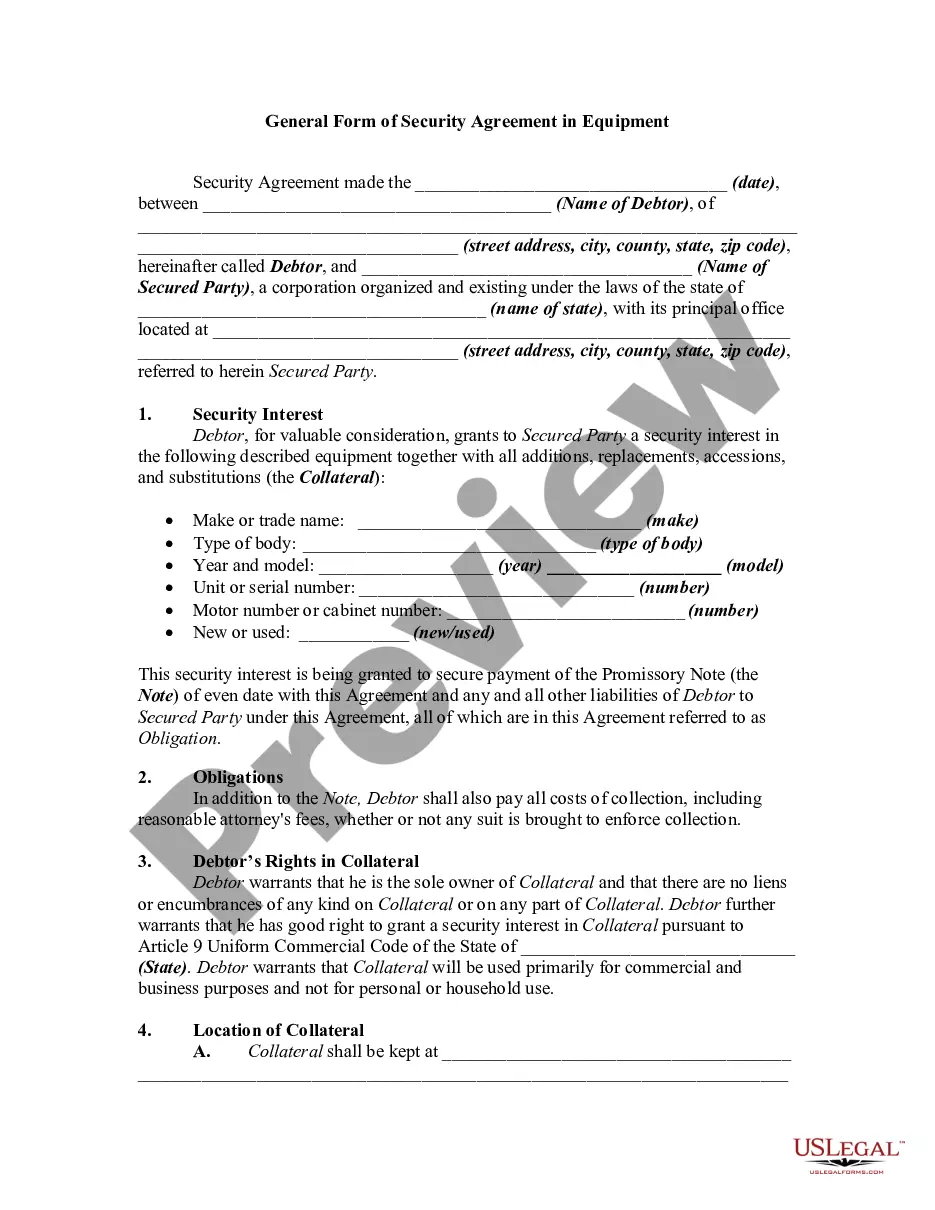
A secured transaction is created when a buyer or borrower (debtor) grants a seller or lender (creditor or secured party) a security interest in personal property (collateral). A security interest allows a creditor to repossess and sell the collateral if a debtor fails to pay a secured debt.
The Truth-in-Lending Act (TILA) is part of the Federal Consumer Credit Protection Act. The purpose of the TILA is to make full disclosure to debtors of what they are being charged for the credit they are receiving. The Act merely asks lenders to be honest to the debtors and not cover up what they are paying for the credit. Regulation Z is a federal regulation prepared by the Federal Reserve Board to carry out the details of the Act. TILA applies to consumer credit transactions. Consumer credit is credit for personal or household use and not commercial use or business purposes.
Illinois General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment An Illinois General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment is a legal document that establishes a debtor-creditor relationship regarding the collateral of equipment. This agreement provides security to the creditor by granting a security interest in the equipment owned by the debtor. It is essential for securing loans or financing related to the acquisition of equipment in the state of Illinois. Keywords: Illinois General Form, Security Agreement, Equipment, Collateral, Debtor-Creditor Relationship, Security Interest, Loans, Financing. Different Types of Illinois General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment: 1. Chattel Mortgage: A type of security agreement where the debtor grants a security interest in the equipment to the creditor. The equipment acts as collateral, and if the debtor defaults on the loan, the creditor can take possession of the equipment. 2. Conditional Sales Contract: This type of agreement allows the debtor to use the equipment while making installment payments to the creditor. The creditor retains ownership rights until the debtor completes all payment obligations. If the debtor defaults, the creditor can repossess the equipment. 3. Equipment Lease Agreement: In this arrangement, the debtor leases the equipment from the creditor and agrees to make regular lease payments. The creditor retains ownership of the equipment, and if the debtor defaults, the creditor can repossess the equipment. 4. Hire Purchase Agreement: This agreement allows the debtor to acquire possession and use the equipment while making installment payments. The creditor retains ownership until the debtor completes all payment obligations. If the debtor defaults, the creditor can repossess the equipment. 5. Equipment Pledge Agreement: The debtor pledges the equipment as collateral to the creditor to secure a loan. If the debtor fails to repay the loan, the creditor can seize and sell the equipment to recover the debt. These agreements ensure that lenders or creditors have a legal claim on the equipment owned by a debtor, providing them with a measure of protection if the debtor defaults on their obligations. Disclaimer: The information provided here is for reference purposes only and should not be considered legal advice. It is recommended to consult a qualified attorney when creating or entering into any legal agreements.Illinois General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment An Illinois General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment is a legal document that establishes a debtor-creditor relationship regarding the collateral of equipment. This agreement provides security to the creditor by granting a security interest in the equipment owned by the debtor. It is essential for securing loans or financing related to the acquisition of equipment in the state of Illinois. Keywords: Illinois General Form, Security Agreement, Equipment, Collateral, Debtor-Creditor Relationship, Security Interest, Loans, Financing. Different Types of Illinois General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment: 1. Chattel Mortgage: A type of security agreement where the debtor grants a security interest in the equipment to the creditor. The equipment acts as collateral, and if the debtor defaults on the loan, the creditor can take possession of the equipment. 2. Conditional Sales Contract: This type of agreement allows the debtor to use the equipment while making installment payments to the creditor. The creditor retains ownership rights until the debtor completes all payment obligations. If the debtor defaults, the creditor can repossess the equipment. 3. Equipment Lease Agreement: In this arrangement, the debtor leases the equipment from the creditor and agrees to make regular lease payments. The creditor retains ownership of the equipment, and if the debtor defaults, the creditor can repossess the equipment. 4. Hire Purchase Agreement: This agreement allows the debtor to acquire possession and use the equipment while making installment payments. The creditor retains ownership until the debtor completes all payment obligations. If the debtor defaults, the creditor can repossess the equipment. 5. Equipment Pledge Agreement: The debtor pledges the equipment as collateral to the creditor to secure a loan. If the debtor fails to repay the loan, the creditor can seize and sell the equipment to recover the debt. These agreements ensure that lenders or creditors have a legal claim on the equipment owned by a debtor, providing them with a measure of protection if the debtor defaults on their obligations. Disclaimer: The information provided here is for reference purposes only and should not be considered legal advice. It is recommended to consult a qualified attorney when creating or entering into any legal agreements.