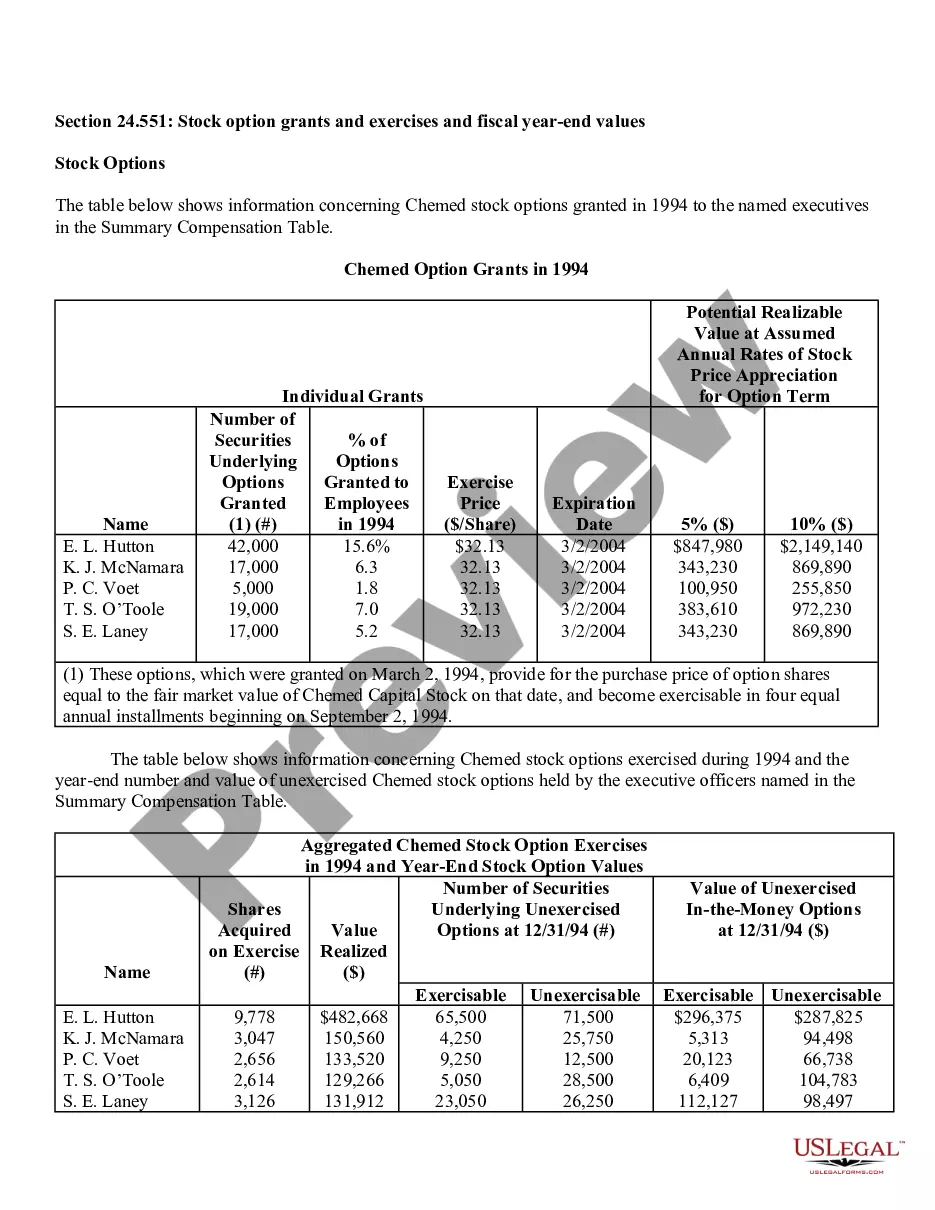
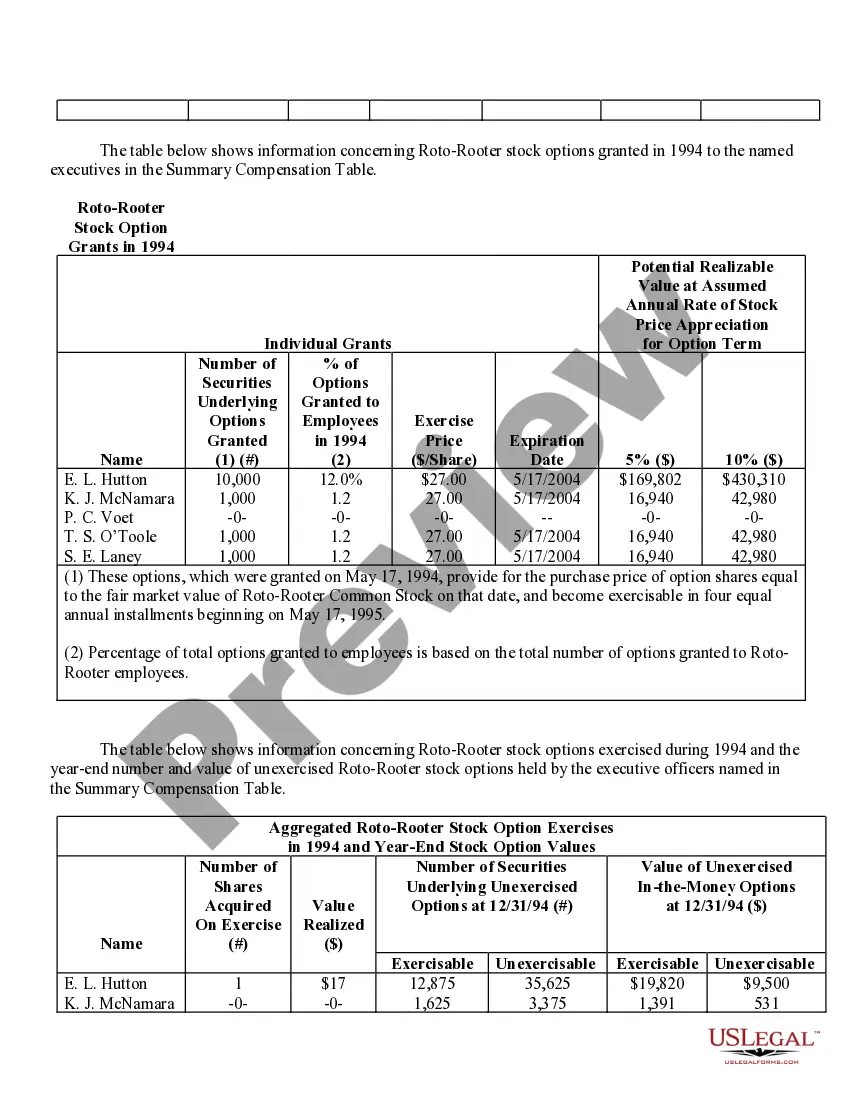
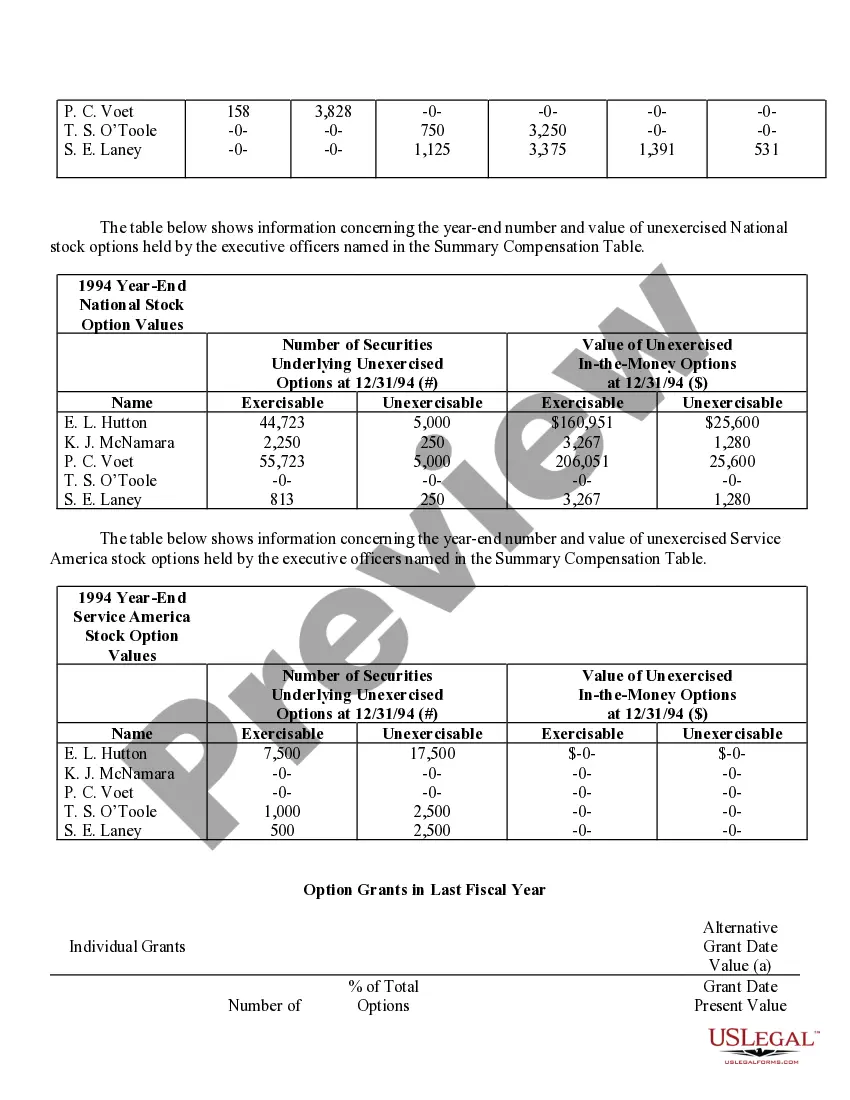
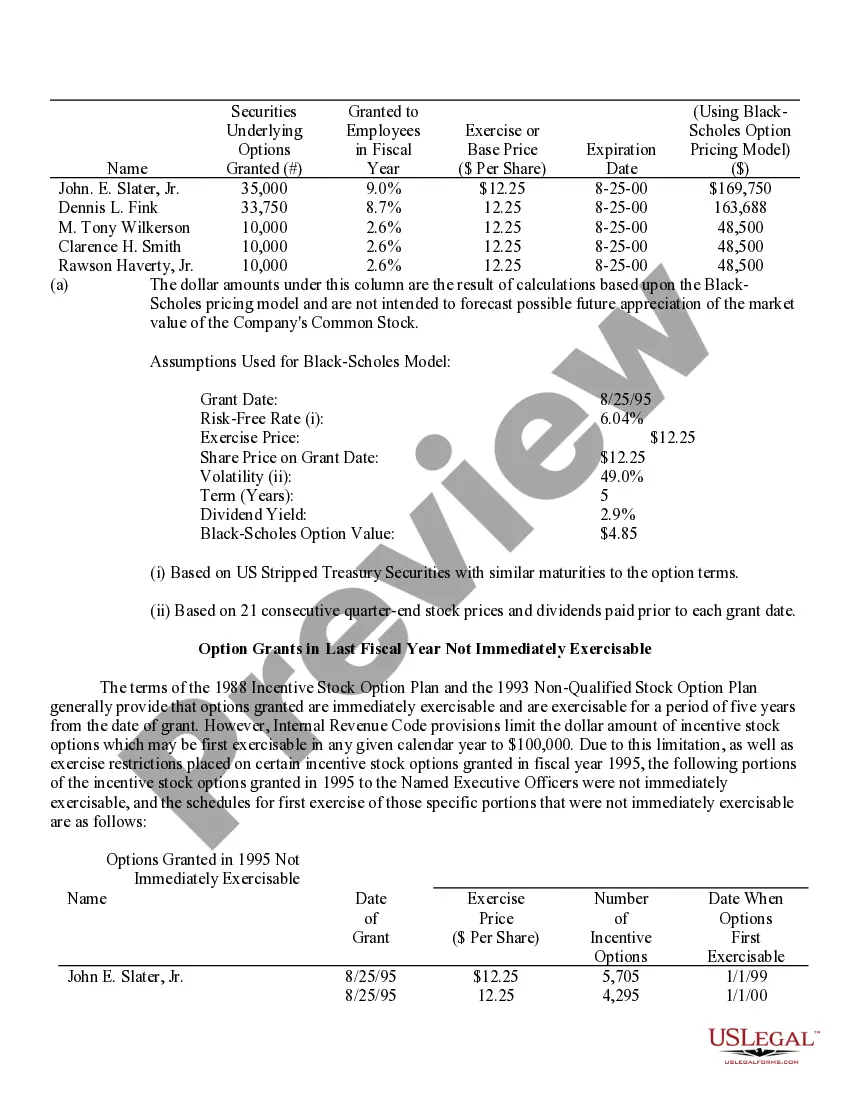
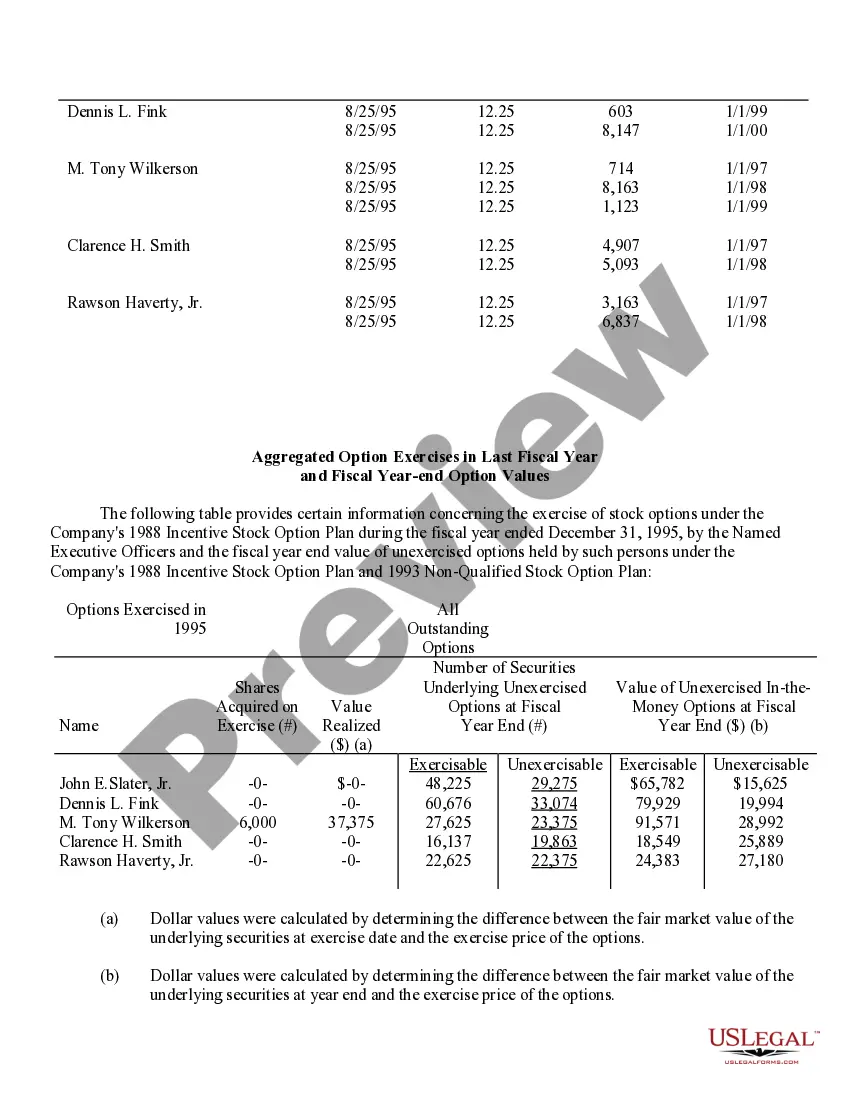
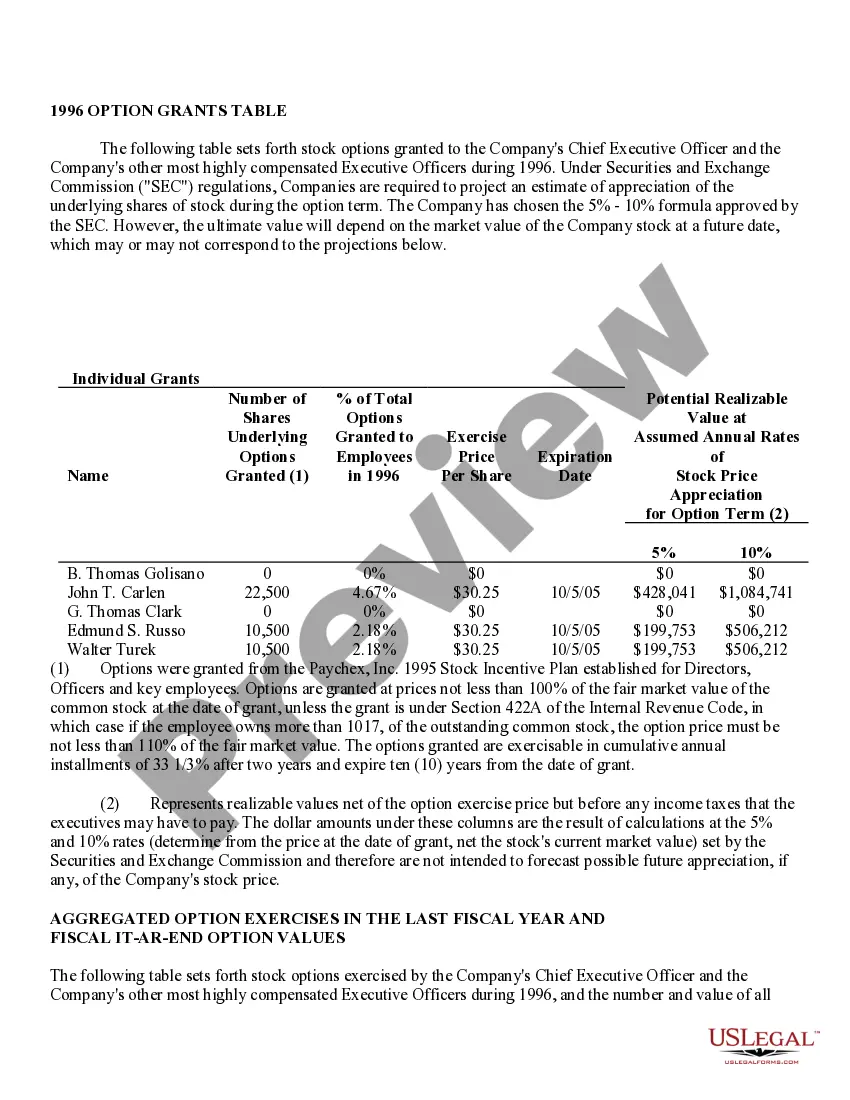
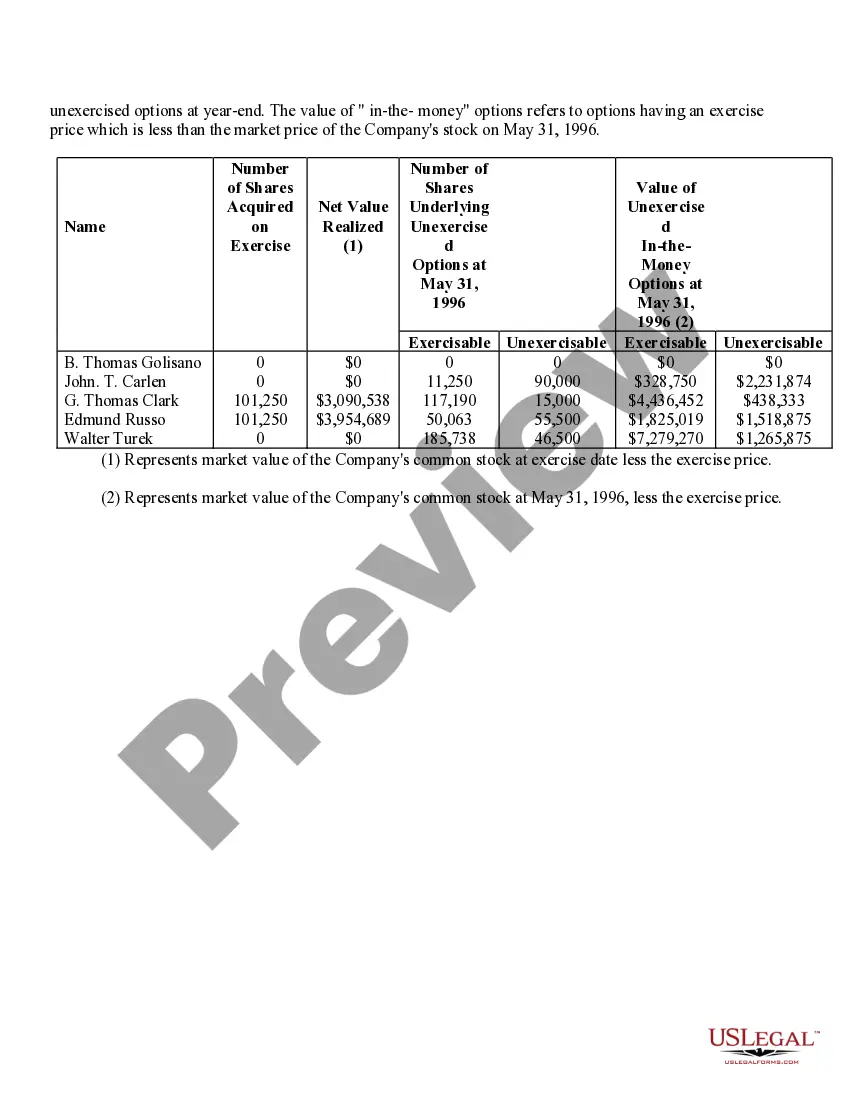
Iowa Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values
Description
How to fill out Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
US Legal Forms - one of several largest libraries of lawful forms in America - offers an array of lawful record web templates you can down load or produce. While using web site, you may get a huge number of forms for company and personal purposes, sorted by classes, states, or keywords.You can find the most recent models of forms like the Iowa Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values within minutes.
If you have a membership, log in and down load Iowa Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values in the US Legal Forms local library. The Down load button will show up on every single type you view. You have access to all earlier acquired forms inside the My Forms tab of your respective bank account.
If you would like use US Legal Forms initially, allow me to share easy instructions to obtain started out:
- Be sure you have picked out the correct type to your metropolis/region. Click the Review button to examine the form`s content. Look at the type outline to ensure that you have selected the right type.
- If the type doesn`t suit your specifications, use the Research field towards the top of the display screen to find the one which does.
- In case you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking on the Acquire now button. Then, select the costs strategy you favor and offer your credentials to register for the bank account.
- Method the deal. Make use of your charge card or PayPal bank account to accomplish the deal.
- Select the file format and down load the form on the device.
- Make adjustments. Fill out, edit and produce and signal the acquired Iowa Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values.
Each and every web template you included in your bank account lacks an expiration day and is your own property eternally. So, if you wish to down load or produce one more copy, just check out the My Forms portion and click on around the type you need.
Get access to the Iowa Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values with US Legal Forms, the most extensive local library of lawful record web templates. Use a huge number of professional and express-distinct web templates that fulfill your organization or personal demands and specifications.
Form popularity
FAQ
When you're granted stock options, you have the option to purchase company stock at a specific price before a certain date. Whether you actually purchase the stock is entirely up to you. RSUs, on the other hand, grant you the stock itself once the vesting period is complete. You don't have to purchase it.
The grant date for your incentive stock options is the date you are given the shares. The grant date is also the date the shares are typically valued and the value often determines your exercise price. The exercise price is the price you pay to buy shares of stock via your option.
A stock grant provides the recipient with value?the corporate stock. By contrast, stock options only offer employees the opportunity to purchase something of value. They can acquire the corporate stock at a set price, but the employees receiving stock options still have to pay for those stocks if they want them.
Those who receive stock grants can't sell their shares until a certain period of time, known as the vesting period. Shares that are received by using stock options can be resold at any time.
Exercise Price ? Also known as the strike price, the grant price is the price at which you can buy the shares of stock. Regardless of the future value of that particular stock, the option holder will have the right to buy the shares at the grant price rather than the current, actual price.
Restricted stock awards represent actual ownership of stock and come with conditions on the timing of their sale. An employee benefits from stock options when they buy the stock at the exercise price and then sell it at a higher price.
Stock option grants are how your company awards stock options. This document usually includes details about: The type of stock options you'll receive (ISOs or NSOs) The number of shares you can purchase.
Every stock option has an exercise price, also called the strike price, which is the price at which a share can be bought. In the US, the exercise price is typically set at the fair market value of the underlying stock as of the date the option is granted, in order to comply with certain requirements under US tax law.