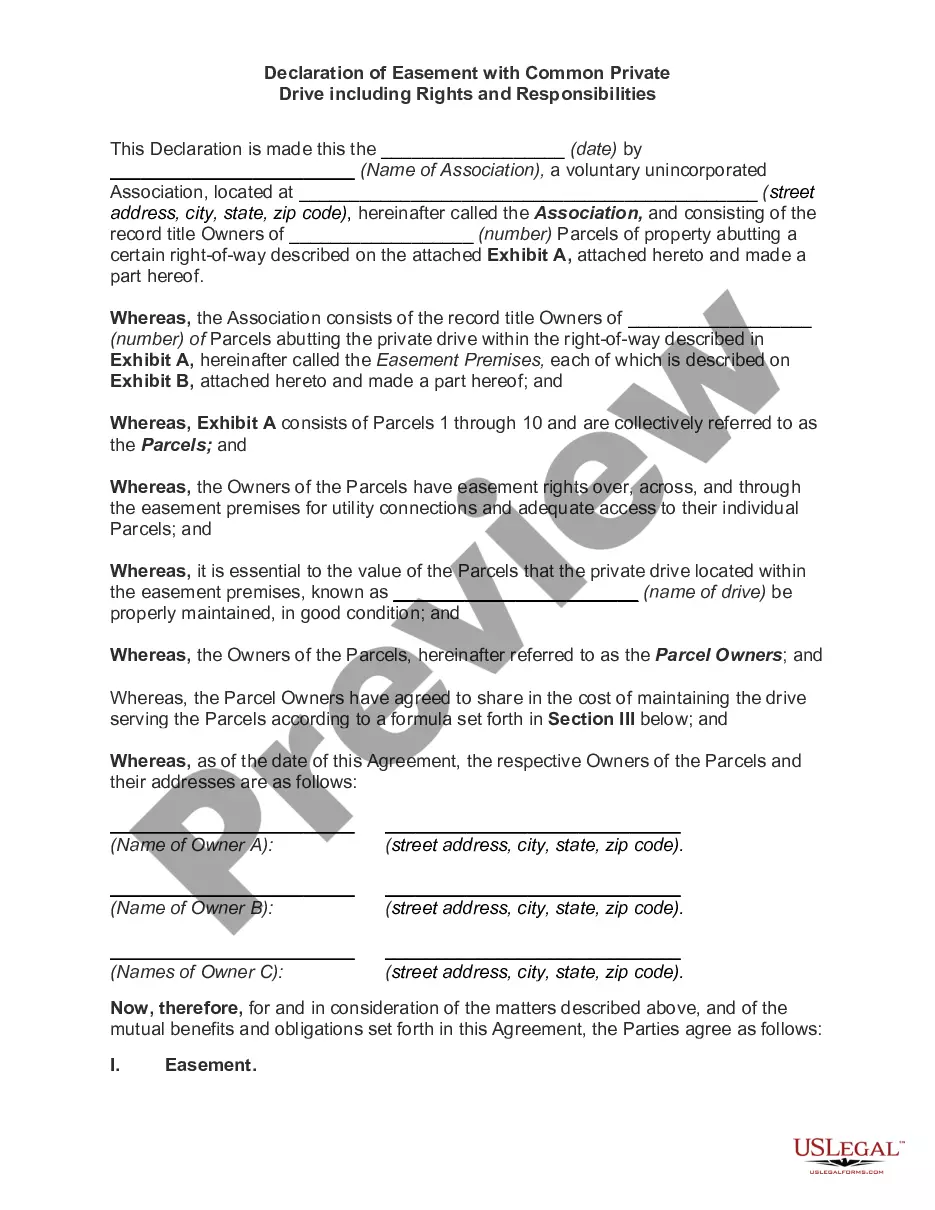
Supervised visitation may be ordered by a court where the non-custodial parent:
" has a drug or alcohol abuse problem;
" has had trouble controlling anger;
" may have been involved in inappropriate sexual behavior with the child;
" engaged in child abuse, neglect or abandonment;
" engaged in domestic violence;
" has a mental illness;
" has a substance abuse problem; and/or
" as a criminal history.
The above list is not exhaustive, but gives examples of situations where a court might order supervised visitation.
Supervised visitation often takes place in a neutral location under the supervision of paid staff. An adult other than the custodial parent must be present at all times during the visit. The adult may be known or unknown to the child, and may be someone agreed upon by the parents or appointed by the court. In any case, the adult must be approved by the court ordering the supervised visitation.
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.
Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitation is a legal document used when a parent or custodian seeks to request supervised visitation in child custody cases. This motion highlights the importance of protective measures to ensure the safety and well-being of the child during visitation periods. The Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitations allows the party filing the motion to present evidence and provide strong reasons as to why supervised visitation is necessary. By filing this motion, the concerned party acknowledges that the noncustodial parent or another person seeking visitation poses a potential risk or danger to the child's physical, emotional, or mental health. The keywords relevant to this topic include: 1. Kansas: Refers to the state jurisdiction where the motion is being filed. 2. Motion: Denotes the legal action taken by a party to request a specific order from the court. 3. Supervised visitations: The specific type of visitation arrangement in which the noncustodial parent's time with the child is closely monitored by a neutral third party or professional. 4. Child custody: The main context within which this motion is filed, as it pertains to the care, control, and guardianship of a child. 5. Custodian: The person who holds legal custody of the child, usually the parent awarded physical custody or a legal guardian. 6. Protective measures: Refers to precautions taken to ensure the child's safety while in the presence of the noncustodial parent or other visitation-seeking individuals. 7. Well-being: Focuses on the overall welfare and best interest of the child, including their physical, emotional, and mental health. 8. Evidence: Refers to documents or testimonies supporting the allegations or claims stated in the motion. In addition to the generic Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitations, there may be different types or variations of this motion, such as: 1. Emergency Motion for Supervised Visitation: Filed in urgent situations where there is an immediate risk to the child's well-being, warranting immediate supervised visitation. 2. Modification Motion for Supervised Visitation: Requesting a change or modification to an existing visitation arrangement to include supervised visitation due to new concerns or circumstances. 3. Termination Motion for Supervised Visitation: Seeking to terminate or discontinue supervised visitation, usually when the noncustodial parent has demonstrated significant improvement or shown evidence of rehabilitation, reducing potential risks to the child. It is important to consult with a legal professional or attorney when filing a Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitations, as laws and procedures may vary, and personalized guidance is crucial for the best outcome in child custody matters.
Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitation is a legal document used when a parent or custodian seeks to request supervised visitation in child custody cases. This motion highlights the importance of protective measures to ensure the safety and well-being of the child during visitation periods. The Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitations allows the party filing the motion to present evidence and provide strong reasons as to why supervised visitation is necessary. By filing this motion, the concerned party acknowledges that the noncustodial parent or another person seeking visitation poses a potential risk or danger to the child's physical, emotional, or mental health. The keywords relevant to this topic include: 1. Kansas: Refers to the state jurisdiction where the motion is being filed. 2. Motion: Denotes the legal action taken by a party to request a specific order from the court. 3. Supervised visitations: The specific type of visitation arrangement in which the noncustodial parent's time with the child is closely monitored by a neutral third party or professional. 4. Child custody: The main context within which this motion is filed, as it pertains to the care, control, and guardianship of a child. 5. Custodian: The person who holds legal custody of the child, usually the parent awarded physical custody or a legal guardian. 6. Protective measures: Refers to precautions taken to ensure the child's safety while in the presence of the noncustodial parent or other visitation-seeking individuals. 7. Well-being: Focuses on the overall welfare and best interest of the child, including their physical, emotional, and mental health. 8. Evidence: Refers to documents or testimonies supporting the allegations or claims stated in the motion. In addition to the generic Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitations, there may be different types or variations of this motion, such as: 1. Emergency Motion for Supervised Visitation: Filed in urgent situations where there is an immediate risk to the child's well-being, warranting immediate supervised visitation. 2. Modification Motion for Supervised Visitation: Requesting a change or modification to an existing visitation arrangement to include supervised visitation due to new concerns or circumstances. 3. Termination Motion for Supervised Visitation: Seeking to terminate or discontinue supervised visitation, usually when the noncustodial parent has demonstrated significant improvement or shown evidence of rehabilitation, reducing potential risks to the child. It is important to consult with a legal professional or attorney when filing a Kansas Motion for Supervised Visitations, as laws and procedures may vary, and personalized guidance is crucial for the best outcome in child custody matters.