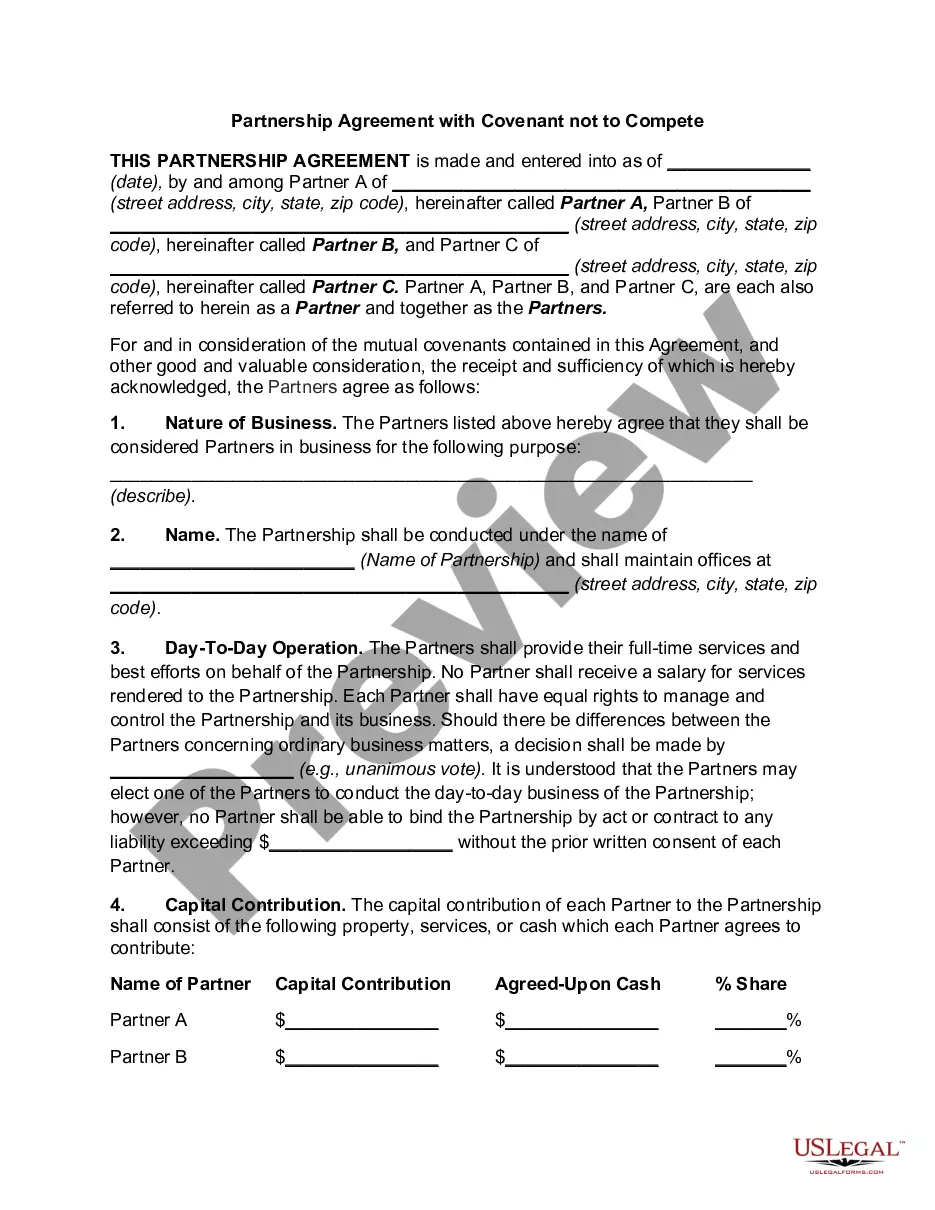
Guam Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete
Description
How to fill out Partnership Agreement With Covenant Not To Compete?
Are you presently in a location where you require documents for either business or personal reasons almost every day? There are numerous legal document templates available online, but finding ones you can trust isn't easy.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of form templates, such as the Guam Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete, which are designed to comply with federal and state regulations.
If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In. Then, you can download the Guam Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete template.
Access all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section. You can obtain another copy of the Guam Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete at any time, if needed. Just click the required form to download or print the document template.
Utilize US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal documents, to save time and minimize errors. The service offers professionally crafted legal document templates that can be used for various purposes. Create an account on US Legal Forms and start simplifying your life.
- Obtain the form you need and ensure it’s for the correct city/state.
- Use the Review button to examine the form.
- Check the summary to confirm that you have chosen the appropriate form.
- If the form isn’t what you’re looking for, use the Search field to find the document that meets your needs and requirements.
- Once you find the right form, click Purchase now.
- Select the payment plan you want, fill in the necessary details to create your account, and complete the purchase using PayPal or a credit/debit card.
- Choose a convenient document format and download your copy.
Form popularity
FAQ
You Can Void a Non-Compete by Proving Its Terms Go Too Far or Last Too Long. Whether a non-compete is unenforceable because it covers too large of a geographical area or it lasts too long can depend on many factors. Enforceability can depend on your industry, skills, location, etc.
Courts consider several elements when determining the reasonableness of a covenant not to compete, including (1) the time and territory encompassed by the covenant, (2) the territory in which the employee worked, (3) the area in which the employer operated, (4) the nature of the business and (5) the nature of the
The well-known general rule is that a covenant not to compete is only enforceable if its terms are reasonable and necessary to protect the legitimate business interests of the employer.
The well-known general rule is that a covenant not to compete is only enforceable if its terms are reasonable and necessary to protect the legitimate business interests of the employer.
A covenant not to compete has three elements: (1) a limitation on the work that may be pursued by the employee, (2) a definite time, and (3) a definite geographical area. The time and geographical restrictions are usually straightforward; the limitation on work is a little more complex.
A covenant not to compete will be deemed valid if it only restricts the employee's opportunity to compete while they remain employed with the employer requiring the covenant, but imposes no restrictions on the employee once they separate from the employment.
In a sale of business contract, a covenant not to compete usually prevents the buyer of the business from doing the same type of business in a specified area for a certain period of time.
Texas courts have recognized three main categories of acceptable consideration: (1) tying the non-compete to a confidentiality agreement; (2) an employer's agreement to provide specialized training; and (3) an award of stock options. Stock Option Award.
Traditionally, covenants not to compete were designed to prevent unfair competition and were confined to corporate executives, persons with knowledge of trade secrets, sales persons and client-based professionals (e.g., physicians and accountants).
Here are five ways to beat a non-compete agreement.Prove your employer is in breach of contract.Prove there is no legitimate interest to enforce the non-compete agreement.Prove the agreement is not for a reasonable amount of time.Prove that the confidential information you had access to isn't special.More items...