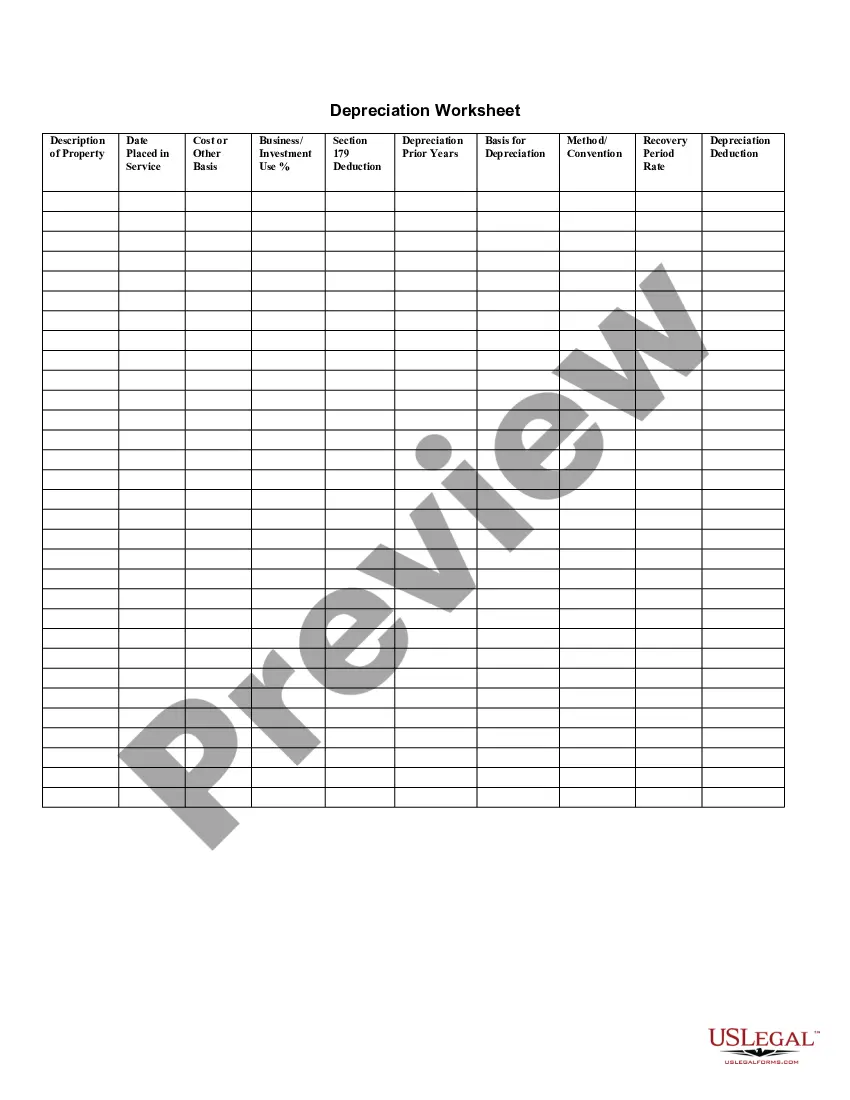
Guam Depreciation Schedule
Description
How to fill out Depreciation Schedule?
Selecting the most suitable registered document format might pose a challenge.
Clearly, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how will you identify the official type you require.
Take advantage of the US Legal Forms site. This service provides thousands of templates, including the Guam Depreciation Schedule, which you can utilize for business and personal purposes.
You can preview the form using the Review button and read the form description to confirm it is the correct one for you.
- All of the forms are vetted by experts and comply with federal and state regulations.
- If you are currently registered, Log Into your account and click the Acquire button to obtain the Guam Depreciation Schedule.
- Use your account to search through the legal forms you have acquired in the past.
- Visit the My documents section of your account to download another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are easy instructions to follow.
- First, make sure you have chosen the correct form for your area/state.
Form popularity
FAQ
The portion of the business standard mileage rate that is treated as depreciation will be 27 cents per mile for 2020, 1 cent more than 2019, one of the few amounts that is increasing.
27, 2017, and placed in service during calendar year 2020, the depreciation limit under Sec. 280F(d)(7) is $18,100 for the first tax year; $16,100 for the second tax year; $9,700 for the third tax year; and $5,760 for each succeeding year, all unchanged from 2019. Under Sec.
The depreciation method used for rental property is MACRS. There are two types of MACRS: ADS and GDS. GDS is the most common method that spreads the depreciation of rental property over its useful life, which the IRS considers to be 27.5 years for a residential property.
What happens if you don't depreciate rental property? In essence, you lose the opportunity to claim a massive tax benefit. If/when you decide to sell the property, you will still pay depreciation recapture tax, regardless of whether or not you claimed the depreciation during your tenure as the owner of the property.
For new or used passenger automobiles eligible for bonus depreciation in 2021, the first-year limitation is increased by an additional $8,000, to $18,200.
To be depreciable, the property must meet all the following requirements.It must be property you own.It must be used in your business or income-producing activity.It must have a determinable useful life.It must be expected to last more than 1 year.
The total section 179 deduction and depreciation you can deduct for a passenger automobile, including a truck or van, you use in your business and first placed in service in 2021 is $18,200, if the special depreciation allowance applies, or $10,200, if the special depreciation allowance does not apply.
It was scheduled to go down to 40% in 2018 and 30% in 2019, and then not be available in 2020 and beyond. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, enacted at the end of 2018, increases first-year bonus depreciation to 100%. It goes into effect for any long-term assets placed in service after September 27, 2017.
The balance of depreciation is written off in the year after the last class life year. For 5-year property that's the sixth year. So, 1/2 + 5 + 1/2 (the balance remaining in the last year after the class life year) equals 6 years.
To calculate the annual amount of depreciation on a property, you divide the cost basis by the property's useful life. In our example, let's use our existing cost basis of $206,000 and divide by the GDS life span of 27.5 years. It works out to being able to deduct $7,490.91 per year or 3.6% of the loan amount.