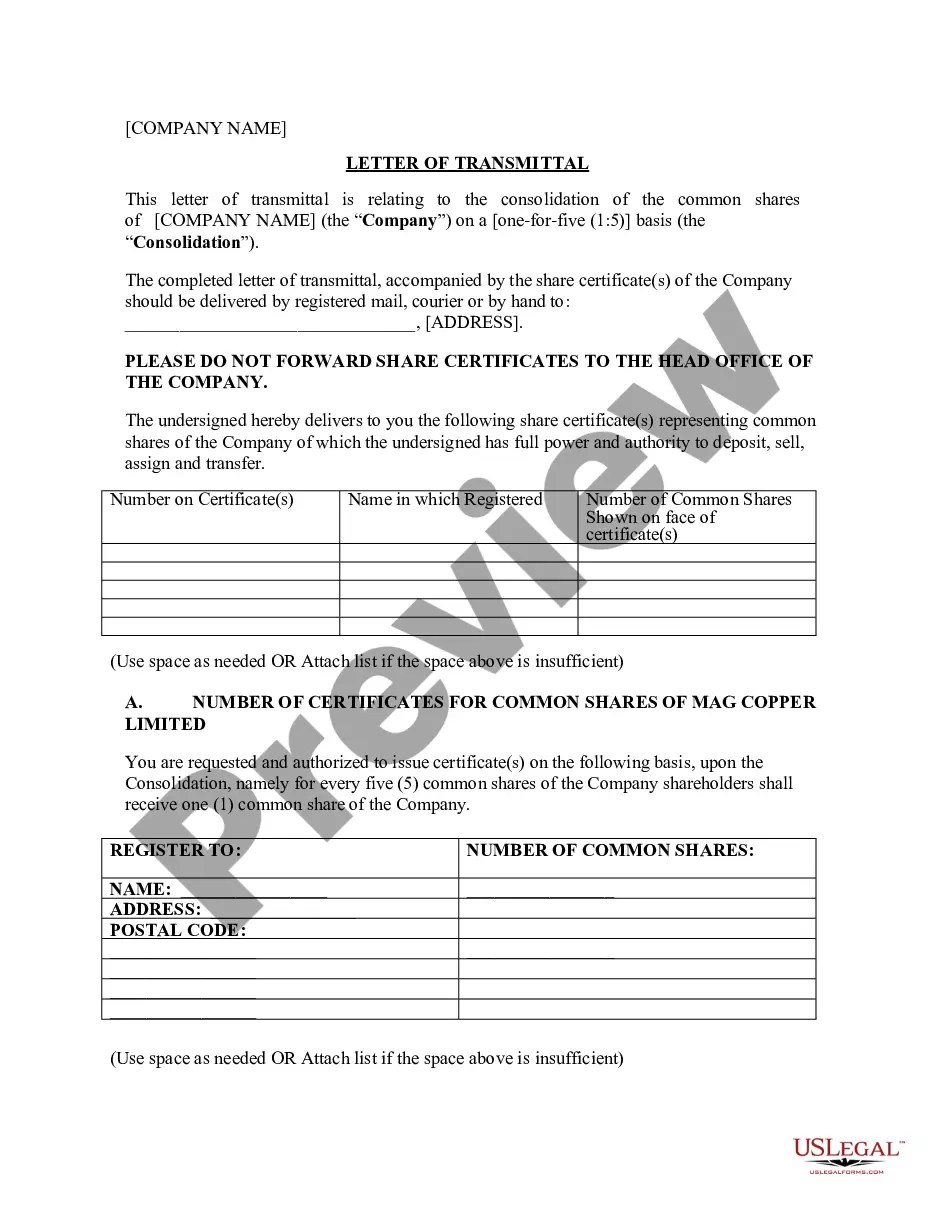
This is a Reasonable Development form. The assignee shall drill all additional wells necessary to develop the leases and the land they cover, necessary to protect them from drainage, as would a reasonably prudent operator; provided, however, without limitation of the foregoing, assignee shall drill all development, protection, or offset wells which may be required under the terms and provisions of the oil and gas leases on the lands, to the depths assigned.
Illinois Reasonable Development refers to a set of principles and guidelines designed to promote sustainable and responsible growth in communities across the state of Illinois. With an emphasis on balancing economic development, environmental preservation, and social equity, Illinois Reasonable Development aims to create vibrant, resilient, and livable communities for present and future generations. Key aspects of Illinois Reasonable Development include: 1. Smart Growth: This approach encourages compact and efficient land use, focusing on revitalizing existing communities rather than sprawling development. It promotes mixed-use developments with a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, reducing the need for long commutes and preserving natural resources. 2. Environmental Conservation: Illinois Reasonable Development emphasizes environmental protection by safeguarding natural resources, wildlife habitats, and sensitive ecosystems. It encourages practices such as green building design, energy efficiency, renewable energy utilization, stormwater management, and waste reduction. 3. Transportation Planning: This component focuses on creating a comprehensive and sustainable transportation system that reduces congestion, air pollution, and reliance on single-occupancy vehicles. Illinois Reasonable Development promotes public transit options, walking and cycling infrastructure, and improved connectivity between residential areas, employment centers, and recreational spaces. 4. Affordable Housing and Social Equity: Illinois Reasonable Development aims to provide diverse housing options that cater to residents with varying income levels. It promotes initiatives to address affordable housing needs, encourage mixed-income neighborhoods, and ensure equitable access to quality education, healthcare, and community services. 5. Community Engagement: Illinois Reasonable Development encourages active public participation throughout the planning and decision-making processes. It recognizes the importance of involving community members, organizations, and stakeholders to ensure that development plans align with local needs, aspirations, and cultural values. Some specific types of Illinois Reasonable Development include: 1. Transit-Oriented Development (TOD): TOD focuses on creating vibrant, mixed-use neighborhoods around transit stations, fostering walk ability, and reducing dependence on cars. It usually includes a blend of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, promoting sustainable urban growth. 2. Conservation Development: This approach combines environmental conservation with residential development, protecting ecologically valuable areas while allowing for responsible housing construction. It encourages clustering of houses, preserving open spaces, and integrating natural features into the development. 3. Brownfield Redevelopment: Brownfield sites refer to abandoned or underutilized lands with real or perceived environmental contamination. Illinois Reasonable Development encourages the cleanup and redevelopment of these sites, transforming them into productive and environmentally sustainable areas. 4. Infill Development: Infill development focuses on utilizing vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas, minimizing sprawl and utilizing existing infrastructure. It often includes adapting and repurposing existing buildings, revitalizing older neighborhoods, and promoting walk ability. Illinois Reasonable Development strives to create communities that are economically viable, environmentally sustainable, and socially equitable. By implementing these principles, Illinois aims to foster long-term prosperity while minimizing adverse impacts on the environment and society.
Illinois Reasonable Development refers to a set of principles and guidelines designed to promote sustainable and responsible growth in communities across the state of Illinois. With an emphasis on balancing economic development, environmental preservation, and social equity, Illinois Reasonable Development aims to create vibrant, resilient, and livable communities for present and future generations. Key aspects of Illinois Reasonable Development include: 1. Smart Growth: This approach encourages compact and efficient land use, focusing on revitalizing existing communities rather than sprawling development. It promotes mixed-use developments with a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, reducing the need for long commutes and preserving natural resources. 2. Environmental Conservation: Illinois Reasonable Development emphasizes environmental protection by safeguarding natural resources, wildlife habitats, and sensitive ecosystems. It encourages practices such as green building design, energy efficiency, renewable energy utilization, stormwater management, and waste reduction. 3. Transportation Planning: This component focuses on creating a comprehensive and sustainable transportation system that reduces congestion, air pollution, and reliance on single-occupancy vehicles. Illinois Reasonable Development promotes public transit options, walking and cycling infrastructure, and improved connectivity between residential areas, employment centers, and recreational spaces. 4. Affordable Housing and Social Equity: Illinois Reasonable Development aims to provide diverse housing options that cater to residents with varying income levels. It promotes initiatives to address affordable housing needs, encourage mixed-income neighborhoods, and ensure equitable access to quality education, healthcare, and community services. 5. Community Engagement: Illinois Reasonable Development encourages active public participation throughout the planning and decision-making processes. It recognizes the importance of involving community members, organizations, and stakeholders to ensure that development plans align with local needs, aspirations, and cultural values. Some specific types of Illinois Reasonable Development include: 1. Transit-Oriented Development (TOD): TOD focuses on creating vibrant, mixed-use neighborhoods around transit stations, fostering walk ability, and reducing dependence on cars. It usually includes a blend of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, promoting sustainable urban growth. 2. Conservation Development: This approach combines environmental conservation with residential development, protecting ecologically valuable areas while allowing for responsible housing construction. It encourages clustering of houses, preserving open spaces, and integrating natural features into the development. 3. Brownfield Redevelopment: Brownfield sites refer to abandoned or underutilized lands with real or perceived environmental contamination. Illinois Reasonable Development encourages the cleanup and redevelopment of these sites, transforming them into productive and environmentally sustainable areas. 4. Infill Development: Infill development focuses on utilizing vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas, minimizing sprawl and utilizing existing infrastructure. It often includes adapting and repurposing existing buildings, revitalizing older neighborhoods, and promoting walk ability. Illinois Reasonable Development strives to create communities that are economically viable, environmentally sustainable, and socially equitable. By implementing these principles, Illinois aims to foster long-term prosperity while minimizing adverse impacts on the environment and society.