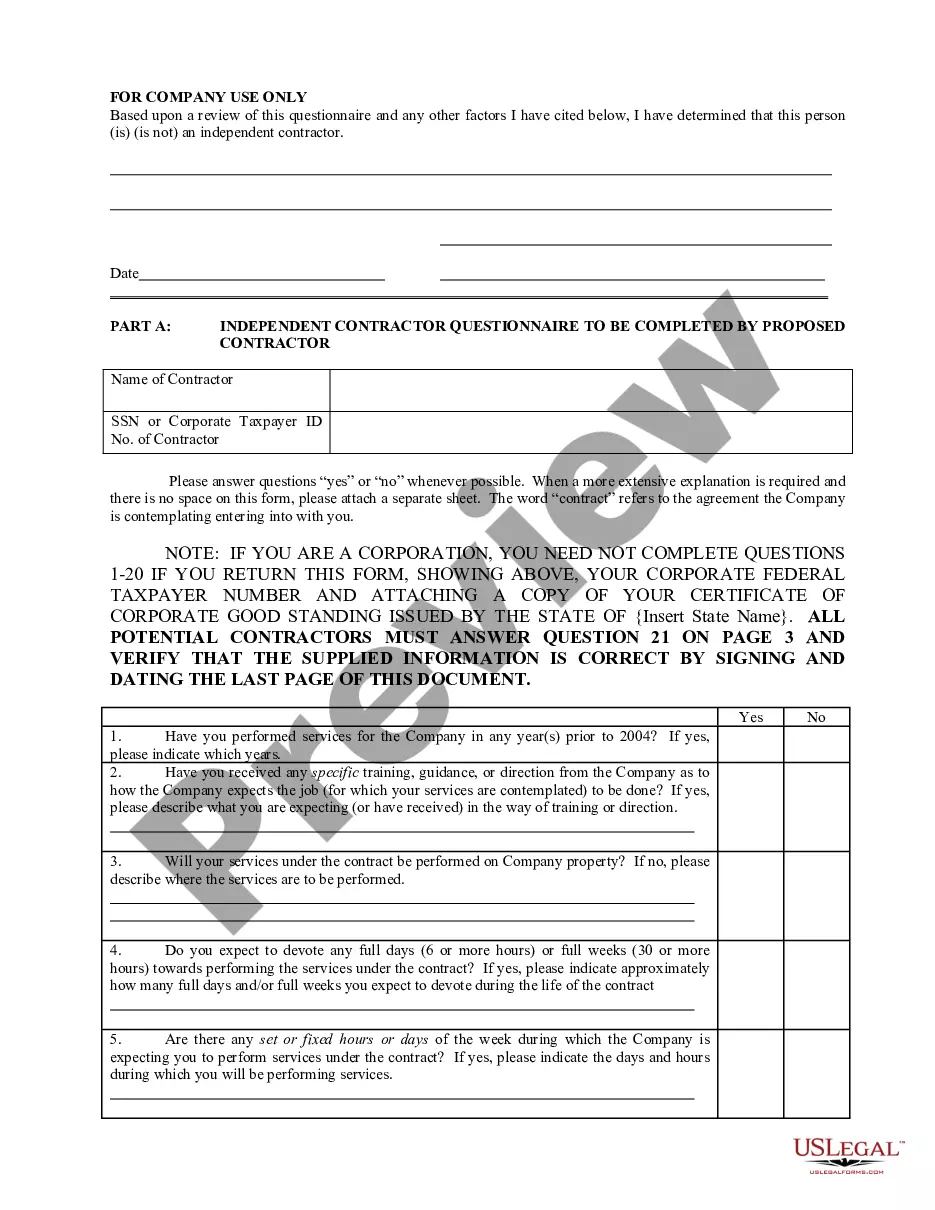
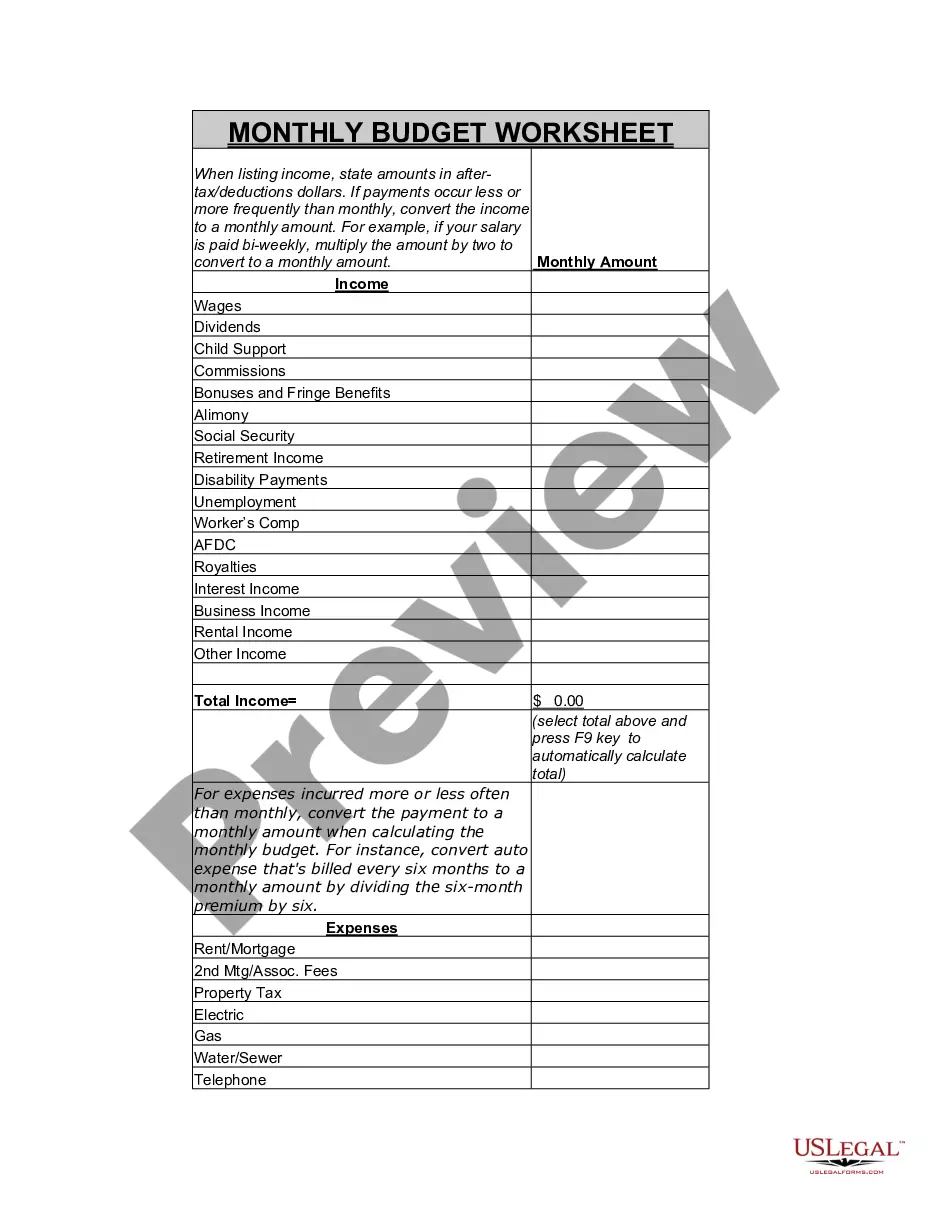
Iowa Memo - Using Self-Employed Independent Contractors
Description
How to fill out Memo - Using Self-Employed Independent Contractors?
Finding the appropriate legal document template can be challenging. Clearly, there are numerous templates available online, but how do you pinpoint the legal form you require? Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
The platform provides a wide array of templates, such as the Iowa Memo - Engaging Self-Employed Independent Contractors, suitable for both business and personal purposes. All templates are reviewed by professionals and comply with federal and state regulations.
If you are already a member, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to obtain the Iowa Memo - Engaging Self-Employed Independent Contractors. Use your account to browse the legal forms you have previously purchased. Proceed to the My documents tab in your account to retrieve another copy of the document you need.
Select the file format and download the legal document template to your device. Complete, modify, print, and sign the obtained Iowa Memo - Engaging Self-Employed Independent Contractors. US Legal Forms is the largest collection of legal forms where you can discover various document templates. Take advantage of the service to download professionally crafted paperwork that adheres to state requirements.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your locality/state.
- You can preview the form using the Preview button and read the form description to confirm it is suitable for you.
- If the form does not fit your needs, use the Search bar to find the appropriate form.
- Once you are confident that the form is adequate, click the Buy Now button to purchase the form.
- Choose the pricing plan you prefer and enter the required information.
- Create your account and complete the order using your PayPal account or credit card.
Form popularity
FAQ
The general rule is that you will be: An employee if you work for someone and do not have the risks of running a business. Self-employed if you have a trade, profession or vocation, are in business on your own account and are responsible for the success or failure of that business.
Independent contractors report their income on Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss from Business (Sole Proprietorship). Also file Schedule SE (Form 1040), Self-Employment Tax if net earnings from self-employment are $400 or more.
Simply put, being an independent contractor is one way to be self-employed. Being self-employed means that you earn money but don't work as an employee for someone else.
If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed. The earnings of a person who is working as an independent contractor are subject to self-employment tax. To find out what your tax obligations are, visit the Self-Employed Individuals Tax Center.
A 1099 employee is a US self-employed worker that reports their income to the IRS on a 1099 tax form. Freelancers, gig workers, and independent contractors are all considered 1099 employees. In contrast, actual company employees are considered W-2 employees.
During President Donald Trump's administration, the DOL issued a final rule clarifying when workers are independent contractors versus employees. The rule applied an economic-reality test that primarily considers whether the worker operates his or her own business or is economically dependent on the hiring entity.
Independent contractors are self-employed workers who provide services for an organisation under a contract for services. Independent contractors are not employees and are typically highly skilled, providing their clients with specialist skills or additional capacity on an as needed basis.
The three types of self-employed individuals include:Independent contractors. Independent contractors are individuals hired to perform specific jobs for clients, meaning that they are only paid for their jobs.Sole proprietors.Partnerships.
Becoming an independent contractor is one of the many ways to be classified as self-employed. By definition, an independent contractor provides work or services on a contractual basis, whereas, self-employment is simply the act of earning money without operating within an employee-employer relationship.
Remember that an independent contractor is considered to be self-employed, so in effect, you are running your own one-person business. Any income that you earn as an independent contractor must be reported on Schedule C. You'll then pay income taxes on the total profit.