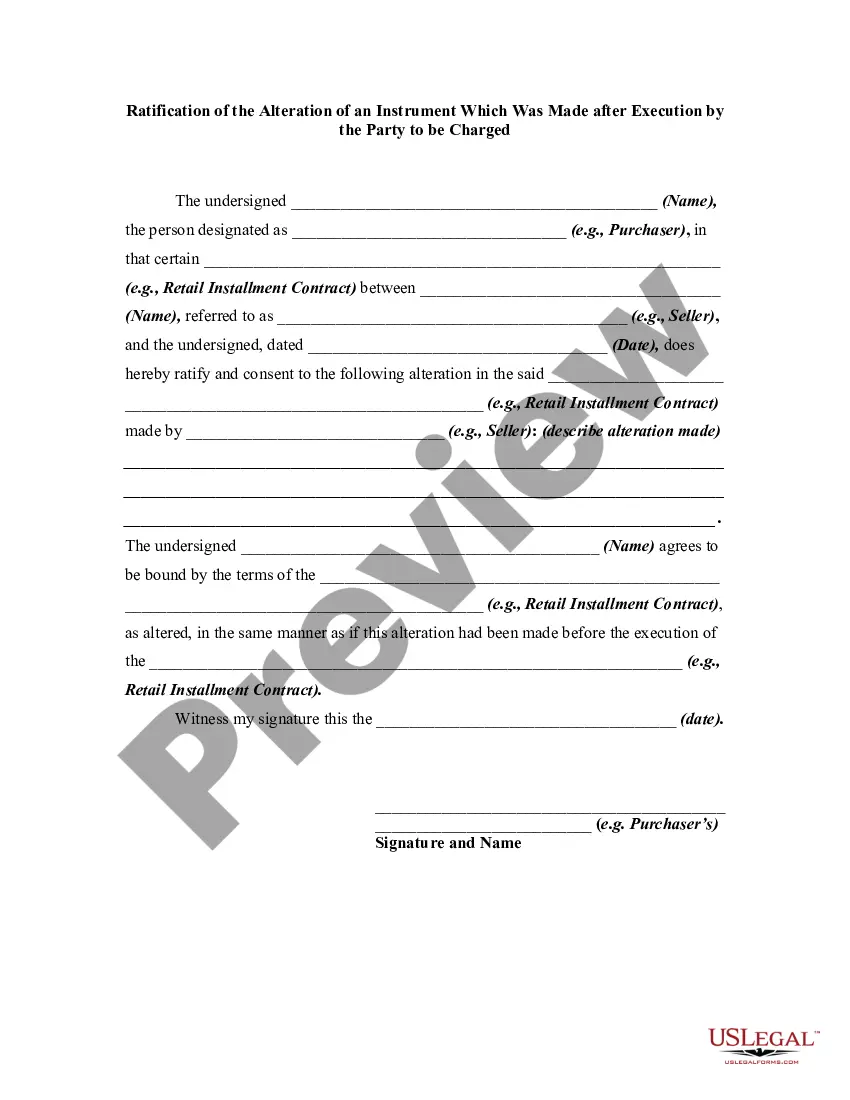
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged
Description
How to fill out Ratification Of The Alteration Of An Instrument Which Was Made After Execution By The Party To Be Charged?
If you require to complete, obtain, or create sanctioned document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest selection of legal forms, which are accessible online.
Employ the site’s straightforward and user-friendly search to find the documents you need.
A variety of templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click the Purchase now button. Select your preferred pricing plan and enter your details to register for an account.
Step 5. Complete the payment. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to process the transaction.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to locate the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged in just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms member, Log In to your account and then click the Obtain button to acquire the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded in the My documents tab of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct state/region.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the form’s content. Remember to check the summary.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search area at the top of the screen to find other versions of the legal form template.
Form popularity
FAQ
Indiana Code 35-45-2-5-3 covers issues related to fraud and deceit. This code is essential for understanding the legal implications of fraudulent activities within various contexts. When considering the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, this insight can help safeguard your legal dealings and uphold the integrity of alterations made to any legal instrument.
Indiana Code 30-5-5-5 addresses various aspects related to trusts and estates. This code can significantly impact the management of trusts in Indiana. As you navigate the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, understanding this context can help you make informed decisions about estate planning and document alterations.
Indiana Code 24-4.5-5-105 pertains to certain consumer protection laws that impact financial transactions. This statute plays a role in protecting consumers while ensuring fair practices in the sale of goods and services. When considering the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, this code can also influence your understanding of how legal documents can be altered for clarity and efficiency.
The tracking device code in Indiana refers to laws governing the use and installation of tracking devices. These regulations ensure that tracking devices are used ethically and within legal boundaries. As you explore matters related to the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, understanding these codes is crucial in your legal considerations.
Indiana Code 24-5-0.5-3 relates specifically to the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged. This provision outlines the legal standards and requirements necessary for altering a legal instrument in Indiana. Understanding this code can help you navigate legal alterations effectively, ensuring compliance with state guidelines.
Section 29 1 5 8 within the Indiana Code specifies the formalities required for the validity of modifications to legal documents. It highlights the importance of adhering to specific procedural guidelines to safeguard against disputes. Gaining insights into this section not only aids your knowledge of the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, but also ensures that your actions align with statutory requirements.
Section 29(1), 7, 23 of the Indiana Code deals with the definitions and interpretations relevant to various legal documents. This section provides clarity on terms that may arise in legal proceedings, thus supporting informed decisions. This knowledge is particularly useful when navigating the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, as it helps ensure that all terminology is understood correctly.
The Indiana Code 29 1 4 1 outlines the default provisions pertaining to contract terms and conditions. It specifies what happens when parties fail to fulfill their contractual obligations. Familiarizing yourself with this code can significantly contribute to your understanding of the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, helping you avoid pitfalls in contract enforcement.
Section 9 30 5 of the Indiana Code addresses the proper methods for modifying legal instruments that have already been executed. It provides the criteria necessary for such modifications to be considered valid. Understanding this section is critical, especially when dealing with the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, as it guides you through the modification process.
Indiana Code 29 1 5 8 relates to the principles of liability and the accountability of parties involved in contractual agreements. This code outlines the responsibilities of individuals in the event of contractual disputes. By knowing the specifics of this code, you enhance your understanding of the Indiana Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, ensuring you manage your legal obligations effectively.