Title: Understanding the Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete: Types and Key Considerations Keywords: Indiana Partnership Agreement, Covenant not to Compete, legal contract, business partnerships, non-compete clause, enforceability, restrictions, assets, dissolution, protection, provisions, competition, terms Introduction: The Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete is a legal contract designed to protect the interests of businesses entering into partnerships within the state. This agreement includes a specific clause, known as a covenant not to compete, which aims to restrict the competitive activities of partners within a specific geographical area and for a defined period after the partnership dissolves. Types of Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete: 1. Comprehensive Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete: This type of partnership agreement encompasses all aspects of the partnership, including management, governance, decision-making, profit sharing, capital contributions, and the covenant not to compete. It provides a comprehensive framework for the partnership's functioning while ensuring the restriction of competitive activities during and after dissolution. 2. Limited Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete: In a limited partnership, there are general partners who manage the business and limited partners who provide capital but aren't involved in managerial decisions. The Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete for limited partnerships specifically outlines the restrictions and obligations of both general and limited partners, ensuring fair competition practices. Key Considerations: 1. Enforceability: Partnership agreements with a covenant not to compete must strike a balance between protecting the partnership's interests and being reasonable in scope. Courts in Indiana carefully evaluate these agreements to determine their enforceability. Hence, it is crucial to ensure the agreement's language, geographic restrictions, and duration of restraint are reasonable to safeguard against potential challenges. 2. Restrictions on Competitive Activities: The covenant not to compete within the Indiana Partnership Agreement prevents partners from engaging in activities that directly compete with the partnership's business. Partners must adhere to the agreed-upon restrictions to preserve the partnership's opportunities, customer base, confidential information, and trade secrets. 3. Protection of Partnership Assets: The partnership agreement should address how partners will handle the partnership's assets in case of dissolution or departure. This ensures that partners do not misuse or compete against the partnership using its assets, intellectual property, clients, or other proprietary information. 4. Dissolution and Restrictive Covenants: When drafting a partnership agreement, it is essential to include provisions that address the covenant not to compete in case of dissolution. These provisions might determine the duration of the restriction, geographic boundaries, whether compensation is provided, and other relevant factors. Clear guidelines will help avoid conflicts between partners during the dissolution process. Conclusion: The Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete encompasses a non-compete clause to safeguard a partnership's interests and prevent unfair competition among partners. It is crucial for partners to understand the types of partnership agreements available and to carefully consider the enforceability of restrictive covenants, the extent of restrictions, and the protection of partnership assets. By drafting a comprehensive agreement, businesses can proactively protect their competitive advantages and ensure a successful partnership.
Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete
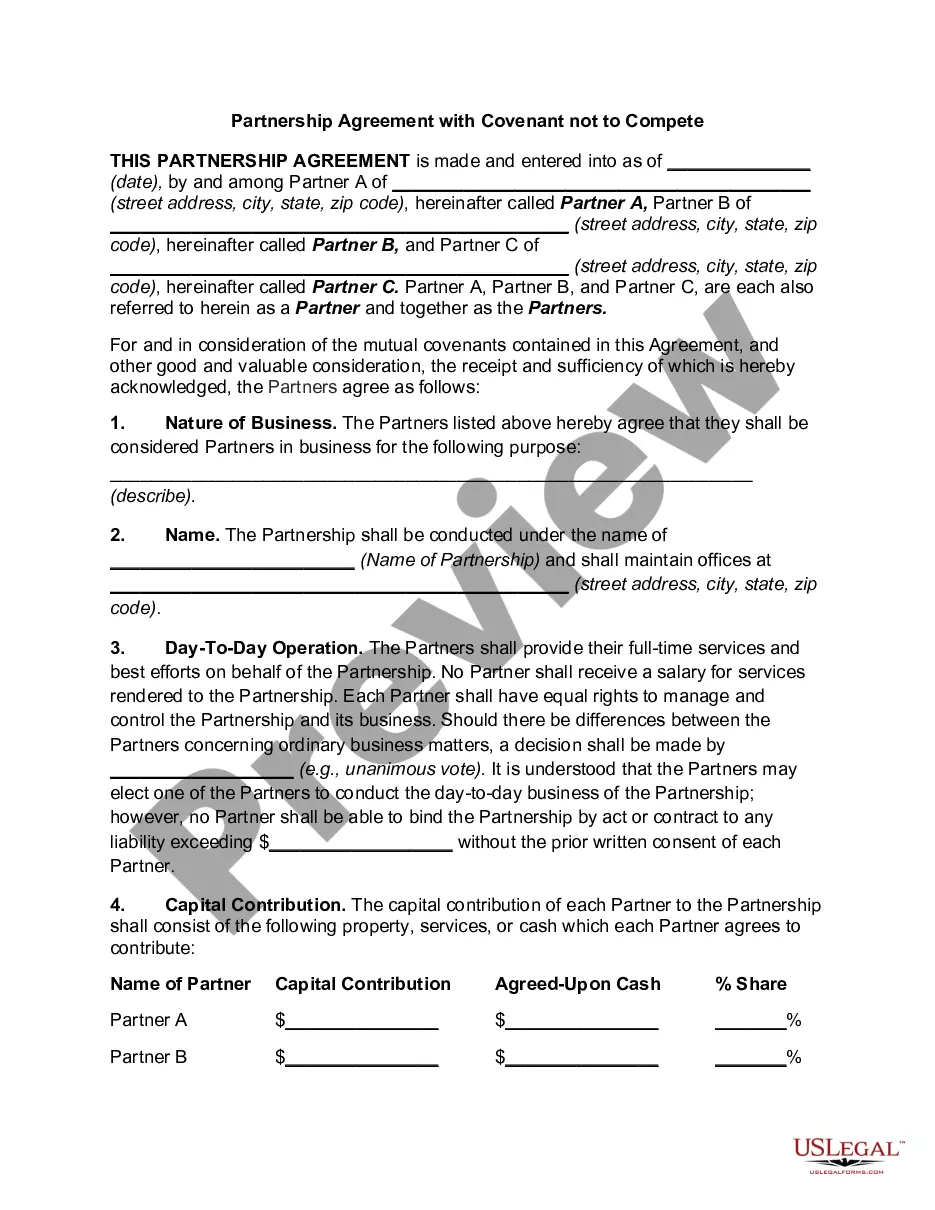
Description
How to fill out Indiana Partnership Agreement With Covenant Not To Compete?
You are able to spend hrs online searching for the authorized record template that fits the federal and state requirements you require. US Legal Forms supplies 1000s of authorized kinds which are reviewed by pros. You can actually download or print out the Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete from my services.
If you have a US Legal Forms profile, you are able to log in and click on the Acquire switch. Afterward, you are able to full, modify, print out, or indicator the Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete. Each authorized record template you get is yours permanently. To get an additional copy associated with a acquired develop, go to the My Forms tab and click on the corresponding switch.
Should you use the US Legal Forms web site the very first time, keep to the easy directions under:
- Very first, make sure that you have selected the best record template for the county/city of your choice. Look at the develop outline to ensure you have selected the proper develop. If accessible, use the Review switch to appear from the record template at the same time.
- If you wish to discover an additional model of the develop, use the Research industry to discover the template that meets your needs and requirements.
- After you have discovered the template you desire, just click Buy now to carry on.
- Select the prices plan you desire, enter your qualifications, and sign up for your account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the deal. You can utilize your charge card or PayPal profile to fund the authorized develop.
- Select the file format of the record and download it in your product.
- Make modifications in your record if necessary. You are able to full, modify and indicator and print out Indiana Partnership Agreement with Covenant not to Compete.
Acquire and print out 1000s of record web templates using the US Legal Forms site, which provides the most important assortment of authorized kinds. Use skilled and condition-specific web templates to handle your organization or individual requires.