A secured transaction is created when a buyer or borrower (debtor) grants a seller or lender (creditor or secured party) a security interest in personal property (collateral). A security interest allows a creditor to repossess and sell the collateral if a debtor fails to pay a secured debt.
The Truth-in-Lending Act (TILA) is part of the Federal Consumer Credit Protection Act. The purpose of the TILA is to make full disclosure to debtors of what they are being charged for the credit they are receiving. The Act merely asks lenders to be honest to the debtors and not cover up what they are paying for the credit. Regulation Z is a federal regulation prepared by the Federal Reserve Board to carry out the details of the Act. TILA applies to consumer credit transactions. Consumer credit is credit for personal or household use and not commercial use or business purposes.
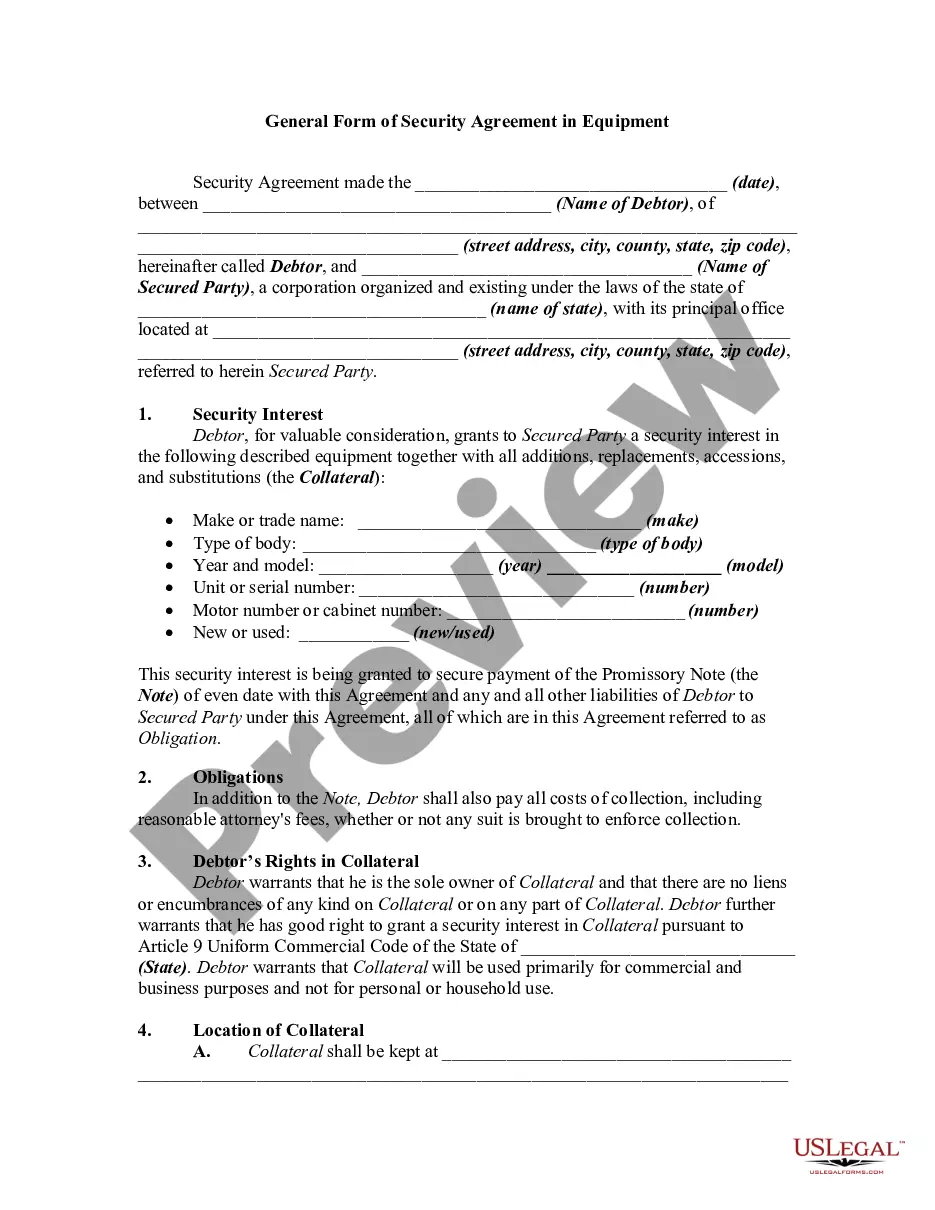
Hawaii General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment is a legal document that establishes a security interest in equipment provided as collateral for a loan or financial transaction. It is designed to protect the rights of the lender or creditor in case the borrower defaults on the loan. The document outlines the details of the agreement, including the identification of the parties involved, a detailed description of the equipment being used as collateral, and the terms and conditions of the security interest. It also specifies the rights and responsibilities of both the lender and the borrower. Keywords: Hawaii, General Form of Security Agreement, Equipment, collateral, loan, financial transaction, lender, creditor, default, agreement, parties, description, terms and conditions, security interest, rights, responsibilities. Different types of Hawaii General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment may include: 1. Purchase Money Security Agreement: This type of agreement is used when the equipment being financed is specifically purchased with the loan proceeds. It grants the lender a security interest in the equipment until the loan is fully repaid. 2. Floating Lien Agreement: In this type of agreement, the security interest extends to a pool of equipment rather than a specific piece of equipment. This allows the borrower to use multiple pieces of equipment as collateral, giving them more flexibility. 3. Cross-Collateralization Agreement: This agreement allows the lender to use multiple types of collateral, including equipment, real estate, or other assets, to secure a loan. It provides additional security to the lender and may result in more favorable loan terms for the borrower. 4. Leasehold Security Agreement: When the equipment is leased rather than owned by the borrower, this type of agreement grants the lender a security interest in the lessee's interest in the lease. It ensures that the lender can reclaim the equipment if the lessee defaults on the loan. These are just a few examples of the different types of Hawaii General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment that exist. Each type may have specific provisions and requirements, so it is essential for both parties involved to carefully review and understand the terms before signing the agreement.