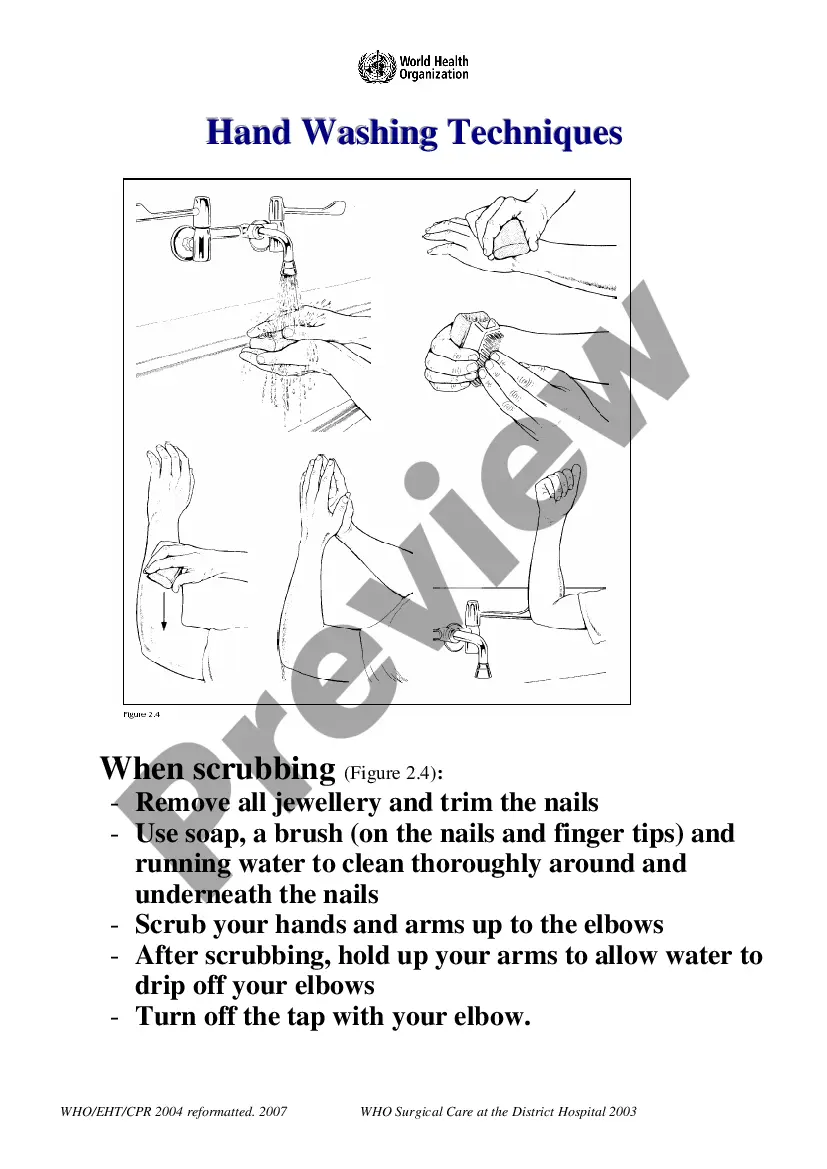
Hawaii Best Practice Protocols: Hawaii Best Practice Protocols refer to the established guidelines and procedures followed in clinical settings in Hawaii to ensure the safety and well-being of patients, healthcare professionals, and the overall quality of healthcare services. These protocols are designed to offer the highest standard of care and incorporate evidence-based practices, local regulations, and cultural sensitivities specific to Hawaii. Clinical Procedures Safety in Hawaii: 1. Infection Control Protocol: Hawaii follows rigorous infection control protocols to prevent the transmission of infections within healthcare facilities. This includes guidelines for hand hygiene, sterilization and disinfection of medical equipment, isolation procedures, and management of infectious waste. 2. Medication Safety Protocol: To ensure patient safety, Hawaii implements strict medication safety protocols. This includes accurate prescription writing, proper administration, monitoring of medication interactions, and education on potential side effects. 3. Patient Identification Procedures: Hawaii emphasizes the importance of accurate patient identification to prevent medical errors. This involves implementing standardized protocols for patient identification bracelets, verifying patient information at each interaction, and using technology like barcode scanning to match patients with their medical records. 4. Emergency Preparedness Plan: Hawaii recognizes the risk of natural disasters, such as hurricanes and earthquakes. Best practice protocols include emergency preparedness plans that outline procedures for patient evacuation, prioritizing care during emergencies, and coordinating with local authorities and resources. 5. Cultural Competency and Sensitivity: Hawaii is a culturally diverse state with unique traditions and beliefs. Best practice protocols incorporate cultural competency training for healthcare professionals to better understand and respect the cultural practices of patients. This ensures effective communication, reduces disparities in care, and promotes patient satisfaction. 6. Fall Prevention Protocol: To minimize the risk of falls among patients, Hawaii healthcare facilities implement best practice protocols related to fall prevention. This includes regular patient assessments, modifying the environment to reduce hazards, providing adequate lighting, using assistive devices when necessary, and educating patients and their families on fall prevention techniques. 7. Radiation Safety Protocol: Hospitals and clinics in Hawaii adhere to radiation safety protocols to protect patients and staff from unnecessary exposure to radiation during diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. This includes the use of lead aprons, shielding devices, and equipment maintenance and calibration. 8. Surgical Site Infection Prevention: Hawaii prioritizes preventing surgical site infections (Skis) by following evidence-based protocols. This includes sterile techniques, preoperative skin cleansing, appropriate use of antibiotics, environmental controls, and postoperative wound care practices. 9. Adverse Event Reporting and Quality Improvement: Hawaii healthcare facilities encourage a culture of safety by implementing protocols for reporting and investigating adverse events. This promotes learning from mistakes, implementing corrective actions, and continuously improving patient care processes. In conclusion, Hawaii Best Practice Protocols encompass a range of clinical procedures and safety measures specifically tailored to the unique healthcare landscape of the state. These protocols aim to ensure the highest level of patient safety, quality of care, and adherence to cultural sensitivities, ultimately promoting the well-being of individuals seeking healthcare services in Hawaii.
Hawaii Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety
Description
How to fill out Hawaii Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety?
Finding the right authorized file format can be quite a have a problem. Obviously, there are a lot of templates accessible on the Internet, but how can you find the authorized kind you will need? Utilize the US Legal Forms web site. The support gives thousands of templates, including the Hawaii Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety, which can be used for company and private requires. All of the types are checked out by professionals and satisfy federal and state requirements.
If you are already authorized, log in for your accounts and click on the Obtain button to get the Hawaii Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety. Make use of accounts to look through the authorized types you might have acquired in the past. Visit the My Forms tab of the accounts and acquire yet another copy from the file you will need.
If you are a new customer of US Legal Forms, listed here are straightforward recommendations so that you can adhere to:
- Initial, be sure you have selected the proper kind for the city/county. It is possible to look through the form using the Preview button and browse the form information to make sure this is basically the right one for you.
- In the event the kind fails to satisfy your requirements, use the Seach field to discover the proper kind.
- When you are sure that the form is suitable, click the Acquire now button to get the kind.
- Pick the rates strategy you desire and enter in the needed details. Create your accounts and buy the order with your PayPal accounts or bank card.
- Choose the document formatting and download the authorized file format for your device.
- Comprehensive, revise and printing and indicator the attained Hawaii Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety.
US Legal Forms is definitely the greatest library of authorized types that you will find a variety of file templates. Utilize the service to download skillfully-created files that adhere to state requirements.