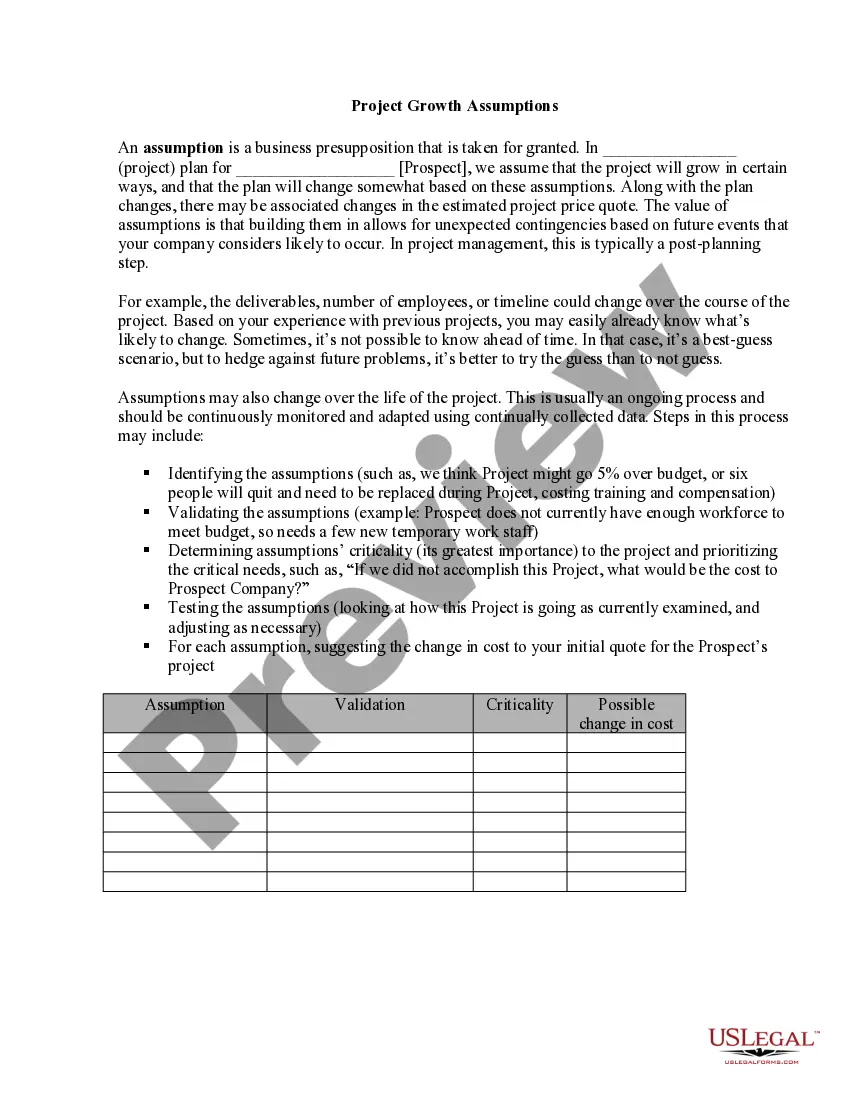
Emancipation is when a minor has achieved independence from his or her parents, such as by getting married before reaching age 18 or by becoming fully self-supporting. It may be possible for a child to petition a court for emancipation to free the minor child from the control of parents and allow the minor to live on his/her own or under the control of others. It usually applies to adolescents who leave the parents' household by agreement or demand.
Some of the most common methods for a minor to become emancipated include marriage, reaching the age of majority, entering military service, or by court order. A parent may also formally or informally agree to give up some or all of his/her parental control. For example, a parent might consent to allowing a child to establish a separate household. In other cases, a parent may force the minor to leave and support him/herself. Generally, parental consent is required, except in cases of parental misconduct that causes the minor to leave the home.
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.
In Kentucky, the Consent of Emancipated Minor for Medical Care refers to a legal document that allows minors who have been deemed legally emancipated to provide their own consent for medical treatment and make healthcare decisions without requiring the involvement of their parents or legal guardians. Emancipated minors are individuals who have obtained legal independence from their parents or guardians before reaching the age of majority. Kentucky recognizes two primary types of emancipation: general emancipation and partial emancipation. General emancipation refers to a situation where the minor is completely freed from their parents' control and responsibilities. This status grants them certain legal rights and responsibilities, including the ability to provide consent for medical care. Partial emancipation, on the other hand, grants the minor certain specific rights and responsibilities while still remaining under the guardianship or control of their parents or legal guardians. The ability to provide consent for medical care may be one such right granted under partial emancipation. When an emancipated minor seeks medical care, Kentucky law acknowledges their autonomy in making healthcare decisions. This includes the right to consent or refuse medical treatments, surgeries, procedures, and medications. The Consent of Emancipated Minor for Medical Care document provides healthcare providers with legal evidence that the minor is competent to make these decisions. The document typically includes the following information: the minor's full name, date of birth, and address; a statement confirming the minor's emancipated status; a statement clarifying that the minor assumes sole responsibility for their medical care decisions; an acknowledgement that the healthcare provider(s) may rely upon the minor's consent without seeking parental or guardian authorization; and the date and signatures of the minor and a witness. It's important to note that while this consent allows emancipated minors to exercise their rights in medical decision-making, certain exceptions exist. In cases where a minor's health or life is at risk, healthcare providers may still involve parents or guardians in the decision-making process, despite the minor's emancipated status. In summary, the Kentucky Consent of Emancipated Minor for Medical Care empowers legally emancipated minors to independently make substantial healthcare decisions without parental or guardian involvement. The different types of emancipation recognized in Kentucky are general emancipation and partial emancipation, each conferring varying degrees of independence and rights to the minor. By offering legal proof of their emancipated status, this consent allows minors to exercise their medical decision-making autonomy, ensuring their healthcare needs are met.In Kentucky, the Consent of Emancipated Minor for Medical Care refers to a legal document that allows minors who have been deemed legally emancipated to provide their own consent for medical treatment and make healthcare decisions without requiring the involvement of their parents or legal guardians. Emancipated minors are individuals who have obtained legal independence from their parents or guardians before reaching the age of majority. Kentucky recognizes two primary types of emancipation: general emancipation and partial emancipation. General emancipation refers to a situation where the minor is completely freed from their parents' control and responsibilities. This status grants them certain legal rights and responsibilities, including the ability to provide consent for medical care. Partial emancipation, on the other hand, grants the minor certain specific rights and responsibilities while still remaining under the guardianship or control of their parents or legal guardians. The ability to provide consent for medical care may be one such right granted under partial emancipation. When an emancipated minor seeks medical care, Kentucky law acknowledges their autonomy in making healthcare decisions. This includes the right to consent or refuse medical treatments, surgeries, procedures, and medications. The Consent of Emancipated Minor for Medical Care document provides healthcare providers with legal evidence that the minor is competent to make these decisions. The document typically includes the following information: the minor's full name, date of birth, and address; a statement confirming the minor's emancipated status; a statement clarifying that the minor assumes sole responsibility for their medical care decisions; an acknowledgement that the healthcare provider(s) may rely upon the minor's consent without seeking parental or guardian authorization; and the date and signatures of the minor and a witness. It's important to note that while this consent allows emancipated minors to exercise their rights in medical decision-making, certain exceptions exist. In cases where a minor's health or life is at risk, healthcare providers may still involve parents or guardians in the decision-making process, despite the minor's emancipated status. In summary, the Kentucky Consent of Emancipated Minor for Medical Care empowers legally emancipated minors to independently make substantial healthcare decisions without parental or guardian involvement. The different types of emancipation recognized in Kentucky are general emancipation and partial emancipation, each conferring varying degrees of independence and rights to the minor. By offering legal proof of their emancipated status, this consent allows minors to exercise their medical decision-making autonomy, ensuring their healthcare needs are met.