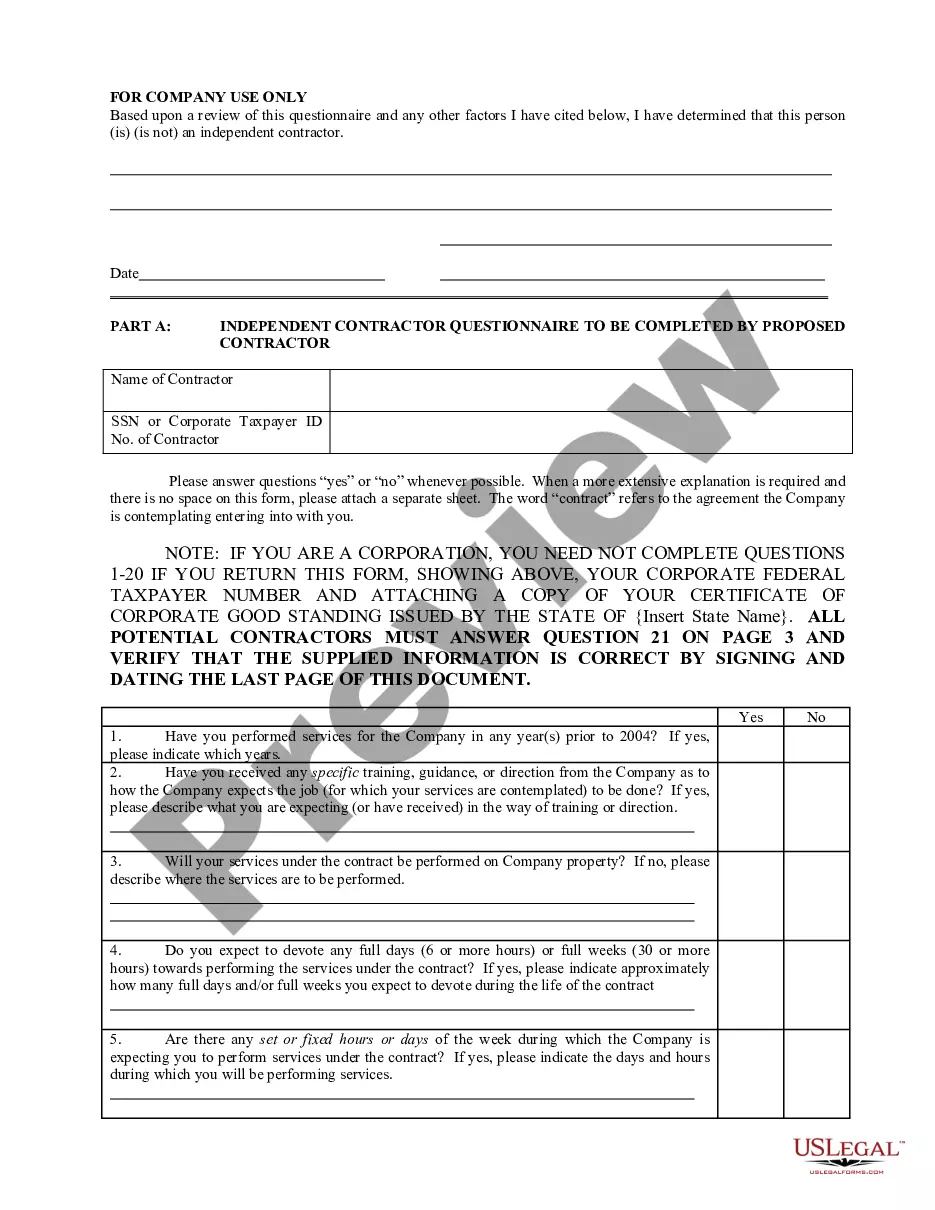
Indiana Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status?
If you require extensive, download, or print legal document templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest repository of legal forms available online.
Make use of the site's straightforward and user-friendly search feature to locate the documents you need.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and states or keywords.
Step 4. Once you have found the form you require, select the Buy now button. Choose the payment plan you prefer and input your credentials to sign up for an account.
Step 5. Process the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the purchase.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to obtain the Indiana Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to find the Indiana Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded in the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Review option to examine the form's content. Don’t forget to read the details.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find other versions of the legal form template.
Form popularity
FAQ
What Is an Independent Contractor? An independent contractor is a self-employed person or entity contracted to perform work foror provide services toanother entity as a nonemployee. As a result, independent contractors must pay their own Social Security and Medicare taxes.
How to demonstrate that you are an independent worker on your resumeMention that time when you had to work on a project on your own.Talk about projects that required extra accountability.Describe times when you had to manage several projects all at once.More items...
A 1099 (Miscellaneous Income) form issued by the business. A narrated conversation with the employer. For FS, self-employed clients can be certified once without income verification. At the time of certification, explain to the client - in writing - that they must begin keeping income records.
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.
Independent contractors are self-employed workers who provide services for an organisation under a contract for services. Independent contractors are not employees and are typically highly skilled, providing their clients with specialist skills or additional capacity on an as needed basis.
How To Become a Licensed Contractor in Indiana. Unlike plumbers, in Indiana contractor licensing is not regulated at the state level. Instead, contractors are required to register or obtain a license through the various municipal governments throughout the state.
Independent contractors doing business in the State of Indiana are required to file a statement and documentation with the Indiana Department of Revenue (DOR) stating independent contractor status. There is a five dollar filing fee and the certificate is valid for one year.
The law defines a worker as an independent contractor if he/she meets the guidelines of the IRS (See statute quote above in section 2). Senate Enrolled Act 576, (Public Law 168), provides that all independent contractors, not just those in the construction trades, may now obtain a clearance certificate.
The basic test for determining whether a worker is an independent contractor or an employee is whether the principal has the right to control the manner and means by which the work is performed.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.