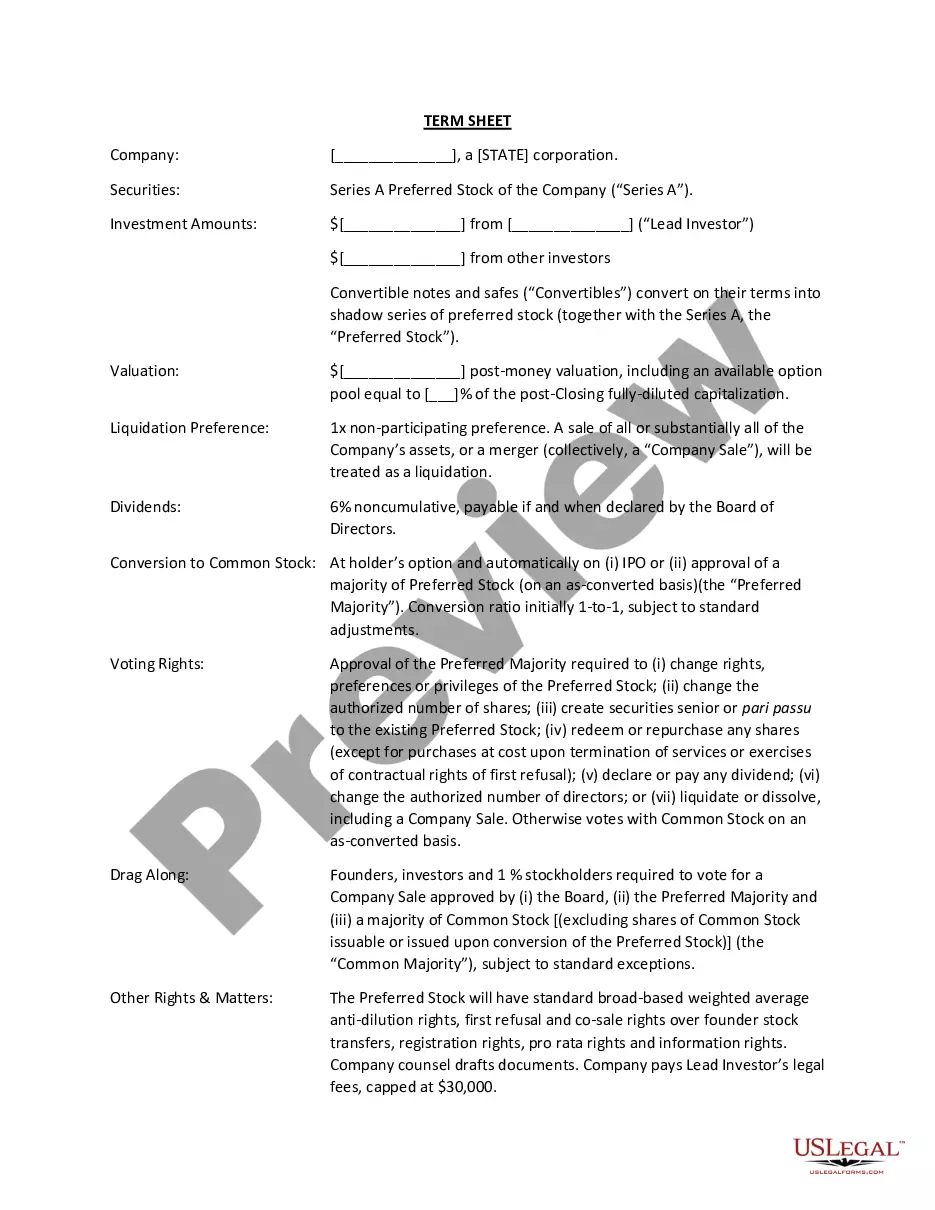
An Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming is a legal structure that allows two or more individuals or entities to come together and collaborate in operating a farming business in the state of Indiana. This partnership is governed by the Indiana Uniform Partnership Act and is responsible for the agricultural activities involved in the business. The Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming allows partners to pool their resources, knowledge, and expertise to establish and manage a farming venture. Partners in this type of partnership typically share in the profits, losses, and liabilities of the farm operation according to the terms outlined in a partnership agreement. There are different types of Indiana General Partnerships for the Purpose of Farming, depending on the specific goals and arrangements of the partners involved. These types include: 1. Active-Active Partnership: In this type of partnership, all partners are actively involved in the day-to-day operations and decision-making processes of the farming business. Each partner contributes labor, capital, or both to the partnership and shares equally in the profits and losses. 2. Active-Passive Partnership: In an active-passive partnership, one partner is actively involved in the farming business while the other partner contributes capital but does not participate in the daily operations. The actively involved partner usually takes on the management responsibilities and shares the profits and losses accordingly. 3. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): An LLP is a type of partnership that limits the personal liability of each partner. In this structure, one or more partners are designated as general partners, who have unlimited personal liability, while the remaining partners are limited partners, whose liability is limited to their investment in the partnership. 4. Family Partnership: A family partnership is formed by family members for the purpose of operating a farming business. This type of partnership allows family members to combine their resources, expertise, and labor to run the farm operation and share in its profits and losses. When establishing an Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming, partners must draft a partnership agreement that clearly outlines the terms and conditions of their partnership. This agreement should include the nature of the partnership, rights and responsibilities of each partner, profit-sharing arrangements, dispute resolution methods, and any other relevant terms that govern the operation of the farming business. In conclusion, an Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming is a collaborative business structure that allows multiple partners to engage in agricultural activities together. Whether it's an active-active partnership, active-passive partnership, LLP, or family partnership, each type offers unique advantages and considerations. The formation of such a partnership requires careful planning, legal documentation, and a shared vision to ensure a successful and profitable farming venture.
Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming
Description
How to fill out Indiana General Partnership For The Purpose Of Farming?
It is possible to commit several hours on the web looking for the authorized papers web template that suits the state and federal requirements you want. US Legal Forms offers a large number of authorized kinds which are analyzed by specialists. It is possible to down load or print out the Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming from the support.
If you have a US Legal Forms account, you may log in and click the Download switch. After that, you may full, change, print out, or sign the Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming. Every authorized papers web template you get is your own property for a long time. To have another duplicate for any acquired kind, visit the My Forms tab and click the corresponding switch.
If you use the US Legal Forms site for the first time, keep to the basic guidelines below:
- First, make certain you have selected the correct papers web template to the area/town of your choosing. Read the kind information to make sure you have chosen the proper kind. If accessible, use the Preview switch to appear from the papers web template as well.
- If you would like find another version in the kind, use the Research industry to get the web template that meets your requirements and requirements.
- Upon having found the web template you would like, just click Get now to carry on.
- Select the rates strategy you would like, key in your references, and register for an account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the deal. You can utilize your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal account to purchase the authorized kind.
- Select the structure in the papers and down load it to the system.
- Make alterations to the papers if required. It is possible to full, change and sign and print out Indiana General Partnership for the Purpose of Farming.
Download and print out a large number of papers layouts while using US Legal Forms Internet site, which offers the largest collection of authorized kinds. Use professional and condition-certain layouts to take on your business or personal requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Corn and soybeans are Indiana's most valuable farm products and Indiana is a leading producer among the states. Other important crops are wheat and hay. Tomatoes are Indiana's leading "vegetable" crop.
These examples all show a producer raising or growing a product and selling that product. They have not further processed or modified the product. These are farming activities and hence would all qualify as farm income.
To qualify for exemption, the purchased property must be directly used in direct production of food or agricultural commodities and must have an immediate effect on the commodity being produced.
And while those crops are extremely important to the state, Indiana has earned its spot in top national rankings for several other commodities. The Hoosier State is 10th nationally in total agricultural production and in the top five for crop production, thanks to the abundance of corn and soybeans.
Indiana homestead laws allow people to claim as much as $10,000 worth of property as a homestead.
A farm is a tract of land cultivated for the purpose of agricultural production. A farm is classified of having $1,000 or more of agricultural products being produced or sold.
A farm is a tract of land cultivated for the purpose of agricultural production. A farm is classified of having $1,000 or more of agricultural products being produced or sold.
According to the USDA, the average size of a farm is 444 acres.
To be named a Hoosier Homestead, farms must be owned by the same family for at least 100 consecutive years and consist of more than 20 acres or produce more than $1,000 of agricultural products per year. The award distinctions are Centennial, Sesquicentennial and Bicentennial for 100, 150 and 200 years respectively.
In Indiana agriculture, corn and soybeans are at the top of the list. These two cash crops make up approximately 60 percent of the agricultural products sold in Indiana. In a typical year, almost half of the cropland in Indiana is corn.