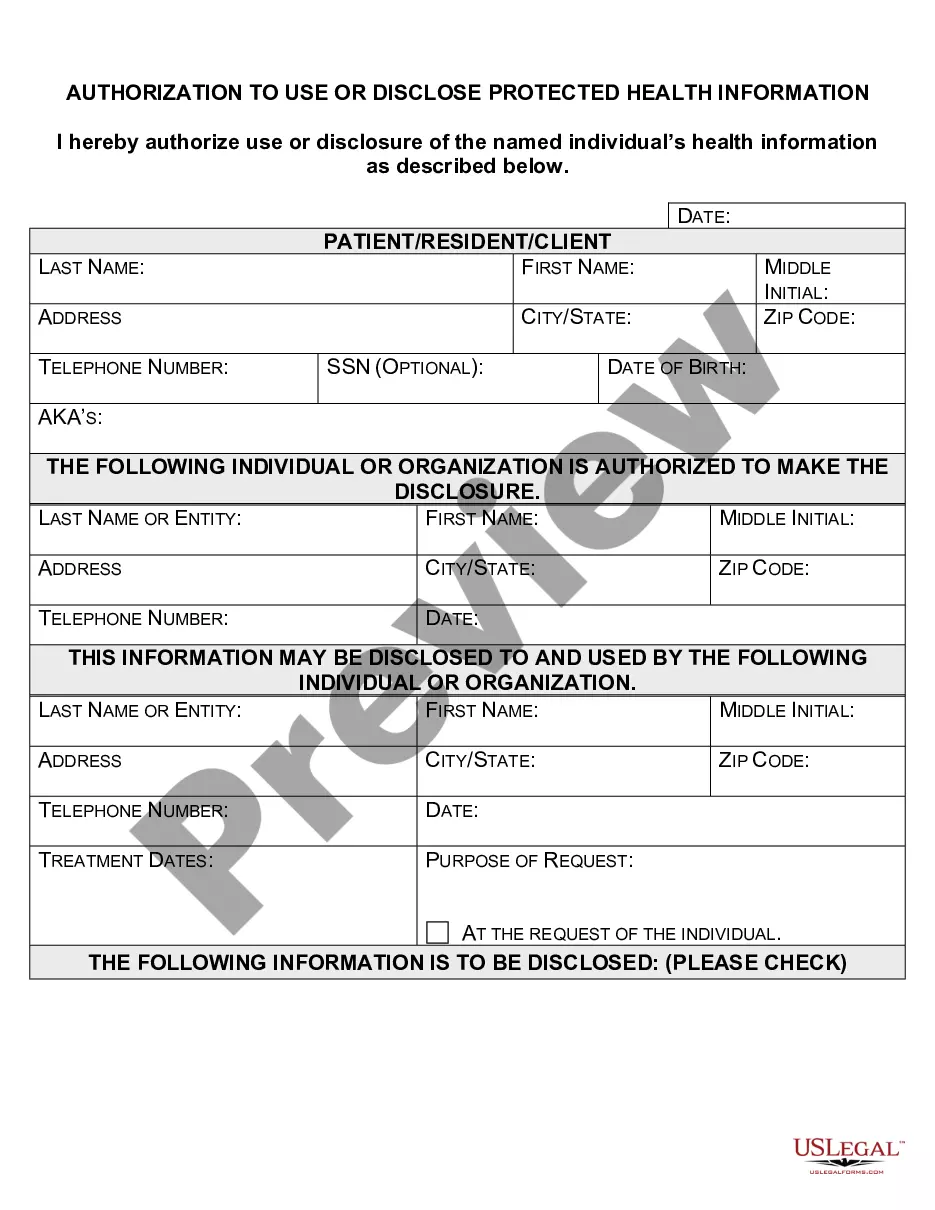
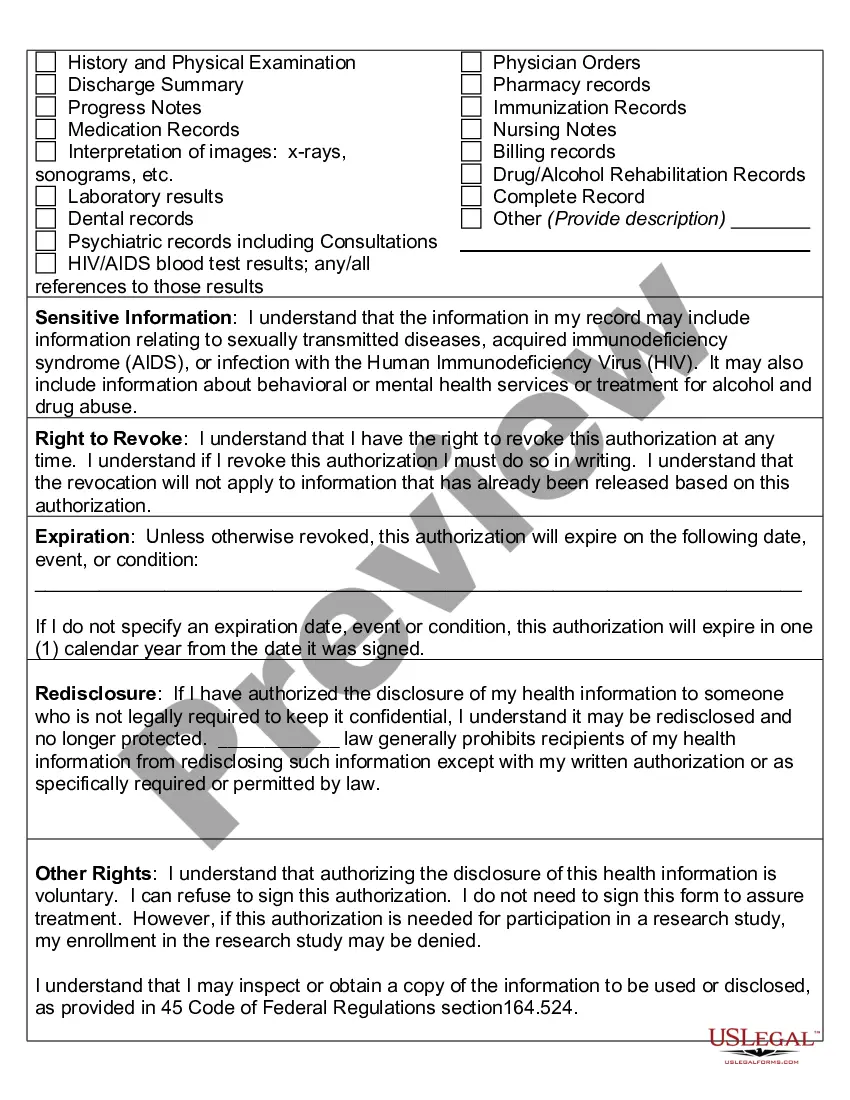
Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information (PHI) is a legal document that grants permission for healthcare providers to share an individual's sensitive medical information with designated parties. This authorization is required under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to ensure the privacy and security of patients' PHI. Keywords: Indiana, Authorization to Use, Authorization to Disclose, Protected Health Information, HIPAA, medical information, sensitive data, healthcare providers, privacy, security There are several types of Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information, depending on the specific purpose and circumstance. Some of these types include: 1. General Authorization: This type of authorization allows healthcare providers to share a patient's PHI for routine purposes, such as treatment, payment, and healthcare operations. It grants broad consent for the use and disclosure of the individual's medical information within the healthcare system. 2. Specific Authorization: Different from a general authorization, this type focuses on a specific purpose or recipient for the disclosure of PHI. For instance, a patient may provide specific authorization for their medical records to be shared with a research institution or a specialist outside their primary healthcare provider. 3. Third-Party Authorization: In certain cases, individuals may authorize the release of their PHI to third parties, such as family members, caregivers, or legal representatives. This type of authorization ensures that designated individuals can access and handle the patient's medical information, often for purposes related to caregiving, guardianship, or obtaining medical records on behalf of the patient. 4. Revocable Authorization: This authorization allows individuals to revoke their consent for the use or disclosure of their PHI at any time. Patients have the right to change their mind and restrict further access to their medical information, except in cases where the provider has already relied on the previous authorization. 5. Research Authorization: In certain cases, individuals may provide explicit authorization for their PHI to be used in research studies or clinical trials. This type of authorization often includes specific details about the research study, purpose, potential risks, and benefits, ensuring that patients are well-informed before their medical information is utilized for research purposes. It is important to note that Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information must comply with HIPAA regulations and other relevant state laws. Failure to obtain proper authorization or mishandling of PHI can result in severe penalties and legal consequences for healthcare providers. These authorizations play a crucial role in maintaining patient privacy while facilitating the appropriate exchange of medical information between authorized parties.
Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information
Description
How to fill out Indiana Authorization To Use Or Disclose Protected Health Information?
Are you currently in a situation that you need to have files for both business or personal uses almost every day time? There are a lot of authorized record templates accessible on the Internet, but discovering ones you can rely on isn`t easy. US Legal Forms provides thousands of kind templates, just like the Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information, that happen to be composed to meet state and federal specifications.
In case you are already familiar with US Legal Forms web site and have an account, just log in. Next, it is possible to down load the Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information format.
Unless you offer an bank account and want to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Get the kind you require and make sure it is for the correct town/state.
- Utilize the Review switch to examine the shape.
- Look at the explanation to ensure that you have chosen the appropriate kind.
- In the event the kind isn`t what you`re looking for, use the Search industry to get the kind that suits you and specifications.
- When you get the correct kind, click Buy now.
- Pick the rates prepare you desire, fill in the specified information and facts to generate your money, and pay money for the transaction using your PayPal or charge card.
- Decide on a convenient document format and down load your backup.
Discover each of the record templates you may have bought in the My Forms food list. You can get a more backup of Indiana Authorization to Use or Disclose Protected Health Information anytime, if possible. Just click the needed kind to down load or printing the record format.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most substantial assortment of authorized kinds, to save lots of time and stay away from mistakes. The services provides professionally produced authorized record templates that you can use for a variety of uses. Create an account on US Legal Forms and initiate generating your life a little easier.