Kansas Term Sheet - Convertible Debt Financing
Description
To become an accredited investor the (SEC) requires certain wealth, income or knowledge requirements. The investor must fall into one of three categories. Firms selling unregistered securities must put investors through their own screening process to determine if investors can be considered an accredited investor.
The Verifying Individual or Entity should take reasonable steps to verify and determined that an Investor is an "accredited investor" as such term is defined in Rule 501 of the Securities Act, and hereby provides written confirmation. This letter serves to help the Entity determine status."
How to fill out Term Sheet - Convertible Debt Financing?
If you have to total, download, or produce legitimate file web templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest collection of legitimate kinds, which can be found on the Internet. Utilize the site`s basic and practical lookup to find the papers you will need. A variety of web templates for enterprise and specific purposes are sorted by classes and says, or search phrases. Use US Legal Forms to find the Kansas Term Sheet - Convertible Debt Financing with a couple of clicks.
If you are previously a US Legal Forms customer, log in to your accounts and click the Acquire switch to get the Kansas Term Sheet - Convertible Debt Financing. You can even entry kinds you previously saved inside the My Forms tab of your own accounts.
Should you use US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions under:
- Step 1. Make sure you have chosen the shape for the proper city/land.
- Step 2. Use the Review choice to examine the form`s content. Do not forget about to learn the outline.
- Step 3. If you are unsatisfied together with the form, utilize the Research industry on top of the display to discover other types in the legitimate form web template.
- Step 4. Once you have discovered the shape you will need, click the Acquire now switch. Opt for the costs prepare you like and add your credentials to register for an accounts.
- Step 5. Approach the purchase. You may use your bank card or PayPal accounts to accomplish the purchase.
- Step 6. Choose the format in the legitimate form and download it on your system.
- Step 7. Comprehensive, revise and produce or indication the Kansas Term Sheet - Convertible Debt Financing.
Every single legitimate file web template you purchase is the one you have for a long time. You possess acces to each and every form you saved inside your acccount. Go through the My Forms area and pick a form to produce or download once again.
Compete and download, and produce the Kansas Term Sheet - Convertible Debt Financing with US Legal Forms. There are many professional and status-particular kinds you can utilize for the enterprise or specific demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
Convertible Note - Reporting Requirements FIRC and KYC of the non-resident investor. Name and address of the investor and AD bank. Copy of MOA / AOA. Certificate of Incorporation. Startup Registration Certificate. Certificate from Practising Company Secretary.
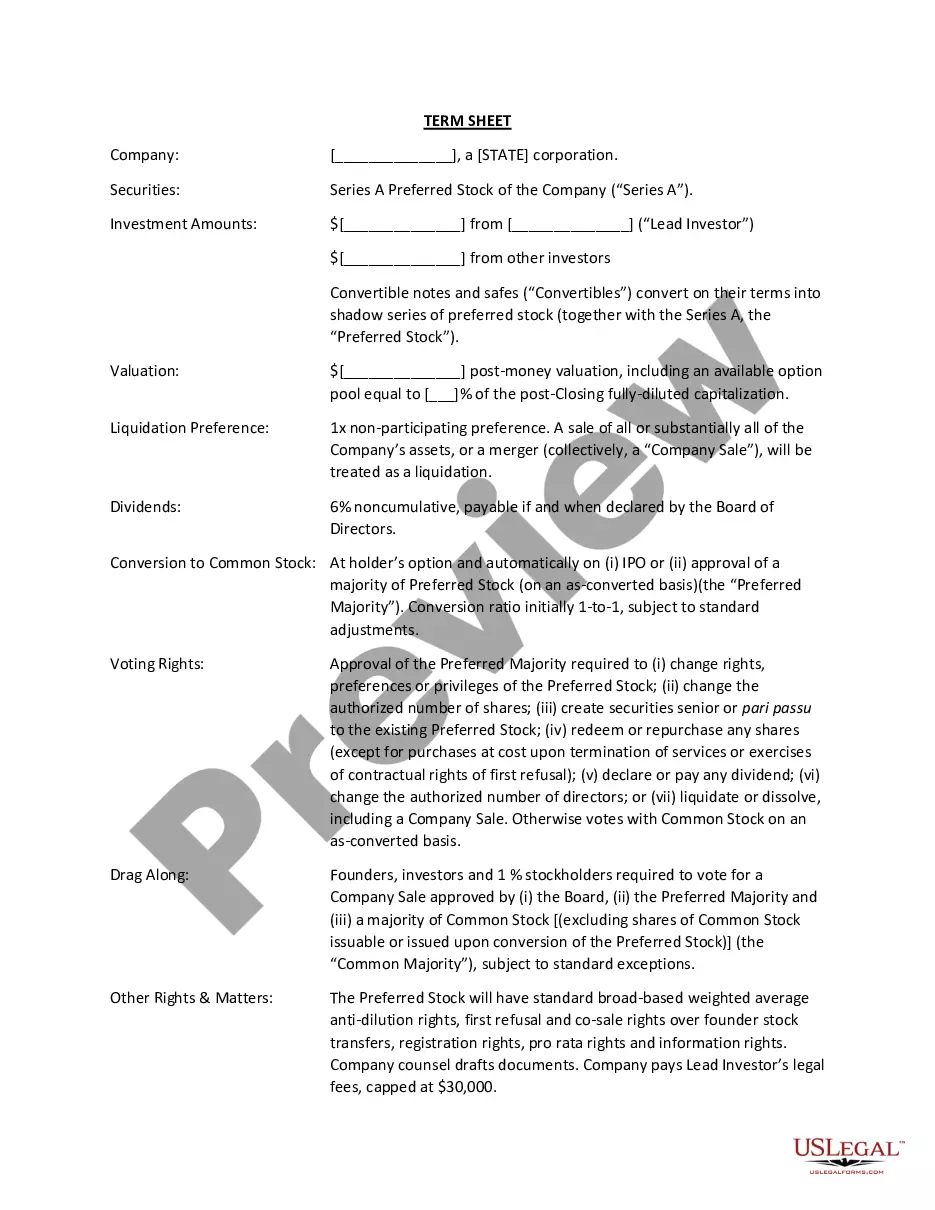
A term sheet is usually a non-binding agreement outlining the basic terms and conditions of the investment. It serves as a template for the convertible note for both parties.
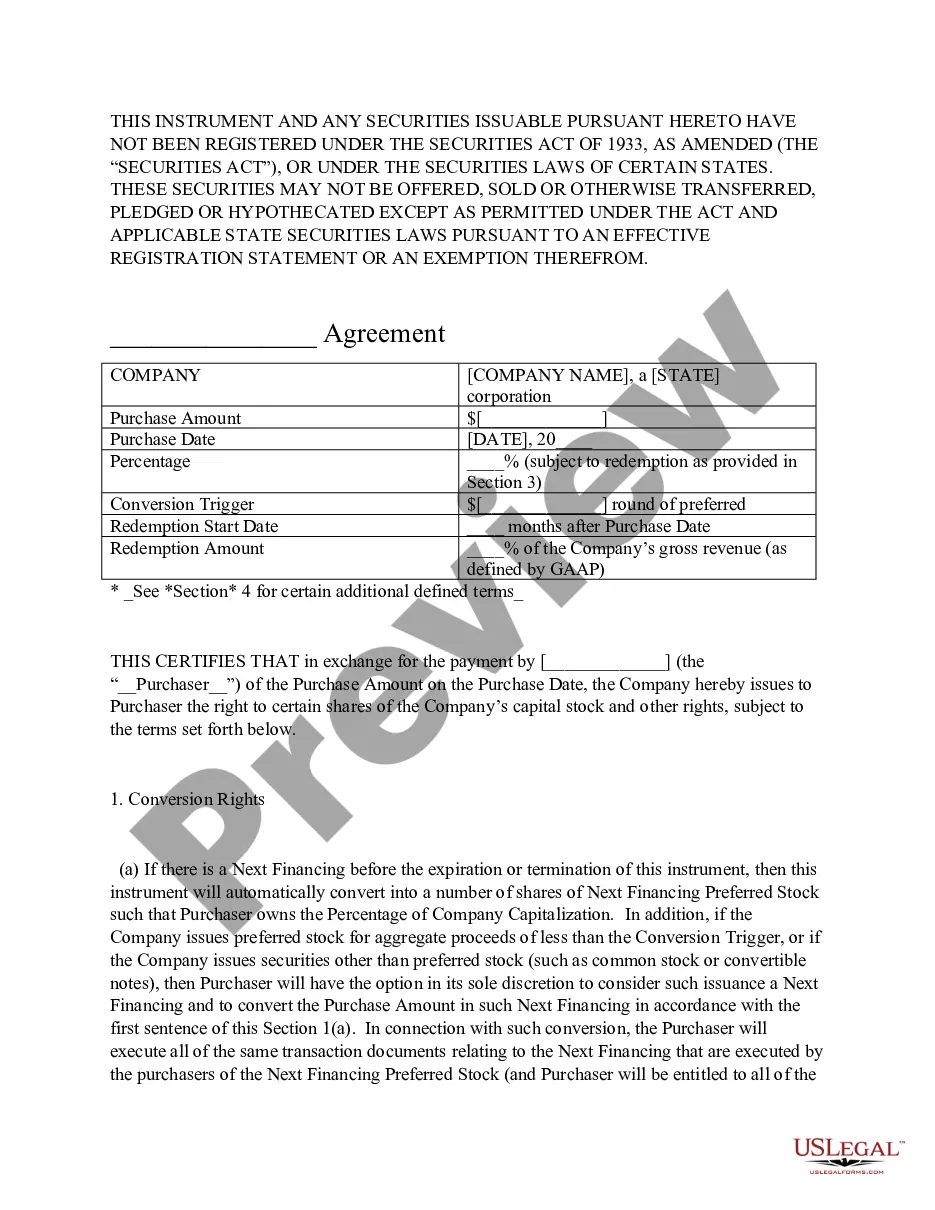
Convertible debt is a debt hybrid product with an embedded option that allows the holder to convert the debt into equity in the future. The ratio is calculated by dividing the convertible security's par value by the conversion price of equity.
For tax purposes, the tax basis of the convertible debt is the entire proceeds received at issuance of the debt. Thus, the book and tax bases of the convertible debt are different. ASC 740-10-55-51 addresses whether a deferred tax liability should be recognized for that basis difference.
The Minimum amount of Investment required is Rs 25 lakhs. CCD'S can be issued at any amount. There is no minimum amount criteria. Convertible Notes can be issued without prior valuation.
Convertible Notes are loans ? so they are recorded on the Balance Sheet of a company as a liability when they are made. Depending on the debt's maturity date, they can either be shown as a current liability (loans maturing within 12 months) or as a Long-term liability (loans maturing over 12 months).
Although it is customary to forego a term sheet, in some cases it may be required if the parties need to negotiate certain terms. It can be advantageous to use a term sheet for the company to easily summarize the terms of the notes for potential other investors purchasing a convertible note.
Typical terms of convertible notes are: interest rate, maturity date, conversion provisions, a conversion discount, and a valuation cap.