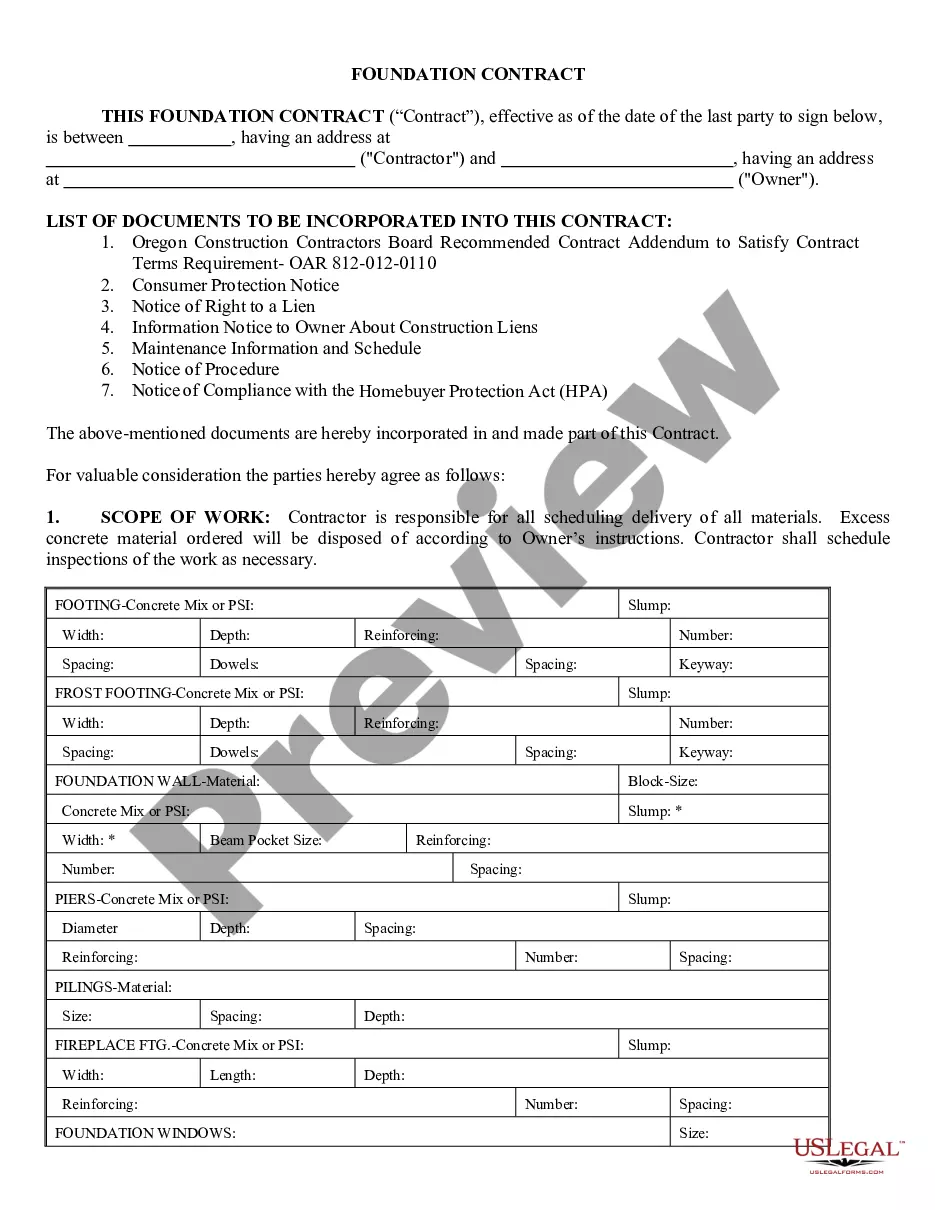
Kansas Assignment of Interest in United States Patent A Kansas Assignment of Interest in United States Patent refers to the legal transfer of ownership of a patent from one party to another, where either the assignor (original owner) or the assignee (new owner) is based in Kansas, a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. This process grants the assignee the rights, title, and interest to the patented invention, allowing them to exclusively utilize, sell, or license the patented technology. An assignment of interest is crucial for inventors, businesses, and investors as it enables the transfer of patent rights and ensures the protection of intellectual property. Keywords: Kansas Assignment of Interest, United States Patent, transfer of ownership, assignor, assignee, patented invention, rights, title, interest, utilize, sell, license, technology, inventors, businesses, investors, intellectual property. Types of Kansas Assignment of Interest in United States Patent: 1. Voluntary Assignment: This type of assignment occurs when the patent owner willingly transfers their rights to another party. It may be a result of a sale, gift, or other contractual agreements between the assignor and assignee. Voluntary assignments are usually carried out to secure financial gains or to allow specialized companies to further develop and commercialize the patented technology. 2. Involuntary Assignment: In some cases, an assignment of interest in a patent may occur involuntarily. This could happen through a court order, bankruptcy proceedings, or as a consequence of a legal dispute. In such cases, the court or relevant authorities may deem it necessary to transfer the patent rights from the assignor to the assignee to settle legal matters or meet financial obligations. 3. Partial Assignment: In a partial assignment, the assignor transfers only a portion of their patent rights to the assignee. This means that both parties will have shared ownership or interest in the patent. The assignor may retain some rights or continue to use the patented technology, while the assignee gains specific rights and benefits associated with the assigned portion. 4. Exclusive Assignment: An exclusive assignment of interest ensures that the assignee receives sole rights and ownership of the patent. This means that the assignor will no longer have any claim or right to the patented invention. The assignee can fully exploit the patent and prevent anyone, including the assignor, from using or benefiting from the patented technology. 5. Non-Exclusive Assignment: In a non-exclusive assignment, the assignor transfers their rights to the assignee while retaining the ability to grant similar rights to other parties. This arrangement allows multiple individuals or organizations to have licenses or rights to use the patented technology, fostering broader dissemination and potential collaborations. 6. Security Assignment: Sometimes, as a form of collateral, a patent owner may assign their patent rights to secure a loan or fulfill other financial obligations. This security assignment allows the lender or creditor to enforce their rights in the patent in case of default or failure to meet the agreed-upon terms. 7. Legal Assignment: A legal assignment occurs when the patent owner passes away, and their rights are transferred in accordance with inheritance laws or a valid will. This ensures a smooth transition of patent ownership to the assigned party or parties, be it an individual or an entity. Keywords: voluntary assignment, involuntary assignment, partial assignment, exclusive assignment, non-exclusive assignment, security assignment, legal assignment, patent rights, shared ownership, sole rights, collateral, inheritance laws, will, court order, bankruptcy proceedings, patent owner.
Kansas Assignment of Interest in United States Patent A Kansas Assignment of Interest in United States Patent refers to the legal transfer of ownership of a patent from one party to another, where either the assignor (original owner) or the assignee (new owner) is based in Kansas, a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. This process grants the assignee the rights, title, and interest to the patented invention, allowing them to exclusively utilize, sell, or license the patented technology. An assignment of interest is crucial for inventors, businesses, and investors as it enables the transfer of patent rights and ensures the protection of intellectual property. Keywords: Kansas Assignment of Interest, United States Patent, transfer of ownership, assignor, assignee, patented invention, rights, title, interest, utilize, sell, license, technology, inventors, businesses, investors, intellectual property. Types of Kansas Assignment of Interest in United States Patent: 1. Voluntary Assignment: This type of assignment occurs when the patent owner willingly transfers their rights to another party. It may be a result of a sale, gift, or other contractual agreements between the assignor and assignee. Voluntary assignments are usually carried out to secure financial gains or to allow specialized companies to further develop and commercialize the patented technology. 2. Involuntary Assignment: In some cases, an assignment of interest in a patent may occur involuntarily. This could happen through a court order, bankruptcy proceedings, or as a consequence of a legal dispute. In such cases, the court or relevant authorities may deem it necessary to transfer the patent rights from the assignor to the assignee to settle legal matters or meet financial obligations. 3. Partial Assignment: In a partial assignment, the assignor transfers only a portion of their patent rights to the assignee. This means that both parties will have shared ownership or interest in the patent. The assignor may retain some rights or continue to use the patented technology, while the assignee gains specific rights and benefits associated with the assigned portion. 4. Exclusive Assignment: An exclusive assignment of interest ensures that the assignee receives sole rights and ownership of the patent. This means that the assignor will no longer have any claim or right to the patented invention. The assignee can fully exploit the patent and prevent anyone, including the assignor, from using or benefiting from the patented technology. 5. Non-Exclusive Assignment: In a non-exclusive assignment, the assignor transfers their rights to the assignee while retaining the ability to grant similar rights to other parties. This arrangement allows multiple individuals or organizations to have licenses or rights to use the patented technology, fostering broader dissemination and potential collaborations. 6. Security Assignment: Sometimes, as a form of collateral, a patent owner may assign their patent rights to secure a loan or fulfill other financial obligations. This security assignment allows the lender or creditor to enforce their rights in the patent in case of default or failure to meet the agreed-upon terms. 7. Legal Assignment: A legal assignment occurs when the patent owner passes away, and their rights are transferred in accordance with inheritance laws or a valid will. This ensures a smooth transition of patent ownership to the assigned party or parties, be it an individual or an entity. Keywords: voluntary assignment, involuntary assignment, partial assignment, exclusive assignment, non-exclusive assignment, security assignment, legal assignment, patent rights, shared ownership, sole rights, collateral, inheritance laws, will, court order, bankruptcy proceedings, patent owner.