This lease rider form may be used when you are involved in a lease transaction, and have made the decision to utilize the form of Oil and Gas Lease presented to you by the Lessee, and you want to include additional provisions to that Lease form to address specific concerns you may have, or place limitations on the rights granted the Lessee in the “standard” lease form.
Georgia Surface Use by Lessee and Accommodation With Use of the Surface
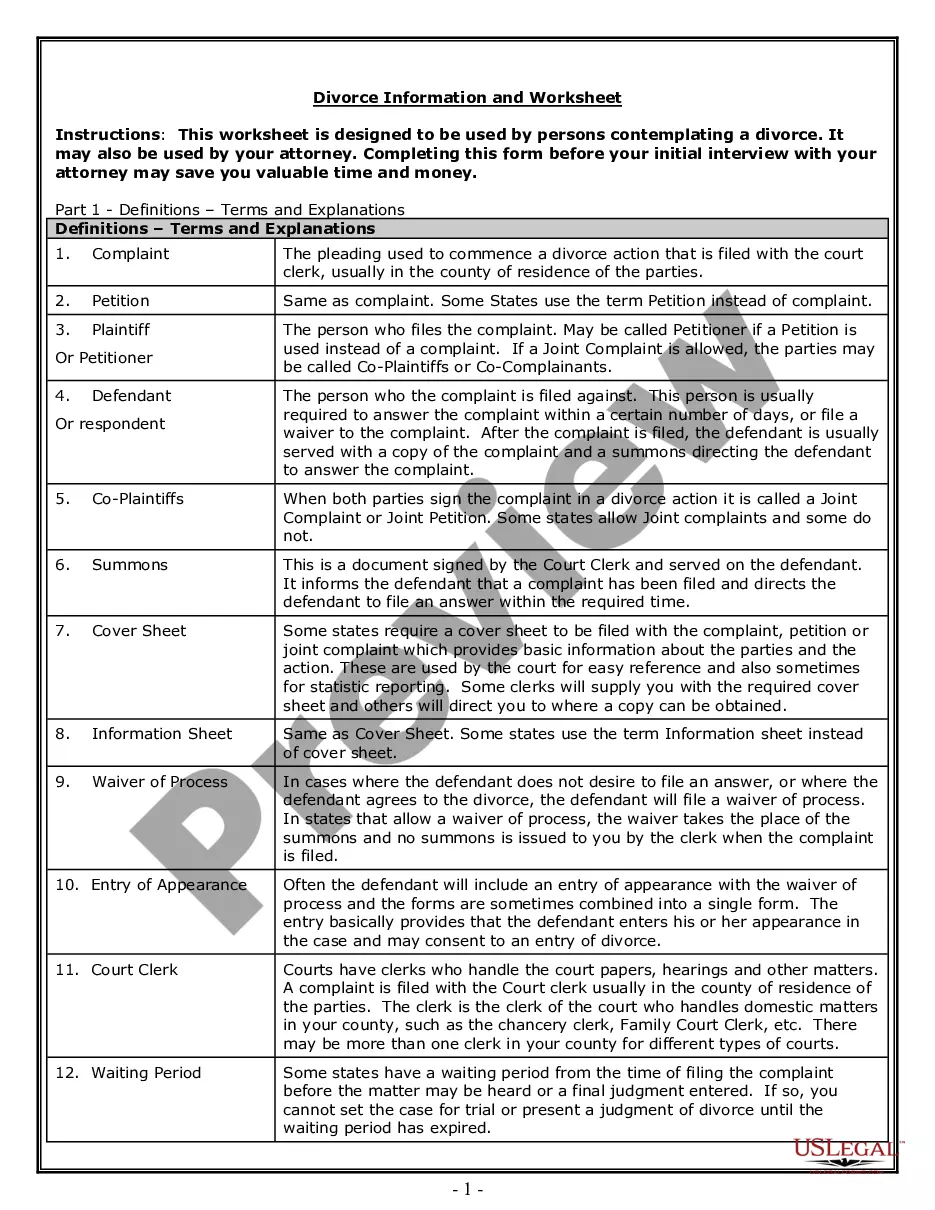
Description
How to fill out Surface Use By Lessee And Accommodation With Use Of The Surface?
If you have to full, download, or printing authorized papers templates, use US Legal Forms, the greatest assortment of authorized types, that can be found on the web. Use the site`s simple and easy handy look for to get the documents you want. Numerous templates for organization and specific reasons are sorted by types and claims, or keywords. Use US Legal Forms to get the Georgia Surface Use by Lessee and Accommodation With Use of the Surface with a couple of click throughs.
Should you be already a US Legal Forms consumer, log in in your accounts and click the Download key to obtain the Georgia Surface Use by Lessee and Accommodation With Use of the Surface. You can also accessibility types you in the past saved from the My Forms tab of your respective accounts.
If you use US Legal Forms the very first time, refer to the instructions below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have selected the form for that right town/nation.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview method to look through the form`s content material. Don`t forget about to see the information.
- Step 3. Should you be not satisfied using the develop, utilize the Lookup industry near the top of the display screen to find other types of the authorized develop web template.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you want, select the Acquire now key. Select the costs strategy you prefer and add your references to register on an accounts.
- Step 5. Process the financial transaction. You may use your bank card or PayPal accounts to complete the financial transaction.
- Step 6. Find the structure of the authorized develop and download it on the gadget.
- Step 7. Full, edit and printing or indicator the Georgia Surface Use by Lessee and Accommodation With Use of the Surface.
Each and every authorized papers web template you get is yours forever. You possess acces to every single develop you saved within your acccount. Select the My Forms section and choose a develop to printing or download yet again.
Remain competitive and download, and printing the Georgia Surface Use by Lessee and Accommodation With Use of the Surface with US Legal Forms. There are many expert and status-particular types you can utilize to your organization or specific requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
Surface rights in Pennsylvania These rights in Pennsylvania are those licenses to the surface interest of any property. This right covers the structure, farmland, or any above ground minerals like water bodies, trees and plants. This right was set ing to Pennsylvania ordinances and local laws.
As in Texas, operators in New Mexico are also subject to the common law Doctrine of Accommodation. The New Mexico Supreme Court adopted a rule similar to Texas' Accommodation Doctrine, which interpreted the rule to mean that the rights held by a mineral lessee create an implied easement by necessity.
Under the Accommodation Doctrine, the surface owner must generally show that the particular surface activities are not ?reasonably necessary? to extract the oil or gas. Haupt Inc. v. Tarrant County Water, 870 S.W.
SOPA creates an obligation to pay damages where oil and gas operations result in any loss of: land value; agricultural production or income; use; access; or improvements.
BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT: The BLM New Mexico Field Office maintains information on mineral rights and has a public information room at 301 Dinosaur Trail, Santa Fe, NM 87508, (505) 954-2000, where that information can be researched.
The general (common law) rule in the case of a split estate is that the mineral estate is ?dominant.? This means that the owner of the surface estate cannot prohibit the owner of the mineral estate from accessing and developing the minerals.