A joint venture is a relationship between two or more people who combine their labor or property for a single business undertaking. They share profits and losses equally, or as otherwise provided in the joint venture agreement. The single business undertaking aspect is a key to determining whether or not a business entity is a joint venture as opposed to a partnership.
A joint venture is very similar to a partnership. In fact, some States treat joint ventures the same as partnerships with regard to partnership statutes such as the Uniform Partnership Act. The main difference between a partnership and a joint venture is that a joint venture usually relates to the pursuit of a single transaction or enterprise even though this may require several years to accomplish. A partnership is generally a continuing or ongoing business or activity. While a partnership may be expressly created for a single transaction, this is very unusual. Most Courts hold that joint ventures are subject to the same principles of law as partnerships.
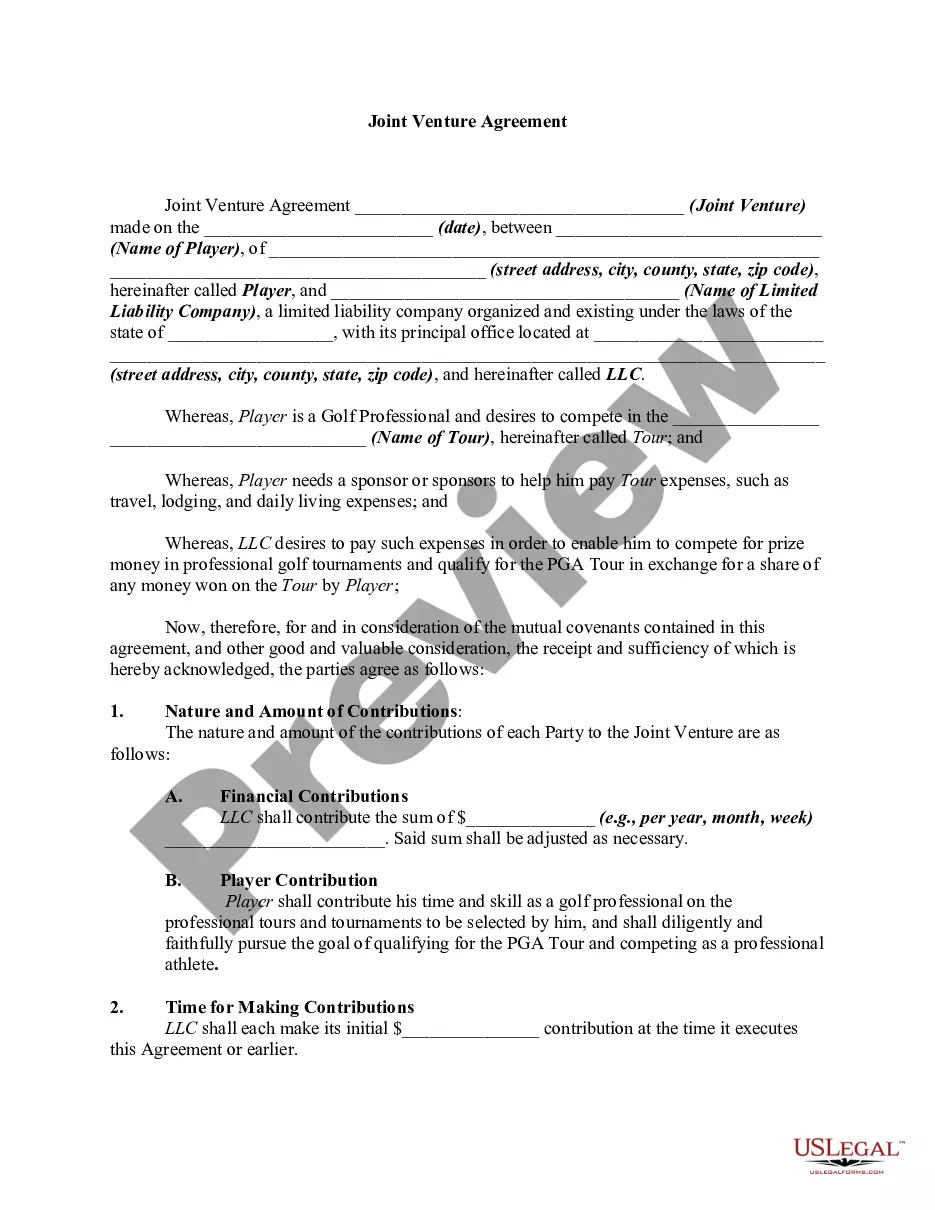
Illinois Joint Venture Agreement between a Limited Liability Company and Professional Golfer to Sponsor and Provide Funds A joint venture is a strategic partnership between two or more entities that join forces to undertake a specific business venture. In the context of the Illinois joint venture agreement between a limited liability company (LLC) and a professional golfer, the purpose is to establish a collaborative effort aimed at mutually benefiting from sponsorship and funding opportunities within the golf industry. Key Terms and Provisions: 1. Parties: The agreement would outline the names and roles of the parties involved: the LLC, which serves as the sponsoring entity, and the professional golfer who brings their skills and expertise to the venture. 2. Purpose: Clarifies the purpose of the joint venture, which is to secure sponsorships and funding to support the professional golfer's career and related activities. This could include participating in professional tournaments, marketing initiatives, and any other golf-related ventures. 3. Contribution: Specifies the resources and contributions each party will bring to the joint venture. The LLC may provide financial support, administrative assistance, marketing strategies, and other resources, while the professional golfer brings their golfing abilities, brand value, and other related assets. 4. Distribution of Profits and Losses: Determines how profits and losses will be allocated between the LLC and the professional golfer. This provision will typically consider the proportions of initial investment, ongoing contributions, and overall involvement of each party. 5. Management and Control: Outlines the decision-making processes and control mechanisms. This provision may establish guidelines for important decisions such as sponsorship agreements, tournaments to participate in, marketing campaigns, and budget allocation. It can also determine the roles and responsibilities of both parties regarding the day-to-day operations of the venture. Types of Illinois Joint Venture Agreements: 1. "Equity Joint Venture Agreement": In this type of joint venture, the LLC and the professional golfer both contribute capital and share ownership in the venture. Profits and losses are distributed according to the equity percentages held by each party. 2. "Contractual Joint Venture Agreement": This agreement is based on a contractual relationship rather than shared ownership. The LLC and the professional golfer collaborate through an agreement that defines their roles, obligations, and profit-sharing arrangements. However, the LLC typically retains more control and decision-making authority in this type of arrangement. 3. "Limited Liability Joint Venture Agreement": This agreement limits the liability of both the LLC and the professional golfer, protecting their personal assets from potential losses or legal claims arising from the joint venture activities. This type of agreement is prevalent when concerns about financial risks are high. In summary, an Illinois joint venture agreement between a limited liability company and a professional golfer aims to forge a partnership in order to sponsor and provide funds to support the golfer's career and related endeavors. The agreement will outline the purpose, contributions, profit-sharing arrangements, and management of the joint venture. Different types of joint venture agreements include equity joint ventures, contractual joint ventures, and limited liability joint ventures, each with their own specific characteristics and legal implications.Illinois Joint Venture Agreement between a Limited Liability Company and Professional Golfer to Sponsor and Provide Funds A joint venture is a strategic partnership between two or more entities that join forces to undertake a specific business venture. In the context of the Illinois joint venture agreement between a limited liability company (LLC) and a professional golfer, the purpose is to establish a collaborative effort aimed at mutually benefiting from sponsorship and funding opportunities within the golf industry. Key Terms and Provisions: 1. Parties: The agreement would outline the names and roles of the parties involved: the LLC, which serves as the sponsoring entity, and the professional golfer who brings their skills and expertise to the venture. 2. Purpose: Clarifies the purpose of the joint venture, which is to secure sponsorships and funding to support the professional golfer's career and related activities. This could include participating in professional tournaments, marketing initiatives, and any other golf-related ventures. 3. Contribution: Specifies the resources and contributions each party will bring to the joint venture. The LLC may provide financial support, administrative assistance, marketing strategies, and other resources, while the professional golfer brings their golfing abilities, brand value, and other related assets. 4. Distribution of Profits and Losses: Determines how profits and losses will be allocated between the LLC and the professional golfer. This provision will typically consider the proportions of initial investment, ongoing contributions, and overall involvement of each party. 5. Management and Control: Outlines the decision-making processes and control mechanisms. This provision may establish guidelines for important decisions such as sponsorship agreements, tournaments to participate in, marketing campaigns, and budget allocation. It can also determine the roles and responsibilities of both parties regarding the day-to-day operations of the venture. Types of Illinois Joint Venture Agreements: 1. "Equity Joint Venture Agreement": In this type of joint venture, the LLC and the professional golfer both contribute capital and share ownership in the venture. Profits and losses are distributed according to the equity percentages held by each party. 2. "Contractual Joint Venture Agreement": This agreement is based on a contractual relationship rather than shared ownership. The LLC and the professional golfer collaborate through an agreement that defines their roles, obligations, and profit-sharing arrangements. However, the LLC typically retains more control and decision-making authority in this type of arrangement. 3. "Limited Liability Joint Venture Agreement": This agreement limits the liability of both the LLC and the professional golfer, protecting their personal assets from potential losses or legal claims arising from the joint venture activities. This type of agreement is prevalent when concerns about financial risks are high. In summary, an Illinois joint venture agreement between a limited liability company and a professional golfer aims to forge a partnership in order to sponsor and provide funds to support the golfer's career and related endeavors. The agreement will outline the purpose, contributions, profit-sharing arrangements, and management of the joint venture. Different types of joint venture agreements include equity joint ventures, contractual joint ventures, and limited liability joint ventures, each with their own specific characteristics and legal implications.