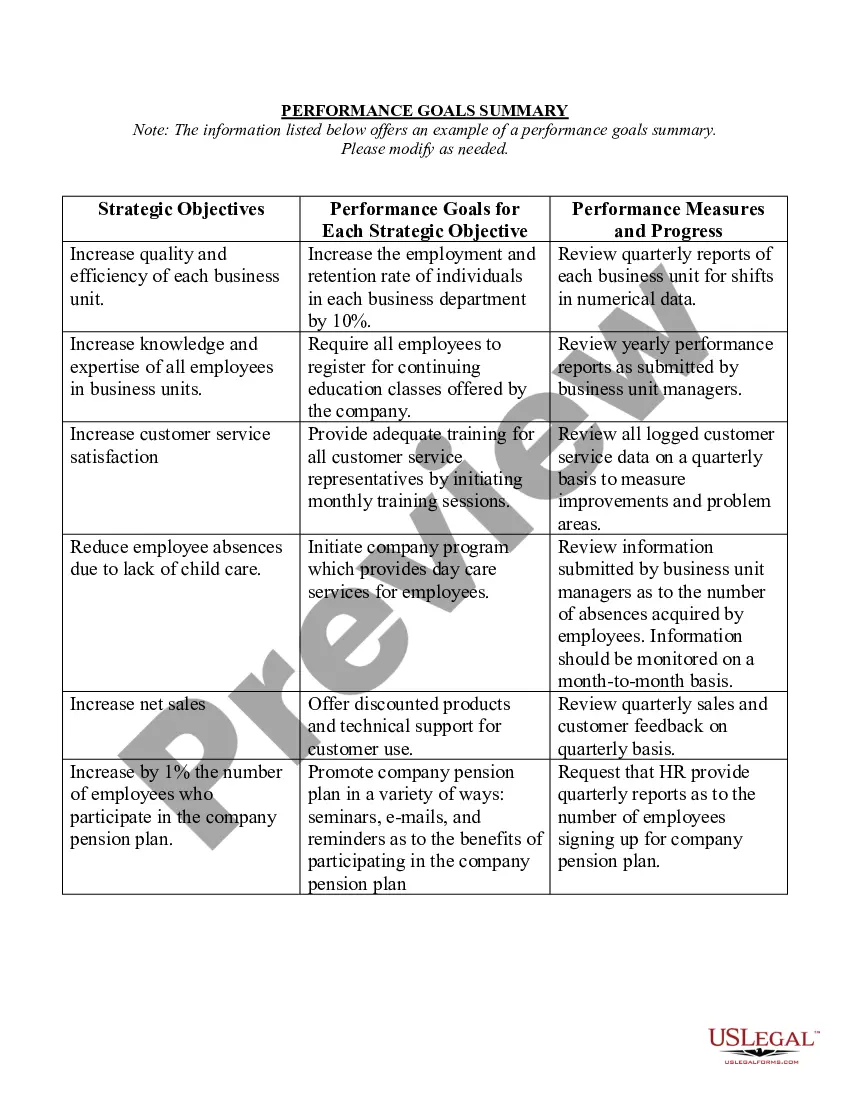
Indiana Jury Instruction - 7.7.1 General Instruction - Comparative Negligence Defense
Description
How to fill out Jury Instruction - 7.7.1 General Instruction - Comparative Negligence Defense?
Are you within a placement the place you need files for either company or individual purposes just about every time? There are plenty of legitimate file layouts available on the Internet, but locating kinds you can trust is not simple. US Legal Forms delivers a large number of develop layouts, such as the Indiana Jury Instruction - 7.7.1 General Instruction - Comparative Negligence Defense, that are published to fulfill federal and state requirements.
If you are already knowledgeable about US Legal Forms internet site and have your account, basically log in. Afterward, you can obtain the Indiana Jury Instruction - 7.7.1 General Instruction - Comparative Negligence Defense format.
Should you not provide an account and want to begin using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Find the develop you need and make sure it is for the proper city/area.
- Utilize the Review switch to check the form.
- See the information to ensure that you have chosen the appropriate develop.
- In case the develop is not what you are looking for, make use of the Lookup discipline to find the develop that meets your needs and requirements.
- Whenever you get the proper develop, click Purchase now.
- Choose the rates program you would like, fill in the desired details to create your bank account, and pay for the transaction utilizing your PayPal or credit card.
- Choose a hassle-free file formatting and obtain your copy.
Locate all the file layouts you have bought in the My Forms food list. You can aquire a extra copy of Indiana Jury Instruction - 7.7.1 General Instruction - Comparative Negligence Defense any time, if needed. Just go through the required develop to obtain or print the file format.
Use US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive selection of legitimate varieties, to save some time and stay away from blunders. The assistance delivers expertly made legitimate file layouts that can be used for an array of purposes. Generate your account on US Legal Forms and begin creating your daily life a little easier.