Under the Uniform Commercial Code, the rights of the parties to a sales transaction, or the rights of third persons, are not generally resolved by the question of who has title to the goods. In lieu of title being a consideration, separate Code provisions enunciate policies and remedies for the parties under a variety of circumstances. Where the Code fails to make specific provisions for a particular situation, then the question of title must be resolved. Where situations are not covered elsewhere, and title is considered, title cannot pass until the goods are identified to the sales agreement. The seller can reserve no more than a security interest in the title to the goods once the goods are shipped or delivered. The parties may stipulate conditions of delivery within the provisions of the Code.
Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis
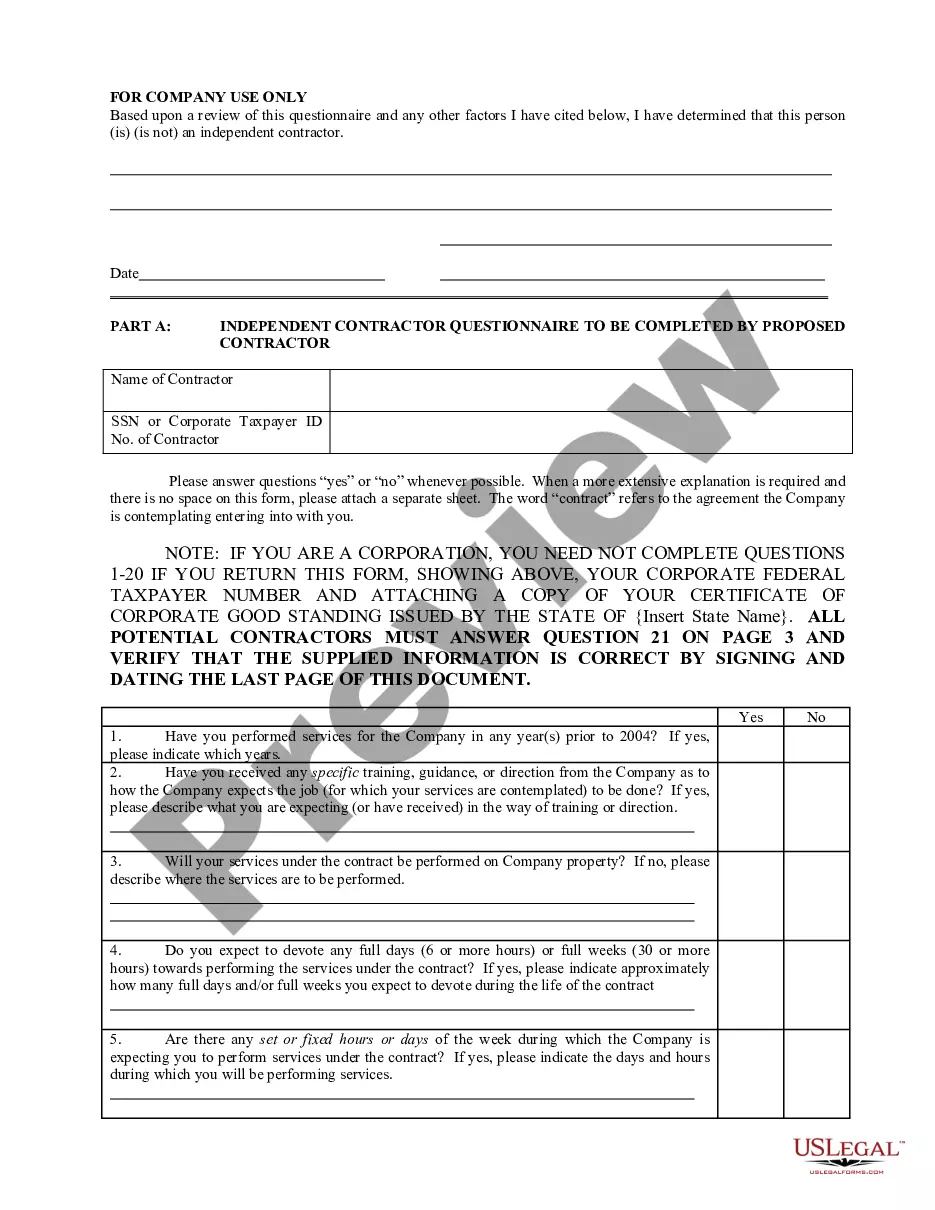
Description
How to fill out Agreement For Sale Of Goods On An Ongoing Basis?
Are you currently in a situation where you frequently require documents for either business or personal reasons.
There are numerous legal document templates accessible online, but finding ones you can rely on is quite challenging.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of document templates, including the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, designed to fulfill state and federal requirements.
Once you find the correct document, click Acquire now.
Choose a payment plan that suits you, fill out the necessary information to create your account, and process your order using your PayPal or credit card.
- If you are already acquainted with the US Legal Forms website and possess an account, simply Log In.
- Then, you can download the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these instructions.
- Search for the document you need and ensure it is appropriate for the correct city/state.
- Use the Review button to evaluate the document.
- Examine the description to confirm you have selected the right document.
- If the document does not meet your expectations, utilize the Lookup field to find the document that satisfies your requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
The seller's basic obligation in a contract for the sale of goods, especially under the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, revolves around delivering goods that meet the specified standards and timelines. This includes ensuring the goods are available at the agreed place and in the correct quantity. Additionally, the seller must provide all necessary documentation to facilitate the transaction, which is vital for smooth operations and compliance.
In any contract, including the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, the seller has crucial obligations. These include delivering the goods as specified, ensuring they conform to the agreed-upon specifications, and providing necessary documentation for the buyer. The seller is also responsible for addressing any issues the buyer may face regarding the goods, enabling a smooth ongoing trading relationship.
In a contract like the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, the client, or buyer, has several key obligations. The buyer must provide payment as specified in the terms of the agreement, ensuring prompt processing to maintain a good relationship. Furthermore, the buyer should inspect the goods upon receipt and promptly communicate any discrepancies or issues to the seller, fostering transparency in the transaction.
The basic performance obligations of the seller, as outlined in the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, include delivering the goods on time and ensuring they are fit for the purpose specified in the contract. The seller must also provide accurate documentation to the buyer, which supports the transfer of ownership and payment. Moreover, the seller should communicate effectively with the buyer throughout the sales process to address any concerns that may arise.
Under the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, the seller must ensure timely delivery of the goods as specified in the contract. The seller is also responsible for providing the necessary documents, such as invoices and shipping receipts, to facilitate a smooth transaction. Additionally, the seller must ensure that the goods match the quality and quantity agreed upon in the contract.
The Deceptive Trade Practices Act serves to eliminate fraud and misrepresentation in business. It emphasizes honesty in advertising and sales, which is crucial when negotiating agreements like the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis. This law facilitates trust between consumers and businesses, strengthening the marketplace.
The Guam Claims Act allows individuals to seek compensation for losses or damages under specific conditions. This act is important for businesses engaged in the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, as it clarifies procedures for filing claims. Knowing your rights under this act can provide peace of mind when entering into contracts.
Inheritance law in Guam governs the distribution of a deceased person's estate. It addresses wills, trusts, and intestacy issues, ensuring that the wishes of the deceased align with legal requirements. Understanding these laws can be beneficial if you are considering agreements related to the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis that may involve inheritances.
The Deceptive Trade Practices Act in Guam aims to protect consumers from misleading business practices. It provides legal recourse for individuals harmed by such actions, especially in transactions tied to the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis. By enforcing this law, Guam maintains a fair marketplace for all.
In Guam, local and federal laws apply, depending on the context. Commercial transactions, such as those linked to the Guam Agreement for Sale of Goods on an Ongoing Basis, generally follow both the Uniform Commercial Code and local statutes. These laws establish how businesses operate and protect the interests of citizens.