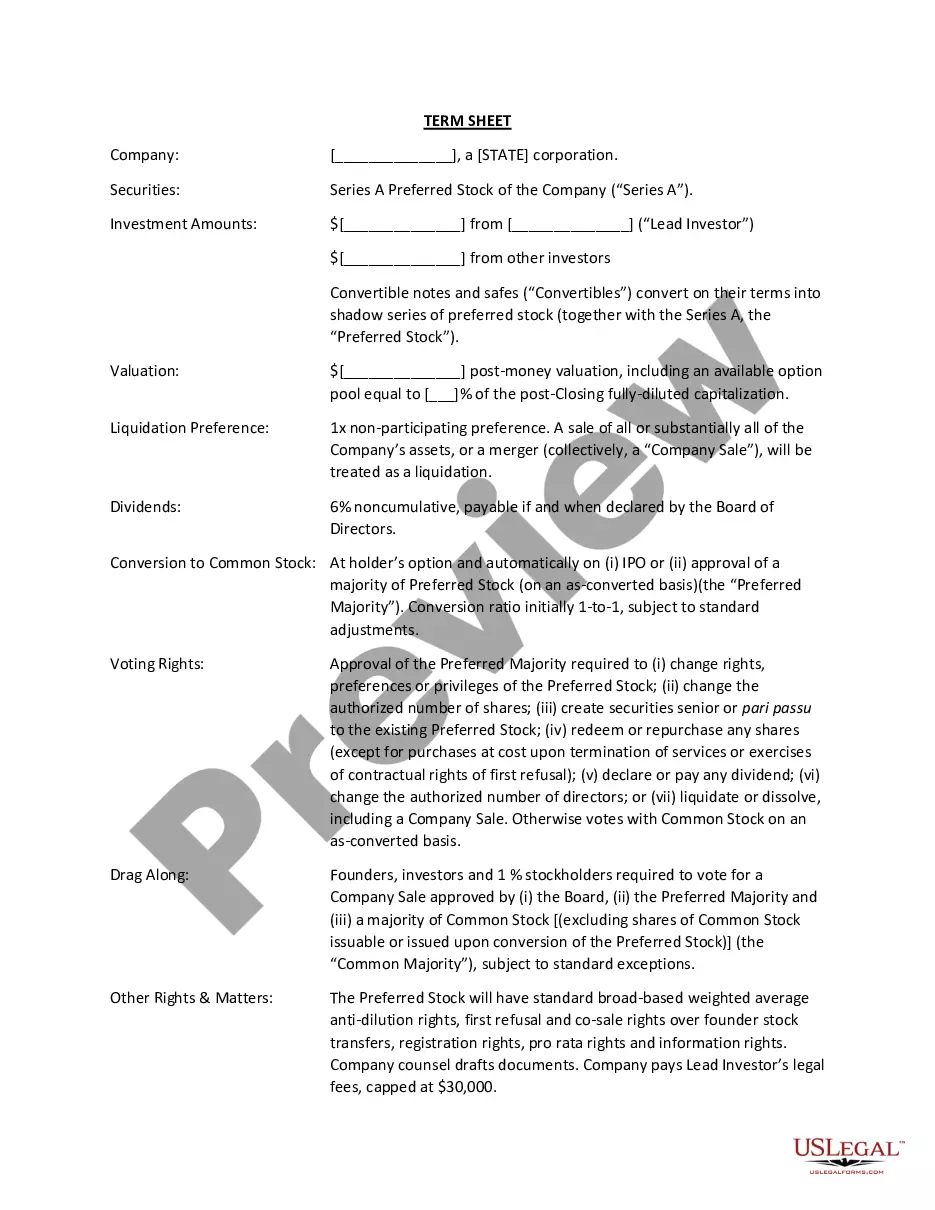
The Governing Law form, the provisions of this assignment relating specifically to title to real property that, due to applicable law, must be governed by the law of the jurisdiction in which the real property is located, shall be governed by the laws of such jurisdiction.
Georgia Governing Law refers to the set of regulations and statutes that prescribe how legal issues and disputes are handled within the state of Georgia. These laws are enforced by the state's judicial system and impact various areas such as business transactions, contracts, personal injury cases, property rights, and more. Understanding the Georgia Governing Law is crucial for individuals, businesses, and organizations operating within the state to ensure compliance and resolve legal matters efficiently. There are different types of Georgia Governing Law that encompass various legal domains. Some key areas covered under this law include: 1. Business Law: Georgia's business law governs the formation, operation, and dissolution of businesses within the state. It includes regulations related to business licensing, corporate governance, contracts, employment, intellectual property rights, and more. 2. Contract Law: Georgia's contract law outlines the rules and principles governing the creation, enforcement, and interpretation of contracts. This includes the essential elements of a contract, contractual obligations and remedies, breach of contract, and the rights and responsibilities of parties involved. 3. Property and Real Estate Law: Georgia's property and real estate law encompass regulations related to buying, selling, leasing, and managing property within the state. This includes laws regarding property ownership, landlord-tenant relationships, easements, zoning regulations, and title transfers. 4. Personal Injury Law: Georgia's personal injury law governs the rights and remedies for individuals who have been harmed or injured due to the negligence or intentional actions of others. It includes laws related to car accidents, medical malpractice, premises liability, product liability, and wrongful death. 5. Family Law: Georgia's family law addresses legal matters related to marriage, divorce, child custody, adoption, child support, alimony, and domestic violence. It aims to uphold the best interests of individuals and families involved in these matters while ensuring fairness and justice. 6. Employment Law: Georgia's employment law lays down rules and regulations governing employer-employee relationships. It covers areas such as wages, non-discrimination, workplace safety, unemployment benefits, workers' compensation, and employee rights. It is essential to consult with qualified legal professionals or refer to the official Georgia statutes and codes to obtain accurate and up-to-date information on the specific Georgia Governing Law relevant to a particular legal issue or jurisdiction within the state. Compliance with Georgia's laws ensures that individuals and entities can operate within the state's legal framework and resolve legal disputes effectively.