In Iowa, clauses relating to initial capital contributions are essential legal provisions that dictate the financial obligations and responsibilities of partners or members when forming a business entity. These clauses ensure each party's contribution towards the initial capital of the business is clearly outlined, providing a structured framework for the company's financial operations. In this comprehensive description, we will explore the different types of Iowa clauses relating to initial capital contributions, highlighting their significance and potential variations. 1. Uniform Limited Partnership Act (ULNA) Iowa Clause: Under this type of clause, partners in a limited partnership in Iowa agree on the specific amount or value of capital contributions they will make to the partnership at its inception. The ULNA Iowa clause ensures transparency and eliminates ambiguity regarding each partner's financial commitment. It allows partners to negotiate and agree upon the initial capital amount to be contributed, as well as the consequences for failing to fulfill these obligations. 2. Revised Uniform Limited Liability Company Act (SULLA) Iowa Clause: This type of clause focuses on limited liability companies (LCS) formed in Iowa. SULLA Iowa clauses outline the capital contributions required from each member or owner to establish the LLC. It helps in determining the ownership interests and voting rights of members based on their contributions. Additionally, SULLA Iowa clauses define the consequences for failure to contribute the agreed-upon capital, including potential reduction of ownership percentage or expulsion from the company. 3. Customizable Capital Contribution Clause: This type of clause allows partners or members in Iowa to tailor their initial capital contribution terms according to their specific business needs. It offers flexibility in determining whether capital contributions will be made in cash, assets, services, or a combination thereof. The customizable clause also addresses the timeframes for initial contributions, potential installment plans, and procedures for valuing non-cash contributions. In any of the aforementioned Iowa clauses, it is crucial to include additional details to enhance their effectiveness and clarity. These can include provisions such as: — Contribution Schedule: A provision specifying the timing and method of contributions, whether they are made as a lump sum or in installments over a designated period. — Default Consequences: Clear guidelines on the consequences for partners or members who fail to fulfill their initial capital commitment, including potential penalties, reduced ownership interests, or the right for other parties to purchase the defaulting party's interest. — Capital Account Maintenance: Guidelines on how partners or members' capital contributions will be recorded, accounted for, and maintained within the company's financial records. This allows for proper tracking of equity, profit allocation, and distribution. — Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Procedures for resolving disputes arising from initial capital contributions, such as mediation or arbitration, to prevent costly litigation and promote fair resolution. In conclusion, Iowa clauses relating to initial capital contributions play a critical role in defining and regulating the financial aspects of business formation. Understanding the different types of these clauses, such as ULNA Iowa clauses, SULLA Iowa clauses, and customizable capital contribution clauses, enables business owners to structure their partnerships or LCS in a way that best suits their unique circumstances. By incorporating key provisions within these clauses, partners or members can establish clear expectations, minimize disputes, and ensure the smooth functioning of their business from the start.
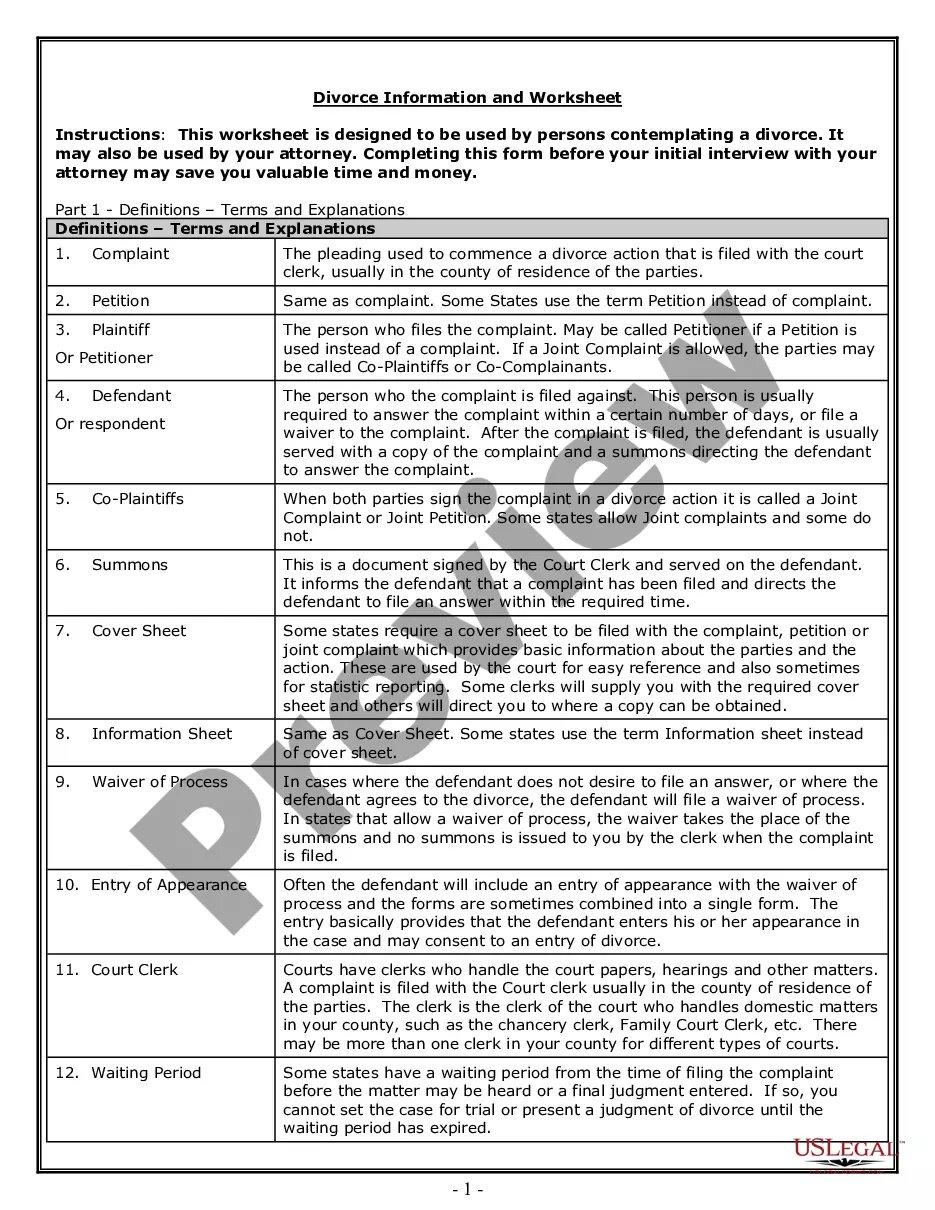
Iowa Clauses Relating to Initial Capital contributions
Description
How to fill out Clauses Relating To Initial Capital Contributions?
Are you in a placement the place you need paperwork for either business or person functions almost every day time? There are tons of authorized papers web templates available on the net, but finding kinds you can trust is not simple. US Legal Forms gives 1000s of develop web templates, much like the Iowa Clauses Relating to Initial Capital contributions, that happen to be composed in order to meet federal and state specifications.
Should you be already acquainted with US Legal Forms website and also have a merchant account, basically log in. After that, you are able to download the Iowa Clauses Relating to Initial Capital contributions format.
Should you not offer an bank account and would like to begin to use US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Obtain the develop you will need and make sure it is to the right town/region.
- Make use of the Review button to check the form.
- Browse the description to ensure that you have chosen the proper develop.
- If the develop is not what you are trying to find, make use of the Research industry to find the develop that fits your needs and specifications.
- Once you get the right develop, simply click Get now.
- Opt for the prices strategy you need, complete the necessary information to make your account, and pay for your order making use of your PayPal or Visa or Mastercard.
- Pick a practical file structure and download your copy.
Locate all of the papers web templates you have bought in the My Forms food list. You can obtain a additional copy of Iowa Clauses Relating to Initial Capital contributions anytime, if possible. Just click the essential develop to download or produce the papers format.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most considerable assortment of authorized types, to save time as well as steer clear of errors. The support gives professionally made authorized papers web templates that you can use for a range of functions. Produce a merchant account on US Legal Forms and begin making your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
Deemed Capital Contributions means for any Member the amounts deemed contributed to the capital of the Company as of the date hereof as set forth on Exhibit A attached hereto and as further adjusted by the Board for subsequent Capital Contributions or other transactions.
Contents Define the parties involved in the agreement and their respective roles. Identify the purpose of the agreement, including the capital contribution amount and any related terms and conditions. Detail any applicable taxes, fees, or charges related to the agreement.
CAPITAL CALL The act of a private equity fund ?calling down? previously pledged capital from its limited partners in order to execute an investment. CAPITAL DISTRIBUTIONS: DEEMED. Reflects the amount of capital that was contributed to a fund via deemed distributions.
What is it? Under the ?cashless contribution? approach, A GP would waive all or a portion of its management fees to ?fund? a subscription by the GP for an interest in the Fund. The entire amount of waived fees would be treated as deemed contributions to fund the GP's interest.
Capital Contributions A capital contribution is essentially an injection of cash into a company. For example, business owners will often take out some type of business loan from a lender or financial institution and then use the proceeds to make a capital contribution back to their company.
What Is Contributed Capital? Contributed capital, also known as paid-in capital, is the cash and other assets that shareholders have given a company in exchange for stock. Investors make capital contributions when a company issues equity shares based on a price that shareholders are willing to pay for them.
This clause should be used when one member contributed real property to the joint venture in exchange for membership interests and another member has contributed capital. The capitalized terms and section references used in this clause should be conformed to the relevant joint venture operating agreement.