A patent is a grant of a property right by the Government to an inventor. The United States Constitution gives Congress the right to provide for patent protection in legislation in order to encourage useful inventions. The patent itself provides a detailed description of the invention, and how it is used or how to make it. Thus, if you obtain a patent you cannot keep the matter secret, which is the province of Trade Secret Law. A patent enables the owner to exclude others from making, using or selling the invention for the life of the patent.
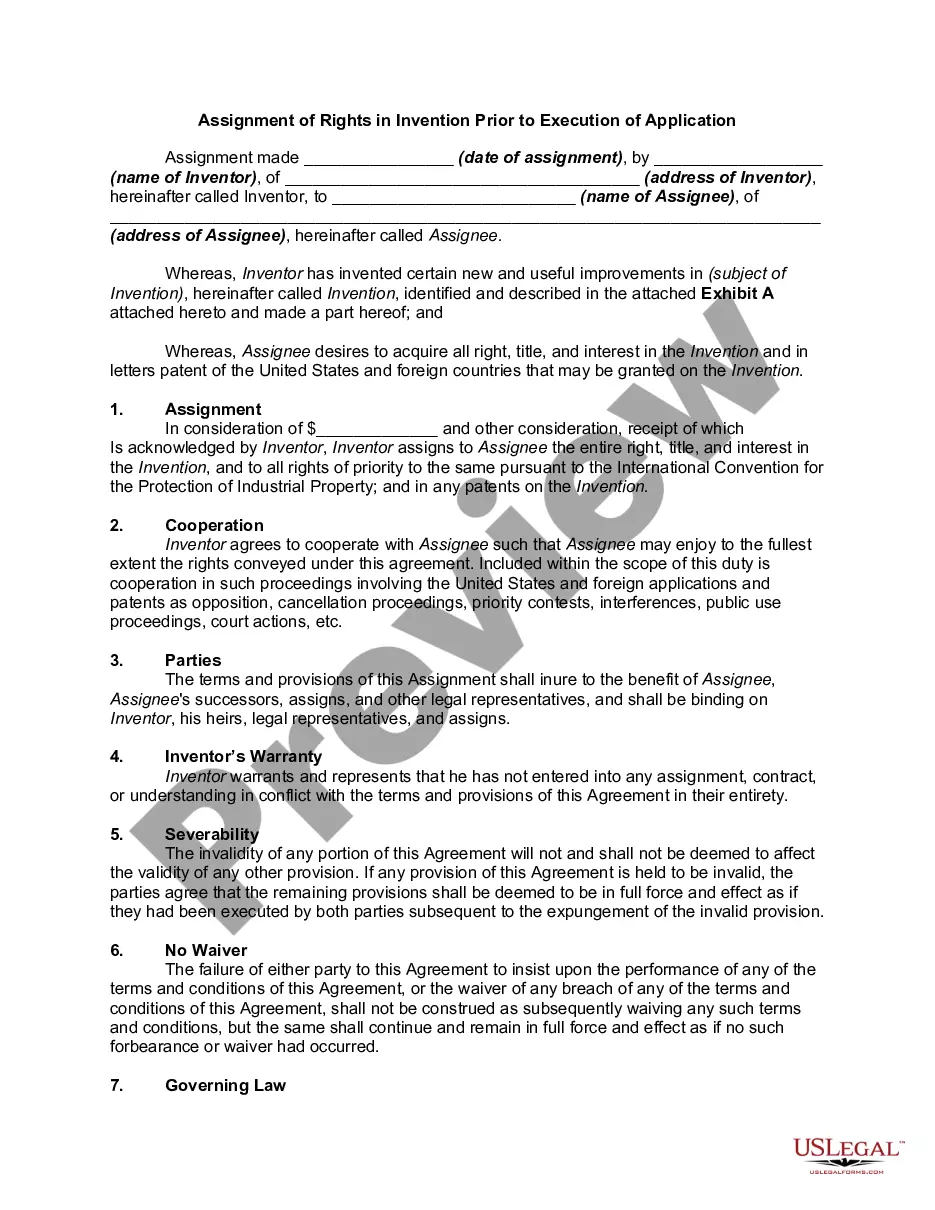
Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is a legal document that pertains to intellectual property rights and the transfer of those rights in relation to inventions made in Guam. This assignment serves as a means to ensure that the ownership and future commercialization of inventions are properly and legally transferred from the inventor to another party, often an employer or sponsor. The Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application can take several forms to accommodate various scenarios and relationships. Some common types include: 1. Employee Invention Assignment: This assignment is typically employed when an inventor creates an invention while working as an employee. The employer, through this assignment, ensures that all rights to the invention, including patents and copyrights, are owned by the company rather than the individual inventor. 2. Independent Contractor Invention Assignment: In this case, an independent contractor or consultant is commissioned to work on a specific project, and any inventions or intellectual property created as a result become the property of the hiring entity through the assignment agreement. 3. University or Research Institution Assignment: When research institutions or universities fund research projects, an assignment is often used to secure ownership of any resulting inventions or innovations. This ensures that the institution can protect its investments and potentially commercialize the invention for further research or commercial purposes. Regardless of the specific type, a Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application typically covers some important elements: a. Transfer of Ownership: The assignment agreement explicitly transfers all rights, title, and interest in the invention from the inventor to the assignee, usually an employing organization or sponsor. b. Description of Intellectual Property: The assignment clearly identifies the invention, its nature, and its functionality, allowing for unambiguous transfer and subsequent protection. c. Scope of Rights: The agreement outlines the scope of the assignment, specifying whether it covers only patent rights or extends to copyrights, trademarks, and other intellectual property rights associated with the invention. d. Considerations: In many cases, the assignment includes considerations, such as monetary compensation or mutual agreements between the parties involved. This ensures that both parties are aware of their respective rights and obligations. e. Enforceability: The assignment agreement is designed to be legally enforceable, protecting both parties from potential disputes regarding the ownership and usage of the invention. Overall, the Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is a crucial legal document that ensures the proper transfer and protection of intellectual property rights for inventions made in Guam. It establishes a clear chain of ownership, protecting the rights and interests of both inventors and assignees.Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is a legal document that pertains to intellectual property rights and the transfer of those rights in relation to inventions made in Guam. This assignment serves as a means to ensure that the ownership and future commercialization of inventions are properly and legally transferred from the inventor to another party, often an employer or sponsor. The Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application can take several forms to accommodate various scenarios and relationships. Some common types include: 1. Employee Invention Assignment: This assignment is typically employed when an inventor creates an invention while working as an employee. The employer, through this assignment, ensures that all rights to the invention, including patents and copyrights, are owned by the company rather than the individual inventor. 2. Independent Contractor Invention Assignment: In this case, an independent contractor or consultant is commissioned to work on a specific project, and any inventions or intellectual property created as a result become the property of the hiring entity through the assignment agreement. 3. University or Research Institution Assignment: When research institutions or universities fund research projects, an assignment is often used to secure ownership of any resulting inventions or innovations. This ensures that the institution can protect its investments and potentially commercialize the invention for further research or commercial purposes. Regardless of the specific type, a Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application typically covers some important elements: a. Transfer of Ownership: The assignment agreement explicitly transfers all rights, title, and interest in the invention from the inventor to the assignee, usually an employing organization or sponsor. b. Description of Intellectual Property: The assignment clearly identifies the invention, its nature, and its functionality, allowing for unambiguous transfer and subsequent protection. c. Scope of Rights: The agreement outlines the scope of the assignment, specifying whether it covers only patent rights or extends to copyrights, trademarks, and other intellectual property rights associated with the invention. d. Considerations: In many cases, the assignment includes considerations, such as monetary compensation or mutual agreements between the parties involved. This ensures that both parties are aware of their respective rights and obligations. e. Enforceability: The assignment agreement is designed to be legally enforceable, protecting both parties from potential disputes regarding the ownership and usage of the invention. Overall, the Guam Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is a crucial legal document that ensures the proper transfer and protection of intellectual property rights for inventions made in Guam. It establishes a clear chain of ownership, protecting the rights and interests of both inventors and assignees.