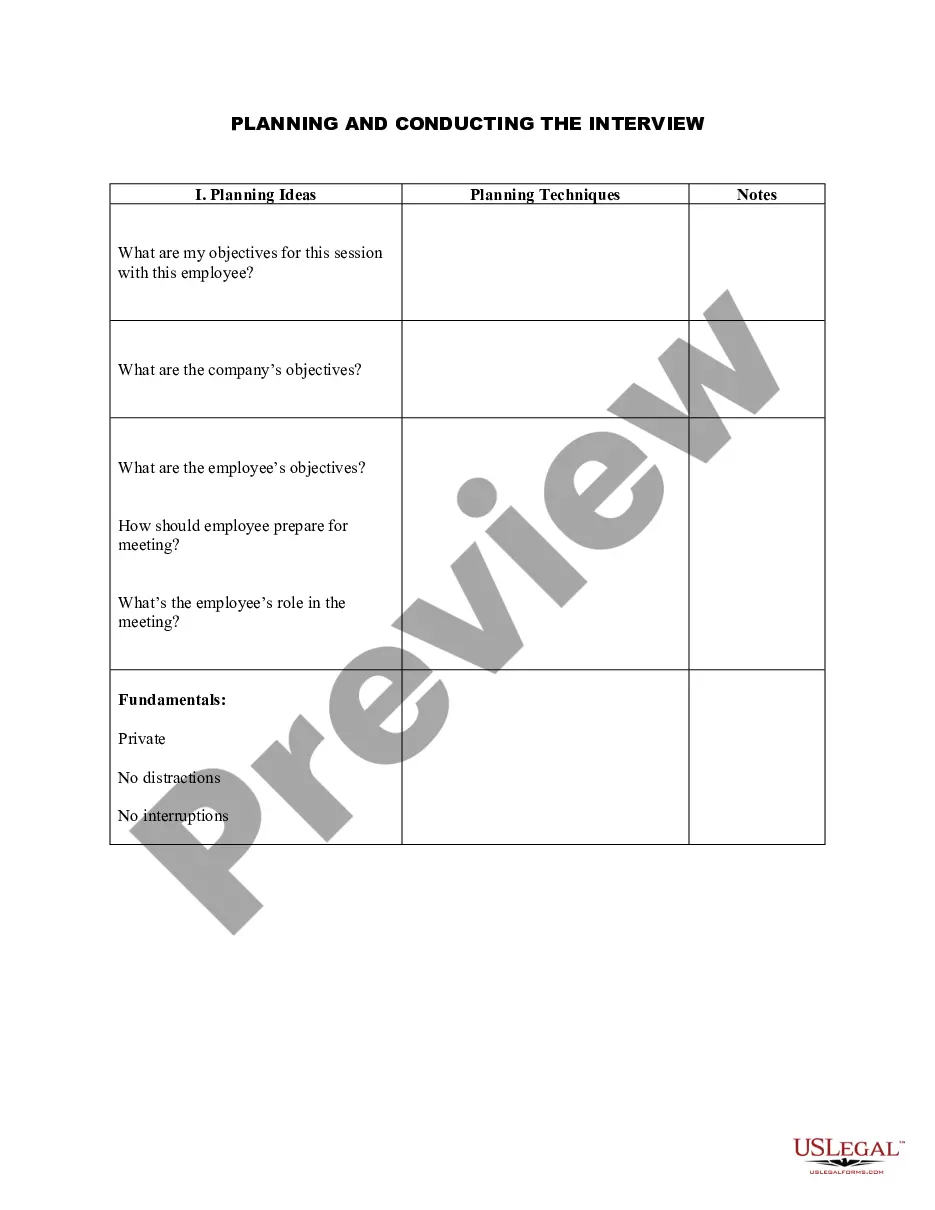
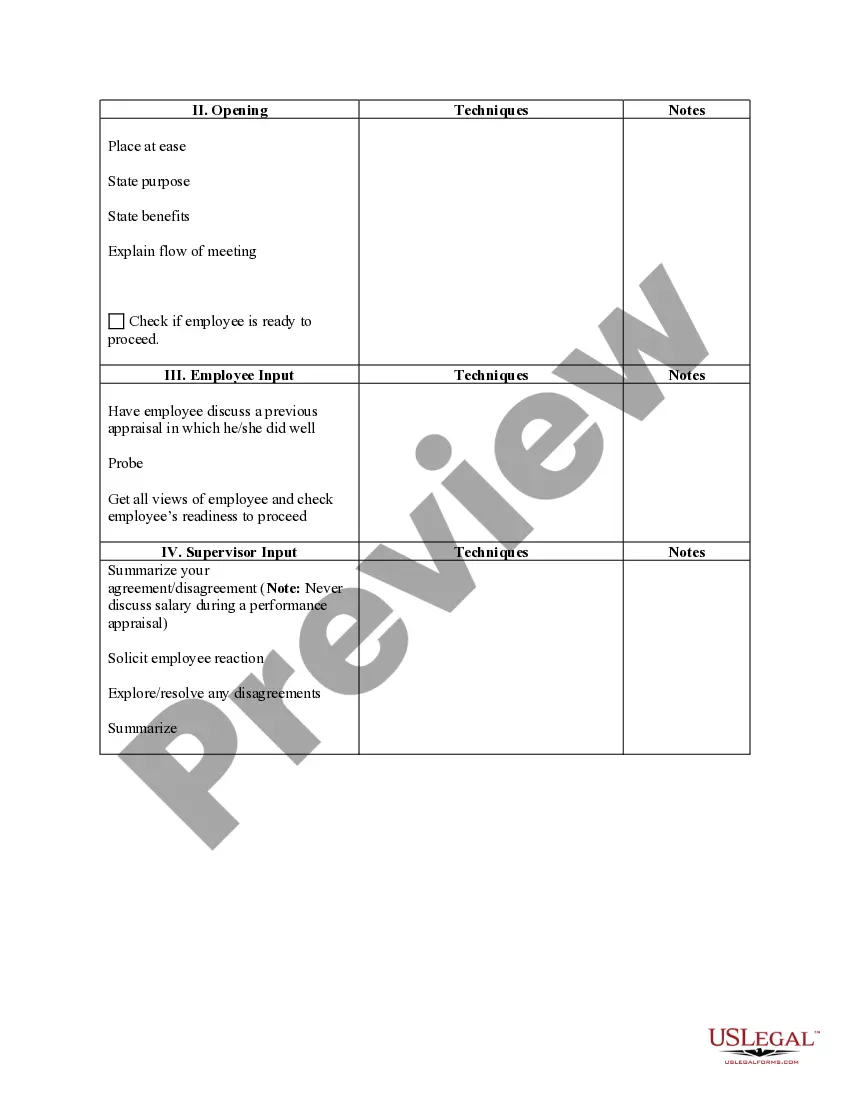
Illinois Planning and Conducting the Interview
Description
How to fill out Planning And Conducting The Interview?
If you require thorough, obtain, or print legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the leading collection of legal forms, available online.
Take advantage of the site’s user-friendly search feature to locate the documents you seek. Various templates for commercial and personal uses are categorized by types and states, or keywords.
Use US Legal Forms to find the Illinois Planning and Conducting the Interview with just a few clicks.
Every legal document template you acquire is your property permanently. You can access every form you downloaded in your account. Click the My documents section and select a form to print or download again.
Be proactive and obtain, and print the Illinois Planning and Conducting the Interview with US Legal Forms. There are countless professional and state-specific forms available for your business or personal requirements.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms customer, Log In to your account and click the Acquire button to obtain the Illinois Planning and Conducting the Interview.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded from the My documents tab in your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview option to review the form’s content. Don’t forget to read the description.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find other versions of the legal form design.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click the Buy now button. Choose your preferred pricing plan and enter your details to register for an account.
- Step 5. Process the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the purchase.
- Step 6. Choose the format of the legal form and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Complete, modify, and print or sign the Illinois Planning and Conducting the Interview.
Form popularity
FAQ
Knowing what to expect can help reduce interview anxiety. Most job interviews can be broken down into three phases: Introduction, Getting to Know You, and Closing.
Structured interviews are prepared in advance with clear objectives. A structured interview uses a question and answer format, with most questions pre-determined in order to elicit specific information.
Stages of the InterviewSTAGE 1: Introduction. Lasting approximately two to three minutes, you are meeting the interviewers and being escorted to the interview room.STAGE 2: Q&A.STAGE 3: Your Questions.STAGE 4: Closing.
CONDUCTING THE INTERVIEWIntroduce yourself.Set the stage.Review the job.Start with generalized questions.Review the applicant's resume.Ask some consistent questions.Vary your questions.Give candidates a chance to ask questions.More items...
Stages of an Interview#1) Introductions. One of the most important steps in the interview process just so happens to be the first.#2) Small Talk. After introductions are finished, it is a good idea conduct a bit of small talk with the candidate.#3) Information Gathering.#4) Question/Answer.#5) Wrapping Up.
Any job interview can be broken down into four general stages: introductions, broad questions and answers, position-related questions, and the conclusion.
CONDUCTING THE INTERVIEWIntroduce yourself.Set the stage.Review the job.Start with generalized questions.Review the applicant's resume.Ask some consistent questions.Vary your questions.Give candidates a chance to ask questions.More items...
How to plan an interviewSelect the best format for your interviews.Choose your interview questions carefully.Keep it relevant to the job.Be consistent with all candidates.Be ready to answer applicants' questions.Arrange a suitable location.Make sure interviewers have the right skills.
The 6 Step Interview Process1.The shortlist. The first step in the interview process is to get shortlisted for interview.The Screening Interview.The First Round Interview.The Second Round Interview.The Third Round Interview.The Job Offer and Background Check.
Step 1: Interview Preparation.Step 2: Starting the Interview.Step 3: Asking the Questions.Step 4: Closing the Interview.Step 5: Assessing the Candidate.