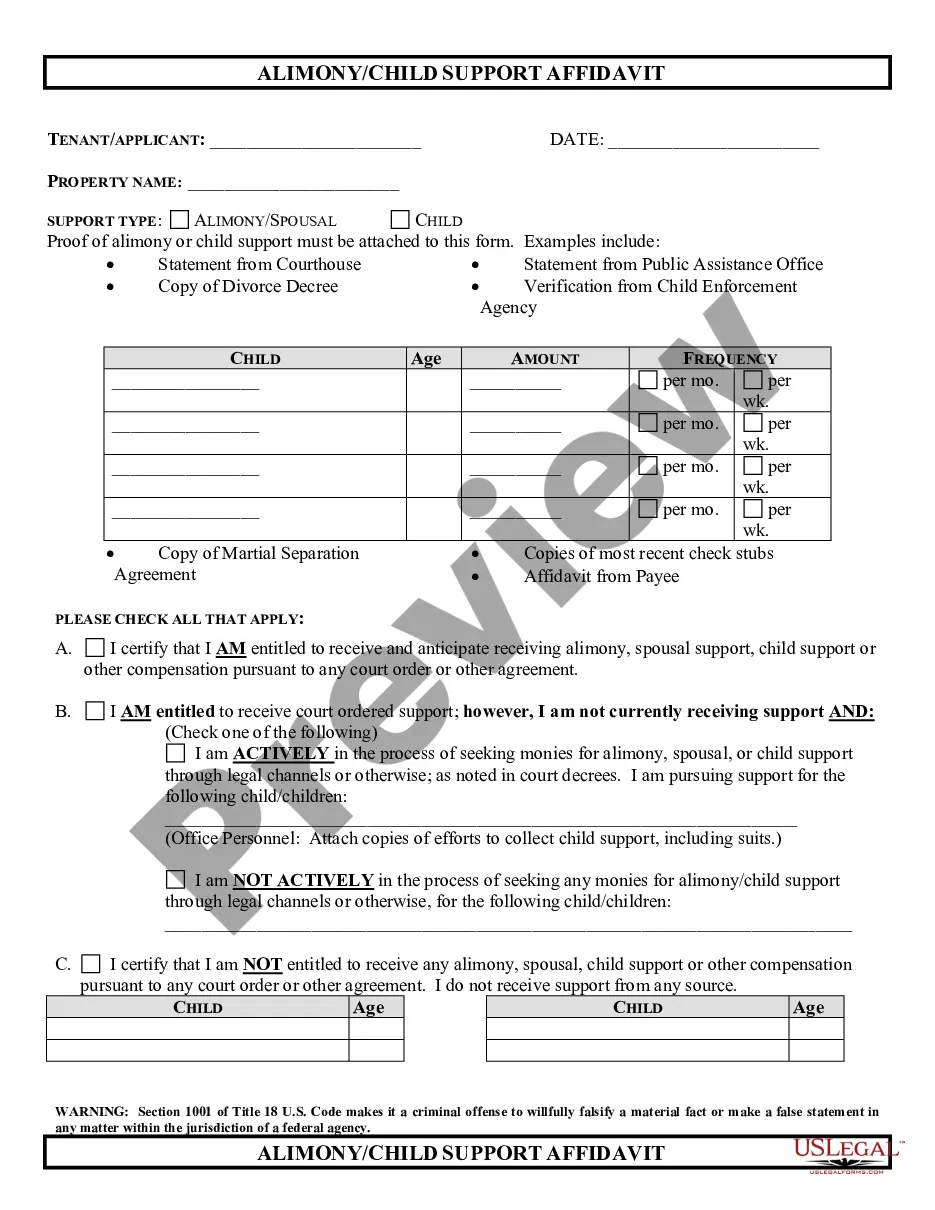
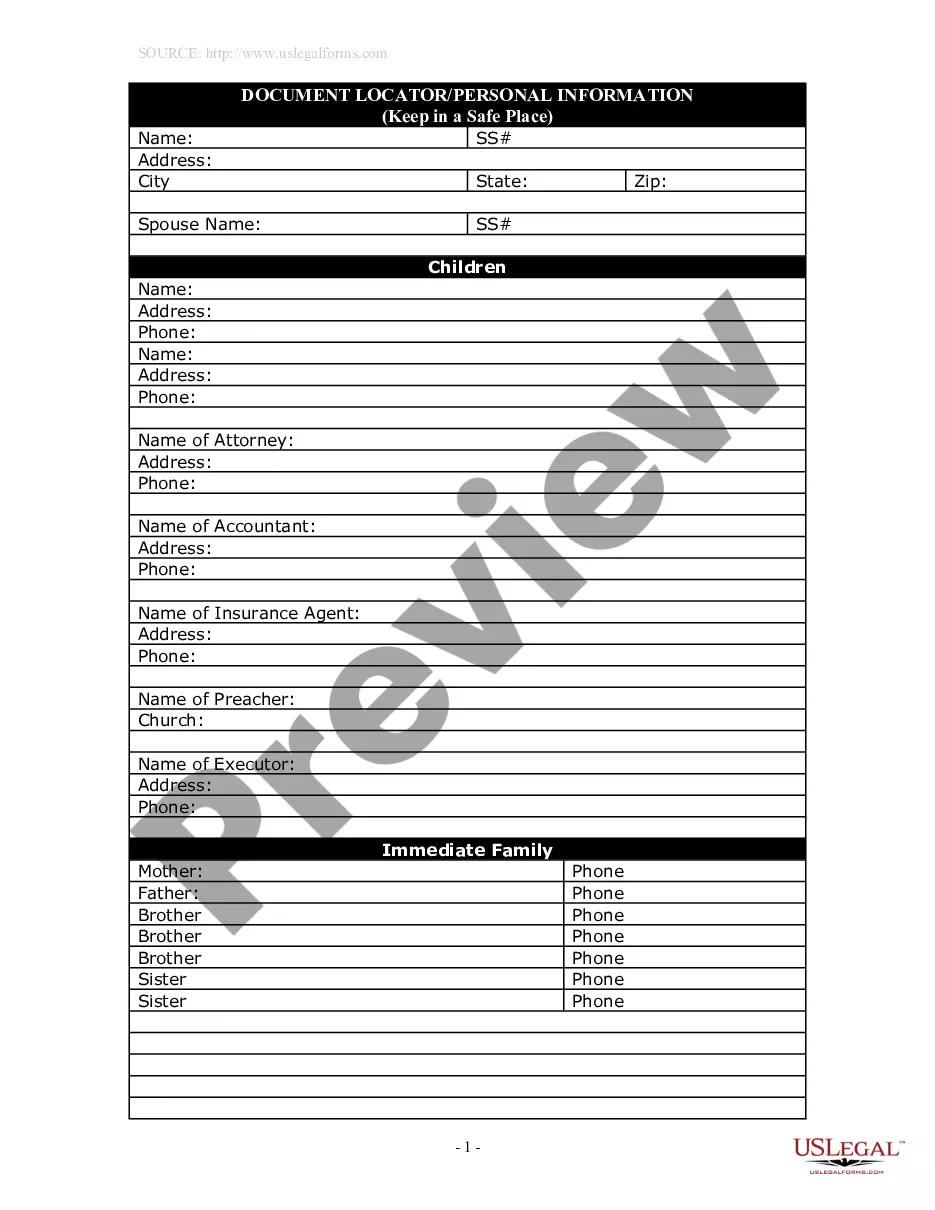
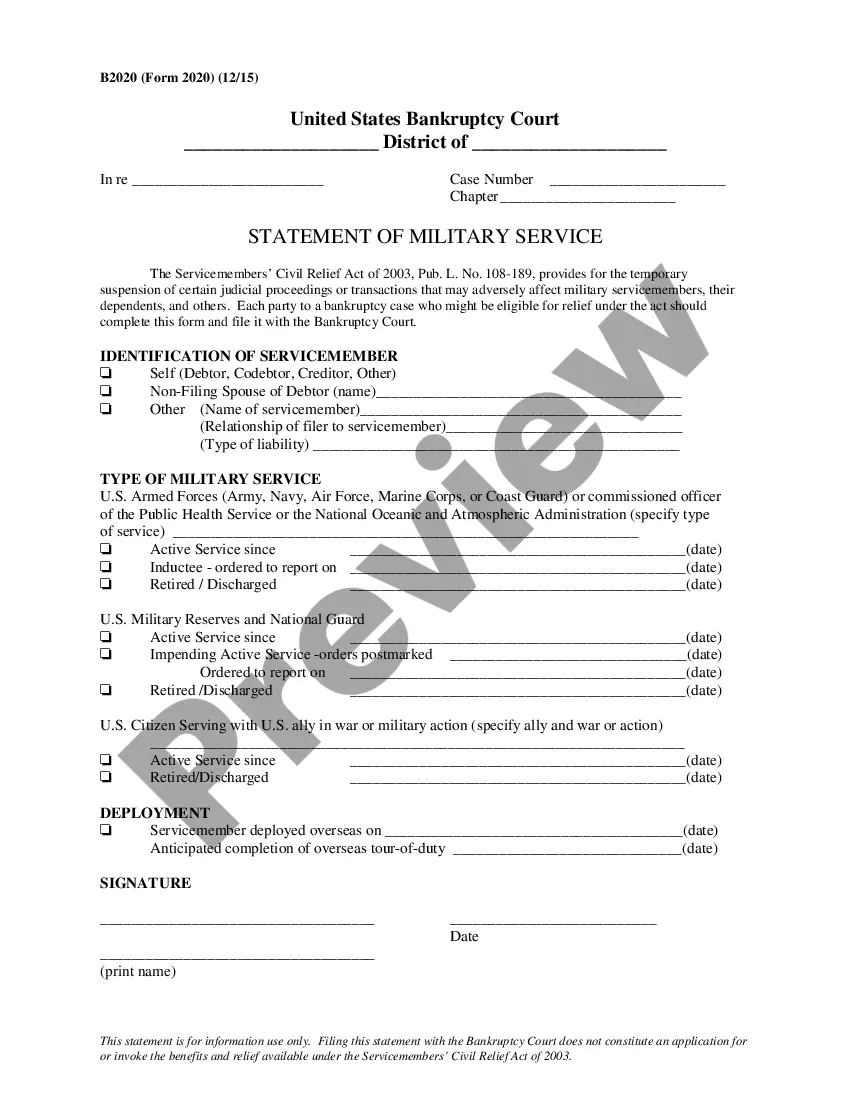
This package includes (1)Information about Divorce, (2) Forms List, (3) Forms Explanations, (4) Instructions and Steps, (5) Checklist, (6) Forms and (7) Access to divorce law summary for your State. The forms include the required petition or complaint, waiver, separation agreement, financial reporting statements, judgment and other forms to complete your divorce.
Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts
Description
How to fill out Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package For Dissolution Of Marriage With Adult Children And With Or Without Property And Debts?
Gain entry to the most comprehensive collection of legal documents.
US Legal Forms serves as a resource to locate any state-specific paperwork within moments, including the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts examples.
There is no need to squander time searching for a court-acceptable template. Our certified experts guarantee that you receive the latest templates consistently.
Once you select a pricing plan, register your account. Make your payment via credit card or PayPal. Download the template to your device by selecting the Download button. That's it! You should complete the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts template and review it. To ensure accuracy, consult your local legal advisor for assistance. Sign up and conveniently locate around 85,000 useful templates.
- To access the document collection, select a subscription and set up your account.
- If you are already registered, simply Log In and hit the Download button.
- The Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts template will be swiftly saved in the My documents tab (a section for all forms you store on US Legal Forms).
- To establish a new account, adhere to the straightforward instructions below.
- If you plan to use a state-specific template, ensure you select the correct state.
- If possible, review the description to understand all the details of the document.
- Utilize the Preview option if available to inspect the content of the document.
- If everything appears accurate, click on the Buy Now button.
Form popularity
FAQ
fault divorce in Hawaii means that neither spouse must prove wrongdoing or fault to obtain a divorce. Instead, couples can simply state that their marriage is irretrievably broken. The Hawaii NoFault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts is designed to streamline this process, making it easier for couples to dissolve their marriage amicably and efficiently.
The best way to navigate a divorce is through clear communication and mutual agreement. Utilizing the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts can greatly simplify this process. By focusing on collaboration, both parties can address their needs and come to a resolution that respects their individual circumstances.
Yes, you can get a divorce without going to court by using the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts. This package allows you and your spouse to reach an agreement on the terms of your divorce while avoiding court appearances. By completing the necessary paperwork and filing it with the court, you can finalize your divorce efficiently and amicably.
To respond to divorce papers in Hawaii, you should file your response with the court and serve it to the other party within the stipulated time frame, typically 20 days. Utilizing the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts can simplify this process by providing the necessary forms and instructions. Make sure to address all issues raised in the divorce papers to avoid complications later. You might want to seek assistance from uslegalforms to ensure that your response is accurate and timely.
An uncontested divorce can be denied if the court finds that certain legal requirements have not been met. For instance, both parties must agree to the terms outlined in the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts. If there are discrepancies or unresolved issues, the court may not approve the divorce. It's essential to ensure that all documents are correctly filled out and that both parties are actively participating in the process.
Yes, you can get a divorce without going to court by utilizing the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts. This package allows you to work collaboratively with your spouse to agree on the terms of your divorce without requiring court appearances. By filling out and filing the necessary documents, you can complete the divorce process efficiently from home. This option minimizes stress and simplifies the overall experience.
The duration of an uncontested divorce in Hawaii can vary, but it typically is much shorter than a contested divorce. With the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts, you might complete all necessary paperwork swiftly, sometimes within a few weeks. Once everything is submitted, the court usually processes your case and finalizes the divorce within a few months. Thus, you can look forward to a quick resolution.
You do not have to go to court for an uncontested divorce in Hawaii when using the Hawaii No-Fault Uncontested Agreed Divorce Package for Dissolution of Marriage with Adult Children and with or without Property and Debts. This package simplifies the process by allowing you to handle most of the necessary paperwork outside of court. By agreeing on the divorce terms, both parties can finalize the dissolution without appearing in front of a judge. Therefore, you can save time, stress, and court costs.