Hawaii Accredited Investor Self-Certification Attachment D
Description
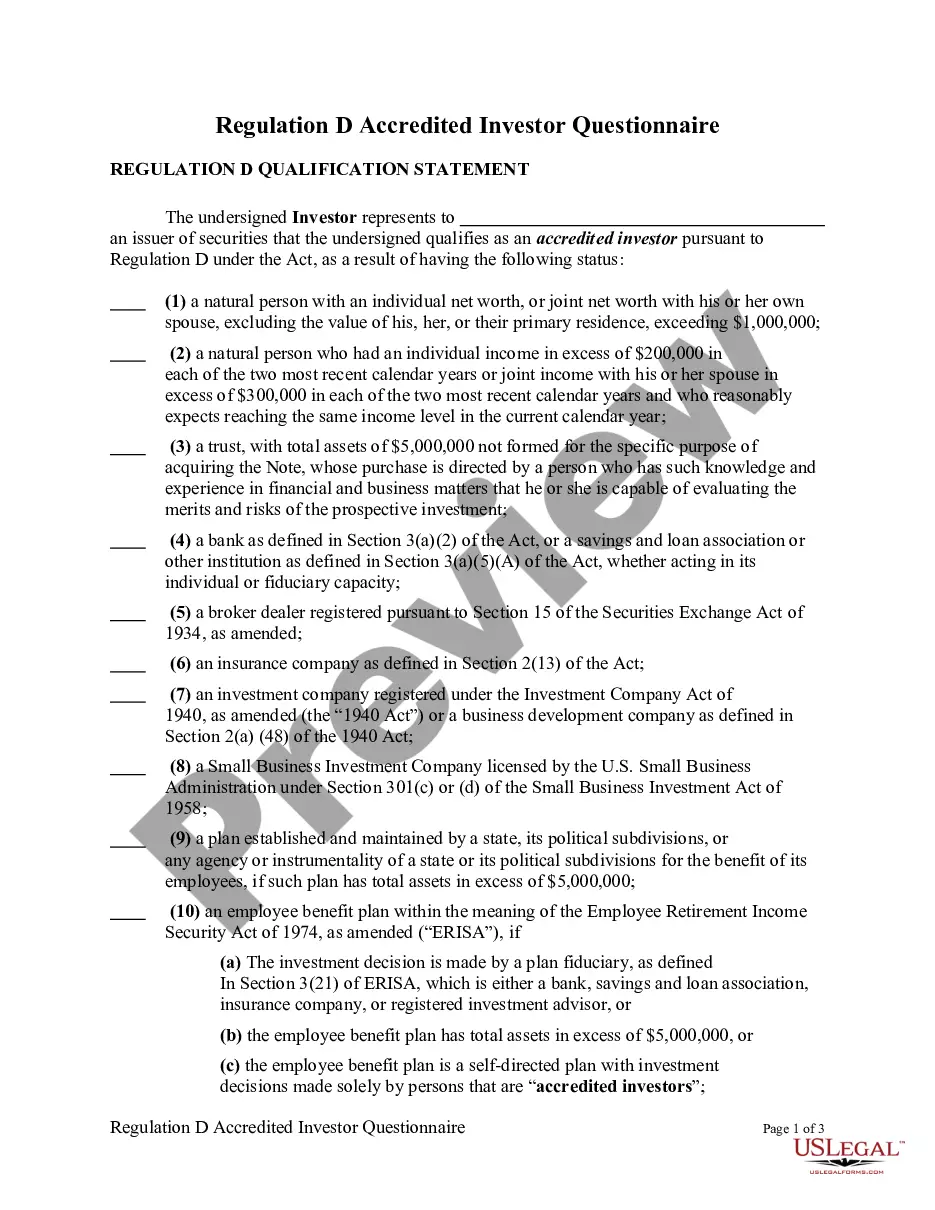
To become an accredited investor the (SEC) requires certain wealth, income or knowledge requirements. The investor must fall into one of three categories. Firms selling unregistered securities must put investors through their own screening process to determine if investors can be considered an accredited investor.
The Verifying Individual or Entity should take reasonable steps to verify and determined that an Investor is an "accredited investor" as such term is defined in Rule 501 of the Securities Act, and hereby provides written confirmation. This letter serves to help the Entity determine status.
How to fill out Accredited Investor Self-Certification Attachment D?
Have you been inside a place in which you require files for both company or specific reasons almost every day? There are tons of legitimate document layouts available on the Internet, but finding types you can trust isn`t easy. US Legal Forms delivers thousands of kind layouts, such as the Hawaii Accredited Investor Self-Certification Attachment D, that happen to be created to satisfy state and federal demands.
In case you are currently knowledgeable about US Legal Forms site and get a merchant account, just log in. Following that, it is possible to download the Hawaii Accredited Investor Self-Certification Attachment D format.
Unless you have an profile and need to begin using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Discover the kind you want and ensure it is to the appropriate city/region.
- Take advantage of the Review switch to analyze the form.
- Browse the description to actually have selected the right kind.
- When the kind isn`t what you are seeking, utilize the Research field to find the kind that suits you and demands.
- If you find the appropriate kind, click Purchase now.
- Select the rates strategy you desire, submit the specified information and facts to generate your bank account, and buy your order using your PayPal or credit card.
- Decide on a practical paper format and download your backup.
Locate every one of the document layouts you may have bought in the My Forms menu. You can get a extra backup of Hawaii Accredited Investor Self-Certification Attachment D any time, if required. Just go through the essential kind to download or printing the document format.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive selection of legitimate forms, to conserve efforts and prevent mistakes. The assistance delivers expertly manufactured legitimate document layouts which can be used for a variety of reasons. Make a merchant account on US Legal Forms and initiate making your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
To confirm their status as an accredited investor, an investor can submit official documents for net worth and income verification, including: Tax returns. Pay stubs. Financial statements. IRS forms. Credit report. Brokerage statements. Tax assessments.
To qualify as an accredited investor, you must have over $1 million in net worth, or more than $200,000 in earned income in the past two calendar years, with the expectation of the same earnings. Financial professionals with Series 7, 65 or 82 licenses also qualify.
If you are accredited based on income, you will need to provide documentation in the form of tax returns, W-2s, or other official documents that show you meet the required income threshold for the prior two years.
Individuals who want to become accredited investors must fall into one of three categories: have a net worth exceeding $1 million on your own or with a spouse or its equivalent; have earned an income surpassing $200,000 ($300,000 if combined with a spouse or its equivalent) during the last two years and prove an ...
Other types of accredited investors The following can also qualify as accredited investors: Financial institutions. A corporation or LLC, not formed for the specific purpose of acquiring the securities offered, with total assets in excess of $5M. Knowledgeable employees of private funds.
Accredited Individual Investor ? By Income IR8A/income tax form declaring personal income not less than S$300,000 (or an equivalent document) A copy of employment letter/contract stating position and income, salary payslip, and bank statement recording such income.
What is an Accredited Investor Under Regulation D? For most cases, an Accredited Investor is an individual whose income is over $200,000/year (for single persons) or $300,000/year (for married couples) or has a net worth over $1,000,000 not including equity in their principal residence.
The simplest way to attain ?accredited investor? status is to ask for a 3rd party verification letter from a registered broker dealer, an attorney or a certified public accountant.