Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals are a set of guidelines and objectives established by the Indiana Hospital Association (IRA) to ensure the highest standard of patient safety across healthcare facilities in Indiana. These goals aim to identify and address potential risks, errors, and hazards that may compromise patient well-being during their hospitalization. One of the primary objectives of Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals is to prevent and reduce the risk of falls. Hospitals must implement protocols to assess patients' fall risk and develop strategies to minimize the likelihood of falls, such as providing non-slip footwear, ensuring well-lit and obstacle-free hallways, and regularly monitoring patients' mobility. Another crucial goal is to prevent healthcare-associated infections (His). Hospitals are required to follow strict infection control measures, including proper hand hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment, and effective sterilization of equipment. Compliance with guidelines for specific infections, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or Clostridium difficile (C. Diff), is also emphasized. The Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals also emphasize medication safety. Hospitals must implement procedures for accurate medication reconciliation, proper labeling, and safe medication administration. Healthcare providers are encouraged to involve patients in the medication management process, ensuring they understand the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects of their medications. Additionally, the goals prioritize the reduction of the risk of surgical errors. Hospitals should implement stringent surgical safety protocols to prevent wrong-site, wrong-patient, or wrong-procedure surgeries. Preoperative verification processes, marking the surgical site, and performing "time-outs" before the procedure are important steps to ensure utmost patient safety. Furthermore, the goals stress the importance of communicating critical test results in a timely manner. Healthcare providers must establish effective systems for reporting significant findings to the appropriate personnel promptly. This helps prevent delays in diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Other Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals may include minimizing the risk of pressure ulcers, preventing patient identification errors, reducing the risk of patient harm associated with clinical alarms, and improving communication among healthcare team members. In summary, the Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals encompass a variety of crucial objectives aimed at enhancing patient safety in healthcare facilities across Indiana. These goals address fall prevention, infection control, medication safety, surgical errors' prevention, timely communication of test results, and several other aspects to ensure the highest quality care for patients.
Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest libraries of lawful varieties in America - gives an array of lawful document layouts you can obtain or printing. While using web site, you can get 1000s of varieties for business and individual purposes, categorized by classes, states, or search phrases.You will find the most recent versions of varieties much like the Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals in seconds.
If you currently have a membership, log in and obtain Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals in the US Legal Forms collection. The Download button can look on each type you look at. You have accessibility to all in the past delivered electronically varieties in the My Forms tab of your bank account.
If you would like use US Legal Forms the first time, listed here are basic guidelines to get you started out:
- Be sure to have chosen the proper type for your city/state. Go through the Review button to review the form`s content. Read the type outline to actually have chosen the appropriate type.
- When the type does not satisfy your needs, take advantage of the Look for industry towards the top of the display to find the one which does.
- In case you are content with the form, affirm your option by clicking the Acquire now button. Then, select the prices plan you favor and provide your accreditations to sign up for the bank account.
- Method the deal. Use your credit card or PayPal bank account to perform the deal.
- Select the file format and obtain the form on your own system.
- Make changes. Fill up, revise and printing and indicator the delivered electronically Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
Each template you put into your money does not have an expiry day and is the one you have forever. So, if you would like obtain or printing an additional duplicate, just visit the My Forms section and click about the type you require.
Obtain access to the Indiana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with US Legal Forms, by far the most considerable collection of lawful document layouts. Use 1000s of expert and express-particular layouts that meet your business or individual demands and needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
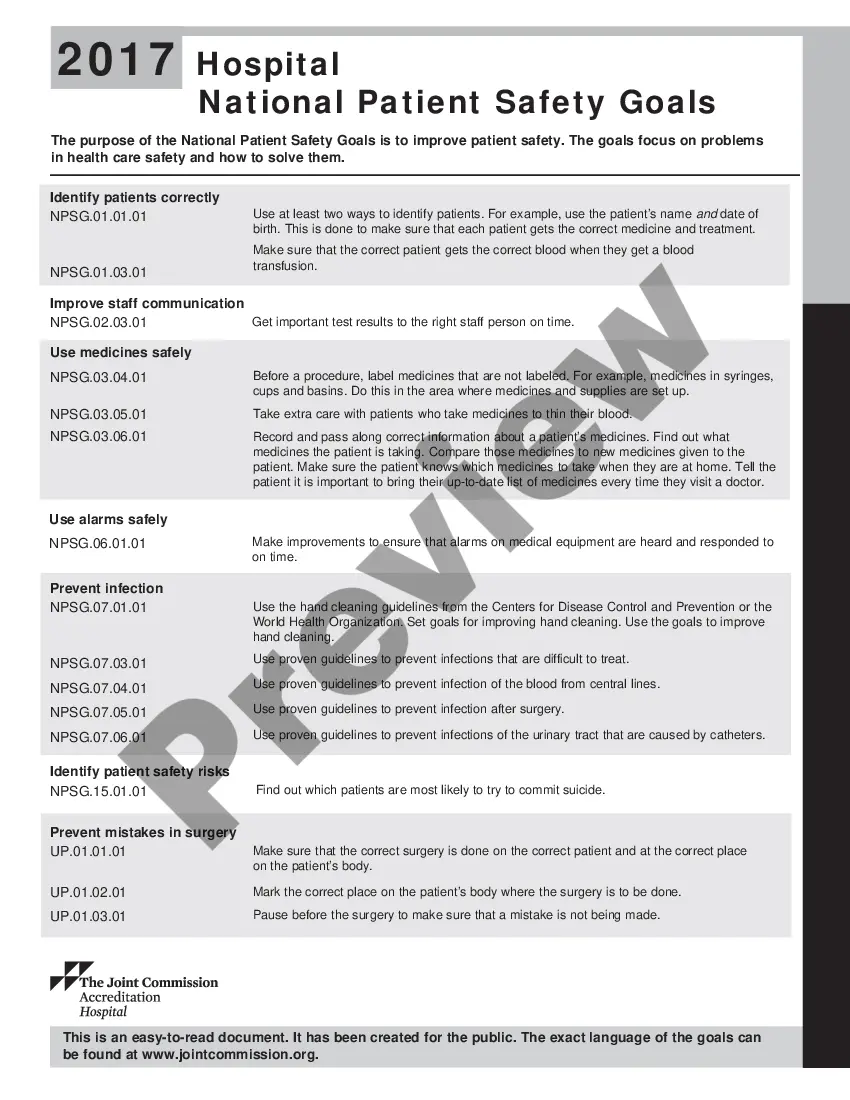
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.09-Aug-2021
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
2022 Joint Commission National Patient Safety Goals1 Identify Patients Correctly.2 Improve Staff Communication.3 Use Medicines Safely.4 Use Alarms Safely.5 Prevent Infection.6 Surgery Verification.04-Jan-2022
01: Improve the safety of clinical alarm systems. Goal 7: Reduce the risk of health care-associated infections. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) hand hygiene guidelines or the current World Health Organization (WHO) hand hygiene guidelines.
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
The purpose of the National Patient Safety Goals is to improve patient safety. The goals focus on problems in health care safety and how to solve them. This is an easy-to-read document. It has been created for the public.