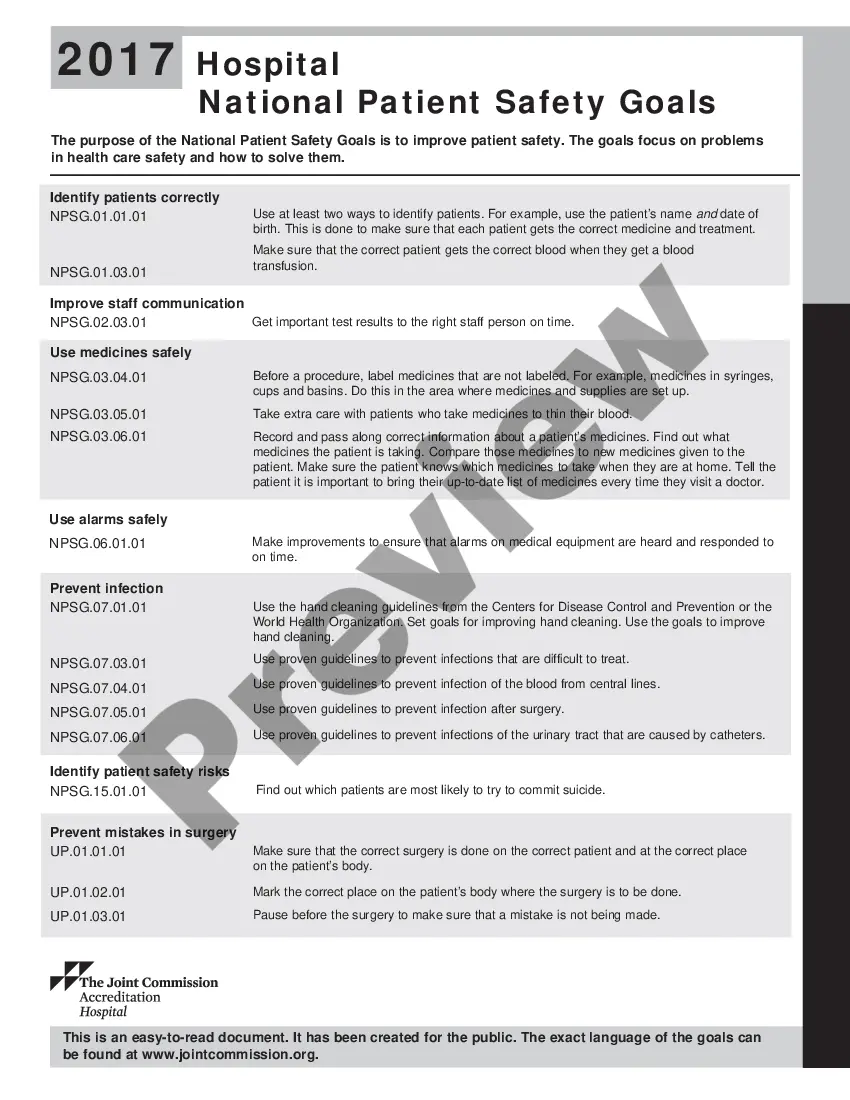
The Hawaii Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (Hangs) are a set of guidelines and initiatives aimed at enhancing patient safety and improving the quality of healthcare services within hospitals in Hawaii. These goals are designed to address various aspects of patient safety, ensure the delivery of high-quality care, and prevent medical errors. Adhering to these goals helps healthcare facilities prioritize patient safety as an integral part of their operations. Here are some relevant keywords associated with the Hangs: 1. Patient Safety: The primary focus of these goals is to ensure patient safety throughout all healthcare processes and procedures. 2. Quality Improvement: The Hangs emphasize the need for hospitals to continuously evaluate their performance and implement quality improvement initiatives to enhance patient care. 3. Medical Errors: The goals aim to reduce and prevent medical errors, both systemic and procedural, by promoting safe practices and establishing protocols for error reporting and analysis. 4. Infection Control: The Hangs prioritize infection control measures to minimize the risk of healthcare-associated infections, such as hand hygiene, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and isolation practices. 5. Medication Safety: These goals focus on preventing medication errors, ensuring accurate medication reconciliation, improving communication about medications, and promoting safe medication administration practices. 6. Fall Prevention: One of the goals is to mitigate falls among patients by conducting fall risk assessments, implementing appropriate interventions, and encouraging effective communication between healthcare providers and patients. 7. Laboratory Safety: The Hangs stress the importance of accurate patient identification, specimen labeling, and proper handling, storage, and transportation of laboratory samples to minimize errors and maintain quality results. 8. Surgical Site Infections (SSI): Goals related to surgical site infections focus on measures such as appropriate preoperative antimicrobial prophylaxis, maintaining sterile environments during surgeries, and ensuring proper wound care post-operation. 9. Communication: Effective communication among healthcare providers, patients, and their families is essential for patient safety. The Hangs emphasize the use of standardized communication tools, clear documentation, and open dialogue to prevent misunderstandings and improve overall care coordination. 10. Emergency Preparedness: These goals require hospitals to establish robust emergency preparedness plans, conduct drills, and train staff to respond effectively to various emergencies, ensuring patient safety during crisis situations. It is important to note that the specific goals and requirements may vary by year or edition, as they are periodically updated to reflect the latest evidence-based practices and emerging patient safety concerns. Healthcare facilities in Hawaii are expected to implement these goals to safeguard patient well-being, enhance care quality, and prevent adverse events.
Hawaii Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Hawaii Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Are you presently in a position the place you need files for both company or individual purposes almost every day time? There are a variety of lawful document themes available online, but locating versions you can depend on isn`t simple. US Legal Forms delivers a huge number of kind themes, just like the Hawaii Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, which are created to fulfill federal and state requirements.
Should you be presently knowledgeable about US Legal Forms web site and possess your account, merely log in. After that, you are able to obtain the Hawaii Hospital National Patient Safety Goals design.
Should you not offer an accounts and want to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Obtain the kind you want and make sure it is for the correct town/county.
- Take advantage of the Review key to analyze the shape.
- See the explanation to ensure that you have chosen the right kind.
- In the event the kind isn`t what you`re looking for, make use of the Look for area to discover the kind that meets your needs and requirements.
- Once you get the correct kind, click on Purchase now.
- Pick the costs plan you would like, complete the required info to make your bank account, and buy your order making use of your PayPal or charge card.
- Decide on a handy paper formatting and obtain your backup.
Locate each of the document themes you might have purchased in the My Forms food selection. You can obtain a more backup of Hawaii Hospital National Patient Safety Goals whenever, if needed. Just click the essential kind to obtain or print out the document design.
Use US Legal Forms, the most considerable collection of lawful kinds, to save lots of some time and steer clear of mistakes. The services delivers skillfully created lawful document themes which you can use for an array of purposes. Produce your account on US Legal Forms and initiate making your daily life a little easier.