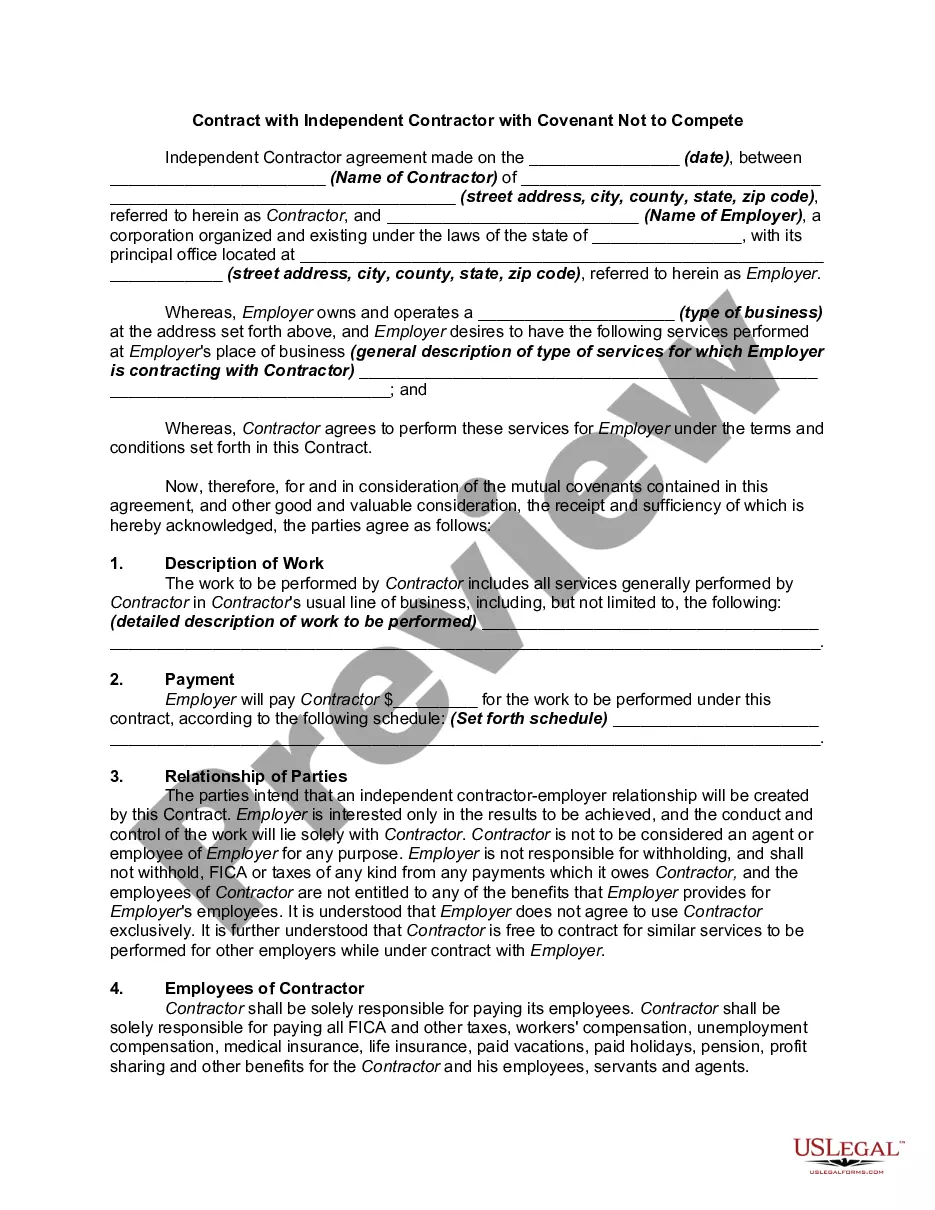
Iowa Systems Integration Services Agreement
Description
How to fill out Systems Integration Services Agreement?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a variety of legal form templates you can obtain or print.
By using the site, you can access thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can find the latest types of documents like the Iowa Systems Integration Services Agreement in moments.
If you hold a membership, Log In and download the Iowa Systems Integration Services Agreement from the US Legal Forms repository. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You have access to all previously saved forms in the My documents section of your profile.
Complete the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the payment.
Select the format and download the document to your device. Make edits. Fill out, modify, and print and sign the saved Iowa Systems Integration Services Agreement. Every template you added to your account has no expiration date and is yours indefinitely. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply navigate to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Iowa Systems Integration Services Agreement with US Legal Forms, the largest repository of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that fulfill your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/area.
- Click the Review option to check the form's details.
- Examine the form description to confirm you have chosen the correct document.
- If the form does not match your requirements, use the Search field at the top of the page to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Purchase now button.
- Then, select your preferred pricing plan and enter your details to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
A systems integrator is an individual or business that builds computing systems for clients by combining hardware, software, networking and storage products from multiple vendors.
Important Contract Terms for Service AgreementsTerm/Duration:Responsibilities/Scope of Work:Payment Terms:Dispute Resolution Terms:Intellectual Property Rights:Liabilities/Indemnification:Modifications/Amendments:Waiver:More items...?
The following list contains the main clauses to look for when entering into a service agreement, including: charge, scope of services, alteration, termination, insurance of liability, confidentiality, possession of IP, and option of law/ dispute resolution.
An integration clause is a provision included in a legal contract that declares that the contract is a complete and final agreement between all the parties that are involved, also known as a final written expression. The clause not only finalizes the substance of the agreement, but it supersedes all informal
How do I write a Service Agreement?State how long the services are needed.Include the state where the work is taking place.Describe the service being provided.Provide the contractor's and client's information.Outline the compensation.State the agreement's terms.Include any additional clauses.More items...?
An integration agreement, also referred to as an integration clause or a merger clause, is a provision in a legal contract that states that the agreement between the parties as outlined in the contract is final and complete.
Integrated agreement is a writing or writings constituting a final expression of one or more terms of the agreement. 2. Written Contracts May Be Fully or Partially Integrated. a. A fully integrated contract is one that is a final and complete expression of all the terms agreed upon between (or among) the parties.
Primary tabs. In contract law, an integration clausealso sometimes called a merger clause or an entire agreement clauseis a provision that states that the terms of a contract are the complete and final agreement between the parties.
What is the purpose of an integration clause in a disability policy? The purpose of an integration clause in a disability policy prevents parties from claiming in the future that they didn't understand the terms or fully agree to them.
In contract law, an integration clausealso sometimes called a merger clause or an entire agreement clauseis a provision that states that the terms of a contract are the complete and final agreement between the parties.