Guam Benchmarking Considerations
Description
How to fill out Benchmarking Considerations?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest repositories of legal documents in the USA - offers an extensive selection of legal template formats that you can download or print.
By using the website, you can access thousands of forms for commercial and personal purposes, organized by categories, claims, or keywords. You can find the newest versions of forms such as the Guam Benchmarking Considerations in just moments.
If you possess a membership, Log In and download Guam Benchmarking Considerations from the US Legal Forms library. The Download option will appear on every form you view. You can access all previously obtained forms within the My documents section of your account.
Each template you add to your account has no expiration date and is yours indefinitely. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply go to the My documents section and click on the form you need.
Access the Guam Benchmarking Considerations with US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive collections of legal document templates. Utilize a multitude of professional and state-specific templates that satisfy your business or personal requirements and specifications.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/region. Click the Preview button to review the form’s details. Read the form description to confirm that you have chosen the right form.
- If the form does not meet your needs, utilize the Search bar at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, affirm your choice by clicking the Buy now button. Then, select the pricing plan you prefer and provide your information to register for an account.
- Process the payment. Use your Visa, Mastercard, or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Select the format and download the form to your device.
- Make modifications. Fill out, edit, print, and sign the downloaded Guam Benchmarking Considerations.
Form popularity
FAQ
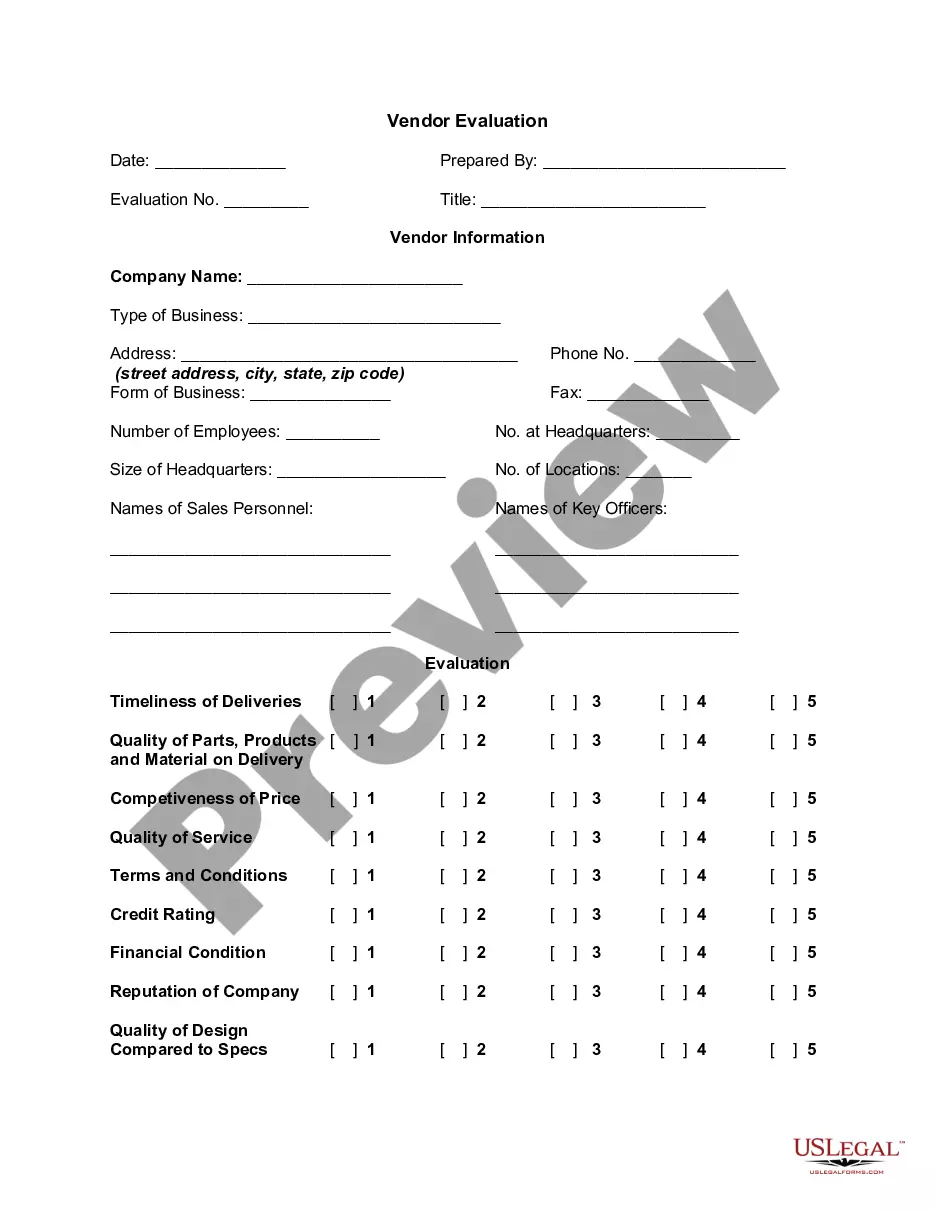
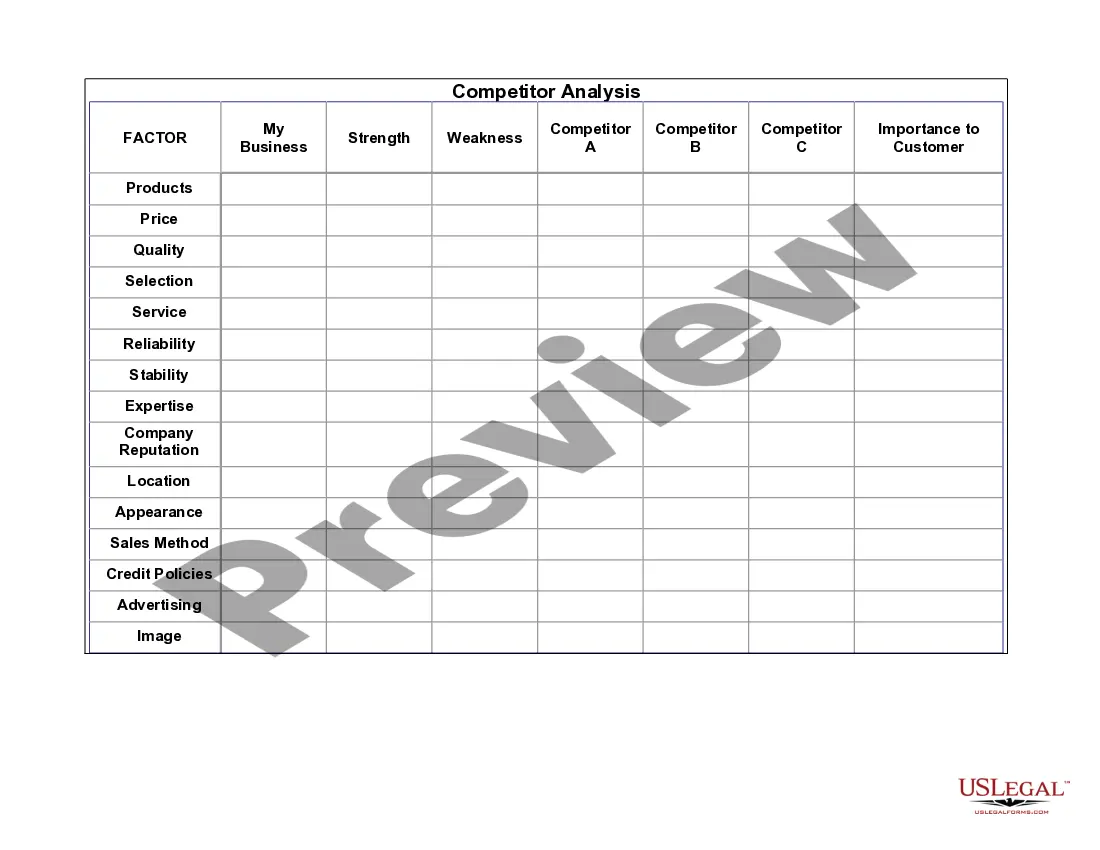
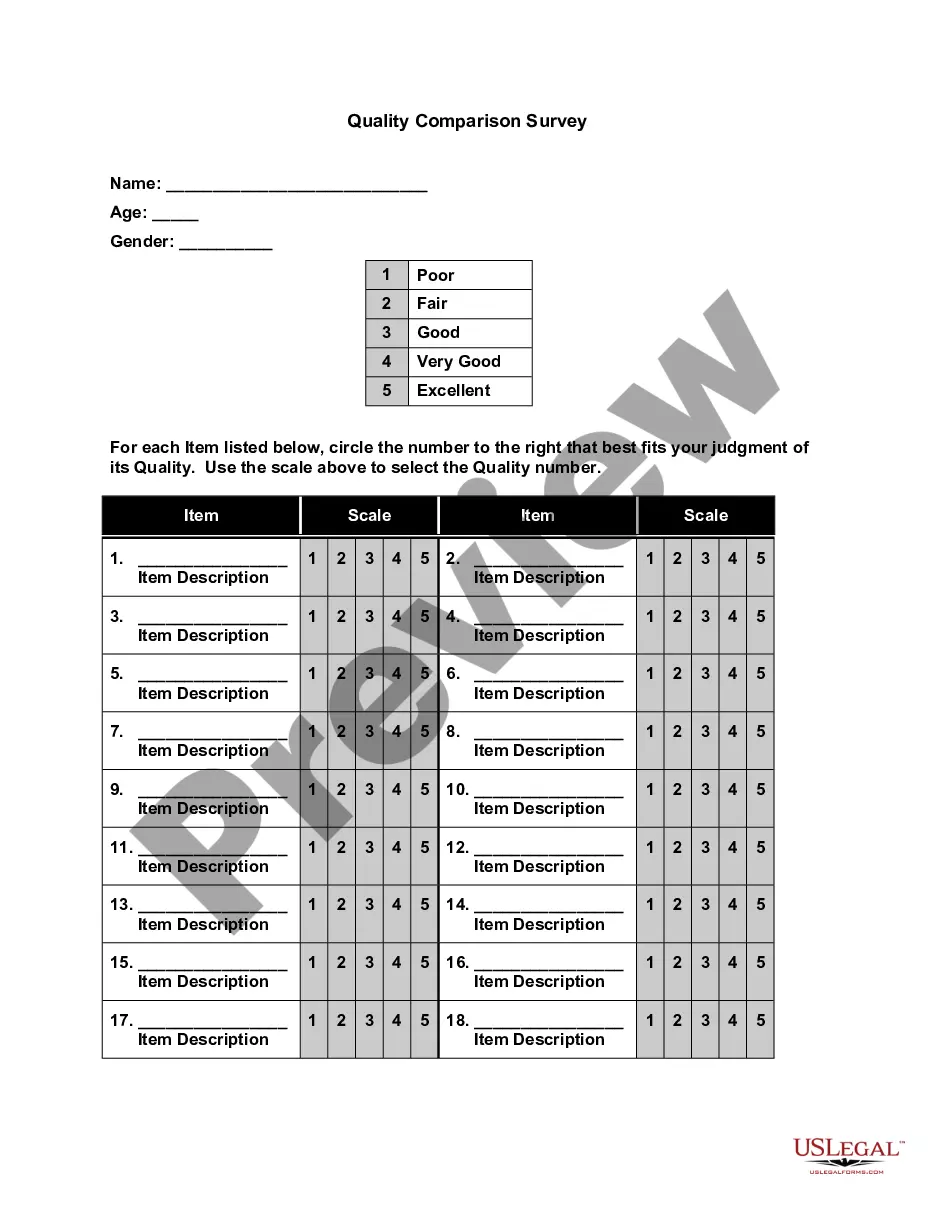
Organizations can utilize benchmarking in various scenarios, such as evaluating employee compensation, assessing operational efficiency, or measuring customer satisfaction. For example, they may compare their employee retention rates against industry standards. By applying Guam Benchmarking Considerations, businesses can leverage benchmarking to drive improvements and often enhance overall performance.
A benchmark job is a role commonly used as a reference point for salary comparisons across various organizations. For instance, positions such as Customer Service Representative or Project Manager often serve as benchmark jobs due to their prevalence in different industries. Keeping Guam Benchmarking Considerations in mind allows for more accurate assessments when using these roles for salary benchmarking.
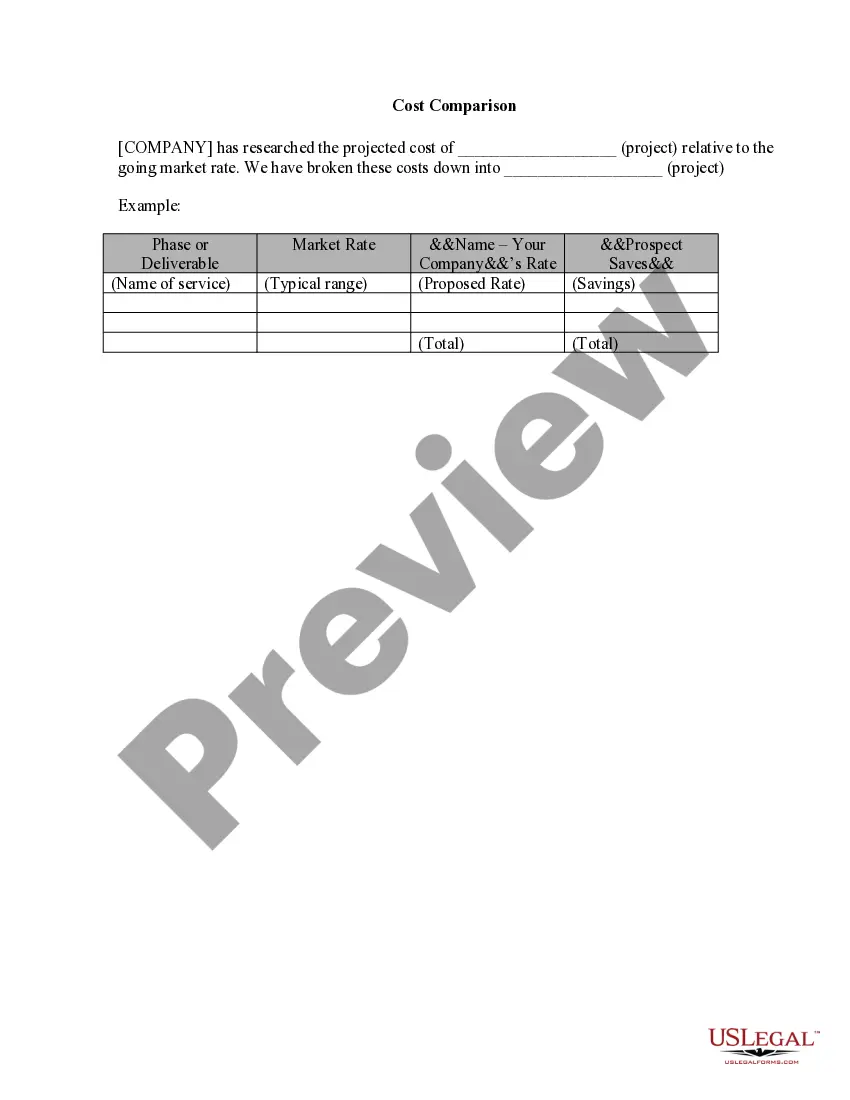
Documenting benchmarking involves creating a structured report that outlines your findings, methodologies, and comparisons. Include data sources, salary ranges, and insights on the competitive landscape. This thorough documentation supports your organization’s decisions and demonstrates compliance with Guam Benchmarking Considerations, thereby strengthening your HR practices.
To benchmark a position, start by identifying the key responsibilities and skills required for the role, then gather data on salaries and job descriptions from various sources. Utilize market surveys and industry reports to collect this information. Keeping Guam Benchmarking Considerations in mind is essential for maintaining relevance and ensuring your approach reflects current market dynamics.
Guam's economic outlook for 2025 shows a positive trend, driven by a rebound in tourism and infrastructure investment. The government aims to diversify the economy while enhancing business opportunities. By considering economic indicators and trends, stakeholders can better inform their Guam Benchmarking Considerations, setting themselves up for success.
The strategic significance of Guam lies in its role as a military base and a logistical center for the Asia-Pacific region. It supports U.S. defense initiatives and fosters international partnerships. Recognizing this significance aids in framing Guam Benchmarking Considerations for businesses looking to navigate the geopolitical landscape.
Guam's priority climate action plan aims to address climate vulnerabilities through community engagement and sustainable practices. The plan includes initiatives for renewable energy, community resilience, and environmental protection. By aligning with this plan, stakeholders can enhance their Guam Benchmarking Considerations and contribute to a sustainable future.
Guam faces several challenges, including economic dependence on tourism and the military, as well as infrastructure issues and environmental concerns. Rising sea levels and climate impacts threaten its ecosystems and communities. Addressing these challenges is key to effective Guam Benchmarking Considerations, ensuring sustainable development and resilience.
Guam sits at a crucial location in the western Pacific, serving as a vital hub for military operations and international trade. Its proximity to Asia makes it an ideal launch point for both commercial and defense activities. Understanding Guam’s strategic importance helps in making informed decisions regarding Guam Benchmarking Considerations, especially for businesses and military entities.
Yes, Guam is considered part of the United States for tax purposes, but with specific local tax laws that differ from the mainland. This unique status affects how residents and businesses approach taxation. Keeping this in mind is crucial as you delve into Guam Benchmarking Considerations and assess how these factors might influence your financial decisions.