Illinois Boilerplate Clauses
Description
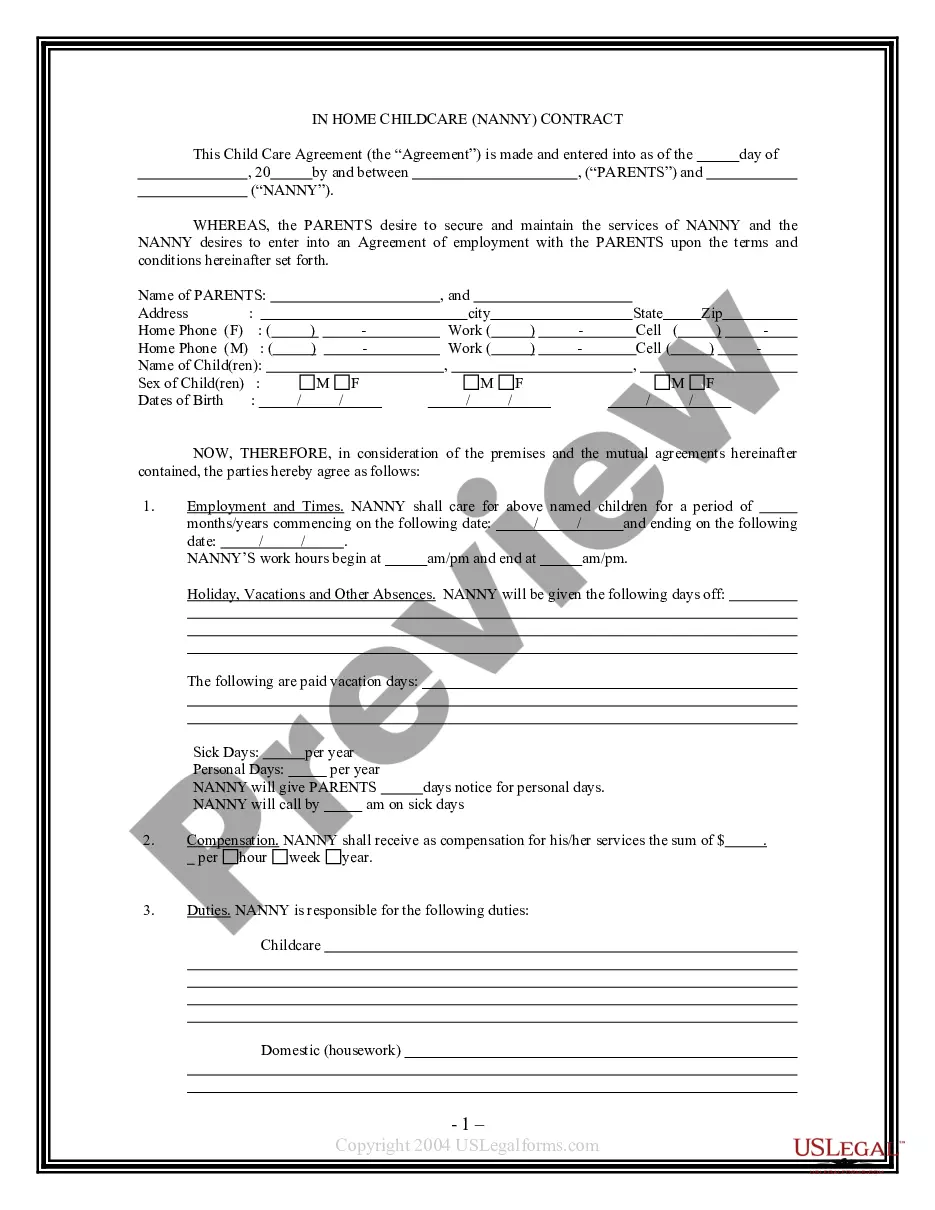
How to fill out Boilerplate Clauses?
Have you been within a placement the place you need paperwork for sometimes company or individual uses almost every day time? There are tons of legitimate record themes available online, but discovering types you can rely isn`t straightforward. US Legal Forms delivers a huge number of develop themes, much like the Illinois Boilerplate Clauses, which are composed to meet federal and state needs.
In case you are presently acquainted with US Legal Forms website and also have a free account, basically log in. After that, you can download the Illinois Boilerplate Clauses design.
Should you not have an account and want to begin using US Legal Forms, abide by these steps:
- Find the develop you require and make sure it is for that correct metropolis/area.
- Use the Review key to analyze the shape.
- Read the explanation to ensure that you have chosen the correct develop.
- In the event the develop isn`t what you`re trying to find, make use of the Search discipline to get the develop that suits you and needs.
- When you get the correct develop, click on Get now.
- Pick the prices program you desire, complete the necessary information to generate your money, and pay for an order using your PayPal or Visa or Mastercard.
- Decide on a handy file format and download your copy.
Get all of the record themes you may have bought in the My Forms food list. You can aquire a further copy of Illinois Boilerplate Clauses any time, if possible. Just go through the necessary develop to download or printing the record design.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most comprehensive collection of legitimate forms, to save time and avoid blunders. The support delivers expertly produced legitimate record themes which you can use for a selection of uses. Make a free account on US Legal Forms and commence making your way of life a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
Boilerplate clauses are the standard terms and conditions which a party inserts in almost all its contracts. These clauses could be assignment, governing law, arbitration, force majeure, severability, counterparts, entire agreement, termination, indemnity etc.
A boilerplate statement or response generally refers to a message used with minimal effort for multiple different situations. Examples include official statements from government officials such as "Our thoughts and prayers are with those affected" or messages left by companies' voicemail such as "Thank you for holding.
The term boilerplate refers to standardized text, copy, documents, methods, or procedures that may be used over again without making major changes to the original.
Although boilerplate provisions vary from contract to contract (another reason to pay attention to them), there are a handful of common ones. Indemnification Clause. ... Escrow Clause. ... Choice Of Law Clause. ... Jurisdiction Clause. ... Notice Clause. ... Confidentiality Clause. ... Arbitration Clause. ... Force Majeure Clause.
Here are some common examples of boilerplate language: A clause that states that, if there is ever a legal dispute, whichever party loses should pay the legal fees of the party that won. A clause stating that parties should not pursue a lawsuit; legal disputes should go through an approved arbitration process.
Standard Boilerplate Provisions in Contracts Choice of law. A choice of law provision determines which state's legal rules will be applied in the event of a lawsuit. Jurisdiction. ... Indemnification. ... Warranties. ... Confidentiality. ... Assignment. ... Waiver. ... Limitations on damages.
Choice of law clause, also known as a governing law clause, that allows the contract parties to choose the substantive law of Illinois to apply to the contract.
The term boilerplate refers to standardized text, copy, documents, methods, or procedures that may be used over again without making major changes to the original. A boilerplate is commonly used for efficiency and to increase standardization in the structure and language of written or digital documents.