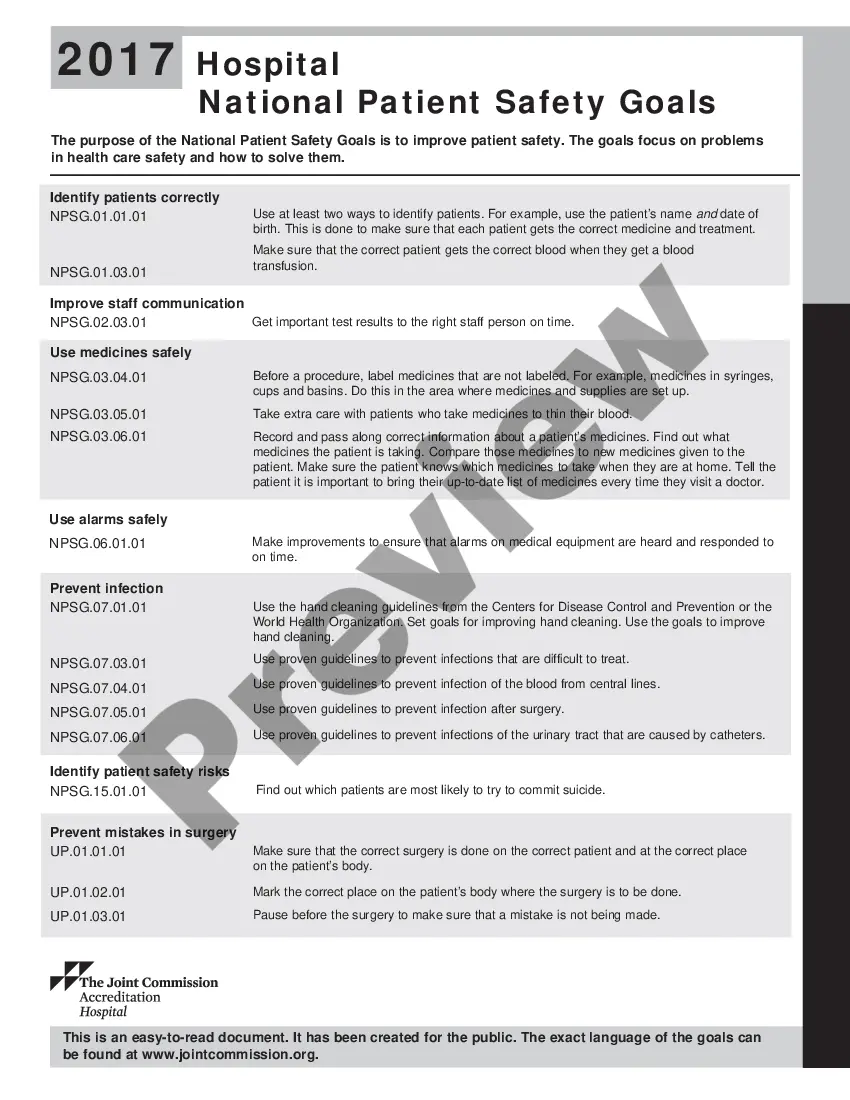
The Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals aim to promote a culture of safety within healthcare facilities across the state of Illinois. These goals are developed by the Joint Commission, an organization that sets standards and accrediting healthcare organizations. The goals provide specific guidelines and measures to ensure patients receive high-quality care and improve patient safety outcomes. One of the primary goals set by the Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals is to identify patients correctly. This involves using at least two patient identifiers, such as name and date of birth, to verify the correct patient before providing any care or treatment. This goal helps prevent patient identification errors and ensures that healthcare providers deliver personalized care to the intended recipient. Another goal focuses on improving the communication between healthcare providers. Effective communication is crucial as it reduces the risk of medical errors, facilitates timely treatment, and enhances patient outcomes. To achieve this goal, healthcare organizations implement standardized communication techniques, such as the "STAR" (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) method, which improves the transfer of critical patient information. Medication safety is also a critical focus area within the Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Medication errors can have severe consequences for patients, so it is essential to establish a robust process for medication management. This includes accurate medication reconciliation, proper labeling of medications, and educating patients about their prescribed medications and potential side effects. To prevent the spread of infections, healthcare facilities are required to adopt various strategies. Hand hygiene is emphasized to reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections. Regular staff training, providing hand sanitizers and handwashing stations, and monitoring adherence to hand hygiene protocols are crucial components of this goal. Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals also prioritize the prevention of falls among patients. This involves conducting fall risk assessments, implementing preventive measures such as bed alarms or non-skid footwear, and educating patients and their families on fall prevention strategies. Other areas of focus within the Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals may include preventing pressure ulcers (bedsores), reducing the risk of surgical site infections, standardizing processes for emergency response, enhancing patient education, and ensuring a safe environment of care for patients. By setting these goals, Illinois hospitals aim to create a safer healthcare system, minimizing risks and improving patient outcomes. It is vital for healthcare professionals and facilities to continuously review and update their practices to align with these goals, ensuring patient safety remains a top priority.
Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Are you in the position the place you need documents for sometimes business or individual functions almost every day time? There are a lot of legal document layouts available on the net, but finding ones you can depend on isn`t effortless. US Legal Forms delivers thousands of kind layouts, much like the Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, that happen to be published to fulfill state and federal demands.
Should you be currently knowledgeable about US Legal Forms internet site and possess a free account, merely log in. Following that, you are able to obtain the Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals format.
Unless you offer an bank account and would like to start using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Get the kind you will need and ensure it is to the correct town/county.
- Use the Review switch to examine the shape.
- See the description to actually have selected the appropriate kind.
- In case the kind isn`t what you are trying to find, take advantage of the Research industry to obtain the kind that meets your requirements and demands.
- Once you discover the correct kind, simply click Buy now.
- Pick the costs prepare you need, complete the desired info to produce your money, and pay for your order using your PayPal or credit card.
- Pick a hassle-free file formatting and obtain your duplicate.
Find all of the document layouts you have purchased in the My Forms menus. You can get a additional duplicate of Illinois Hospital National Patient Safety Goals whenever, if required. Just click on the required kind to obtain or print out the document format.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive selection of legal forms, to save lots of some time and avoid blunders. The services delivers skillfully manufactured legal document layouts which you can use for an array of functions. Generate a free account on US Legal Forms and begin making your way of life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
Goal. Prevent, reduce, and ultimately eliminate healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
2022 Joint Commission National Patient Safety Goals1 Identify Patients Correctly.2 Improve Staff Communication.3 Use Medicines Safely.4 Use Alarms Safely.5 Prevent Infection.6 Surgery Verification.
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
NPSG.03.06.01Maintain and communicate accurate patient medication information.
Measures of infection control include identifying patients at risk of nosocomial infections, observing hand hygiene, following standard precautions to reduce transmission and strategies to reduce VAP, CR-BSI, CAUTI. Environmental factors and architectural lay out also need to be emphasized upon.
Goal 6: Reduce patient harm associated with clinical alarm systems.