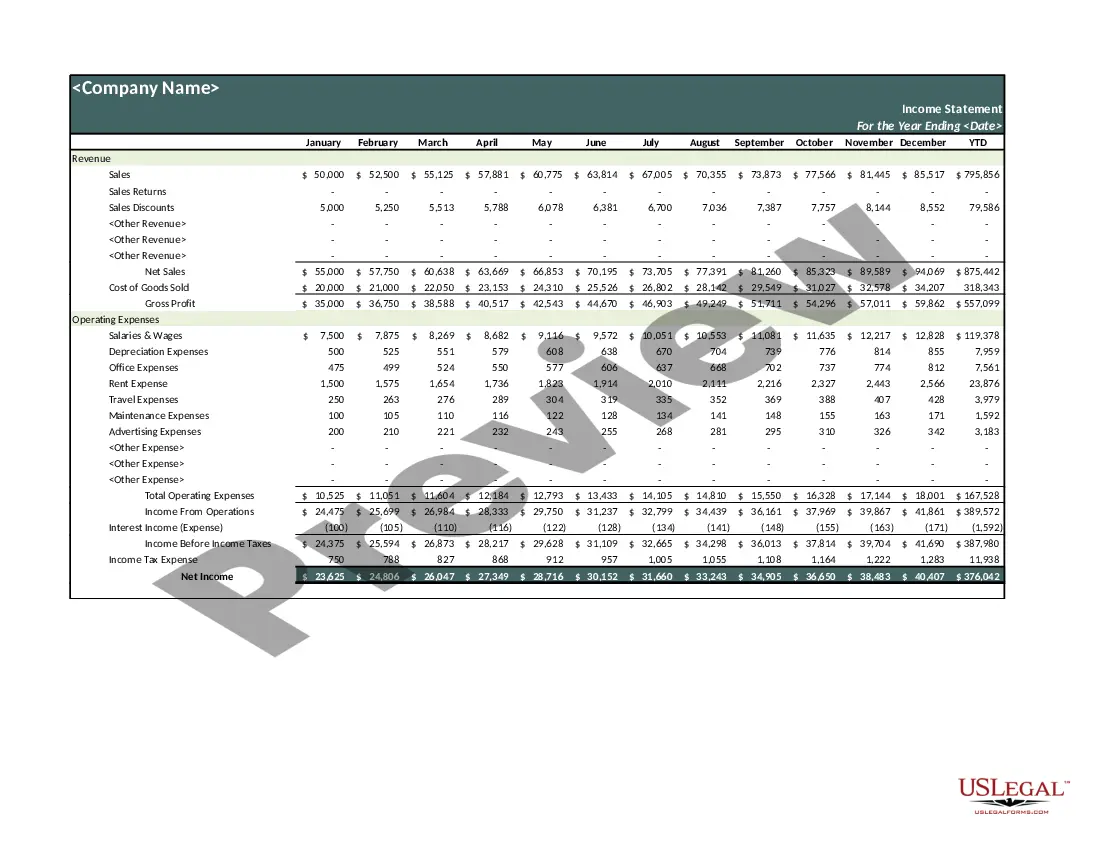
An income statement (sometimes called a profit and loss statement) lists your revenues and expenses, and tells you the profit or loss of your business for a given period of time. You can use this income statement form as a starting point to create one yourself.
Kentucky Income Statement
Description
How to fill out Income Statement?
Selecting the ideal official document format could be a challenge.
Clearly, there are numerous templates available online, but how will you locate the official document you need.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to access the Kentucky Income Statement.
- The service offers thousands of templates, including the Kentucky Income Statement, which you can use for commercial and personal purposes.
- All of the forms are reviewed by experts and comply with state and federal regulations.
Form popularity
FAQ
The primary sources of income for Kentucky residents include agriculture, manufacturing, and healthcare services. These industries contribute significantly to the state's economic landscape. When preparing your Kentucky Income Statement, consider how your earnings from these sectors reflect your financial situation.
An official income statement, often referred to as a tax return, summarizes an individual's income and tax obligations for a specific period. For Kentucky residents, this formal document is crucial for reporting earnings and ensuring compliance with state tax laws. Utilizing a Kentucky Income Statement will guide you through this process with clarity and confidence.
The latest tax law in Kentucky includes provisions for both individual and corporate taxation. Recent reforms may affect tax rates, brackets, and deductions. It's beneficial to consult resources like the Kentucky Income Statement to comprehend how these changes impact your financial responsibilities.
There are ongoing discussions around tax reforms in Kentucky, but officials have not confirmed plans to eliminate the state income tax. Changes can happen, so keep an eye on legislative updates that may affect your Kentucky Income Statement. Staying informed can help you navigate any shifts in tax policies.
As of now, Kentucky is not eliminating its state income tax. However, lawmakers continue to discuss potential reforms that could alter tax structures in the future. Monitoring these developments is essential for anyone completing their Kentucky Income Statement.
The Kentucky 740 form is the primary state income tax return form used by residents of Kentucky. It is crucial for reporting income, claiming deductions, and calculating tax liabilities. By filling out this form accurately, you ensure that your Kentucky Income Statement reflects your financial activities for the year.
Several states have discussed reducing or eliminating their income tax, but Kentucky is not among them at this time. Legislative discussions do evolve, so it is worthwhile to stay informed about potential changes and their implications for the Kentucky Income Statement. Keeping informed allows you to adjust your financial plans accordingly.
Kentucky does have a state income tax, though it is often confused with states that do not impose such a tax. The tax rate is structured with multiple brackets, meaning your tax obligation varies based on your income level. Understanding your obligations through the Kentucky Income Statement can help you in accurately calculating what you owe.
Yes, Kentucky provides specific state income tax forms for residents, mainly the KY 740 form. This form is essential for filing your state taxes based on information from your Kentucky Income Statement. Ensure you have the correct documentation to facilitate a smooth filing process.
Opening an income statement can refer to either accessing a digital document or creating one for your financial reporting. For digital income statements, check your email for attachments or access them on financial websites. If you’re creating a Kentucky Income Statement, consider using USLegalForms, where you can find templates to guide you.