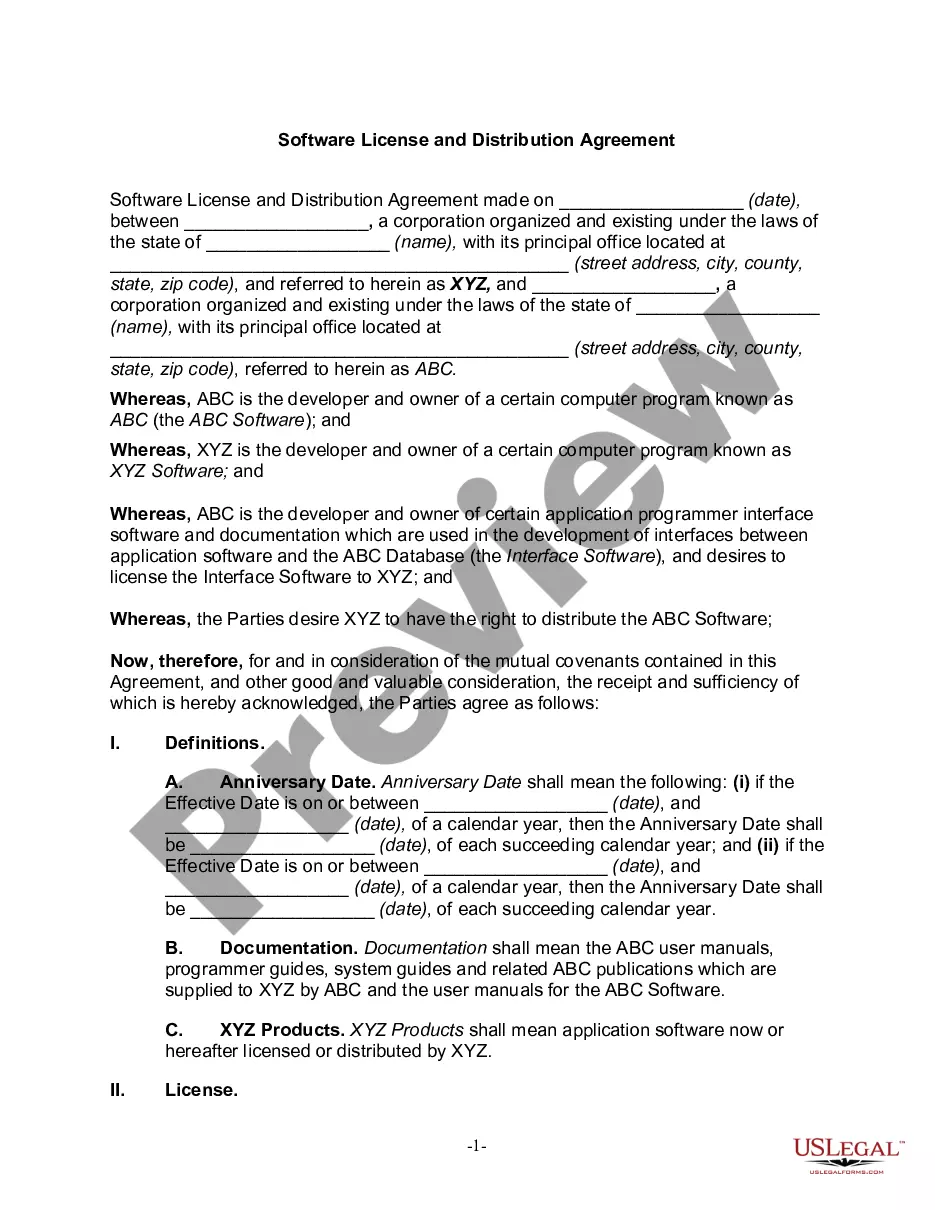
Hawaii Technology Transfer Agreement
Description
How to fill out Technology Transfer Agreement?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - provides a variety of legal form templates that you can purchase or create.
On the website, you can find thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, categorized by types, states, or keywords. You can access the latest versions of forms like the Hawaii Technology Transfer Agreement within moments.
If you already have an account, sign in and obtain the Hawaii Technology Transfer Agreement from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will be available on every form you view. You can access all previously acquired forms in the My documents section of your account.
Every template you add to your account does not expire and is yours indefinitely. Therefore, if you want to download or print another copy, simply go to the My documents section and click on the desired template.
Access the Hawaii Technology Transfer Agreement with US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Verify that you have selected the appropriate form for your city/state. Click the Preview button to review the form's details. Read the form description to ensure that you have chosen the correct document.
- If the form does not meet your needs, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- Once you are satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Buy now button. Then, select the pricing plan you wish to use and provide your details to create an account.
- Process the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the purchase.
- Choose the file format and download the form to your device.
- Edit. Fill out, modify, print, and sign the downloaded Hawaii Technology Transfer Agreement.
Form popularity
FAQ
Technology Transfer ProcessStep 1: Invention Disclosure.Step 2: Evaluation.Step 3: Patent Application.Step 4: Assessment and Marketing.Step 5: Licensing of Patents.Step 6: Commercialization.
This model refers TT as the transfer of the embodied knowledge assets between organizations. The TT process in this model consists of four categories that include 1) Transfer Scope, 2) Transfer Method, 3) Knowledge Architecture, and 4) Organizational Adaptive Ability.
Examples of technology transfer can be found across virtually every scientific and industrial area, from pharmaceuticals and medical devices to alternative energy solutions, computing, transport, artificial intelligence, robotics, agriculture, aerospace, environmental improvements and many more.
Technology transfer activities can be broadly split into three phases; preparation, installation and utilisation. These three phases are, in turn, affected by technological, organisational and environmental factors.
A technology transfer agreement is a legal contract used when a company, referred to as the licensor, licenses industrial or intellectual property rights to a licensee. Intellectual property subject to a technology transfer agreement can include: Patents. Utility models. Trademarks.
Technology transfer (TT) refers to the process of conveying results stemming from scientific and technological research to the market place and to wider society, along with associated skills and procedures, and is as such an intrinsic part of the technological innovation process.
Technology is the way we apply scientific knowledge for practical purposes. It includes machines (like computers) but also techniques and processes (like the way we produce computer chips).
This begins with the discovery of novel technologies at research institutions, followed by the disclosure, evaluation and protection of these technologies. The next steps include marketing, potential licencing agreements and the development of products based on the technical inventions.
These seven elements are following; transferor, transferee, mechanism of transfer, technology, transferor environment, transferee environment and greater environment.
Technology transfer agreements can be bifurcated into vertical and horizontal technology transfer. Vertical Technology Transfer is when there is a conduction of new technologies from a new range of technology while the technology is still exploration and advancement.