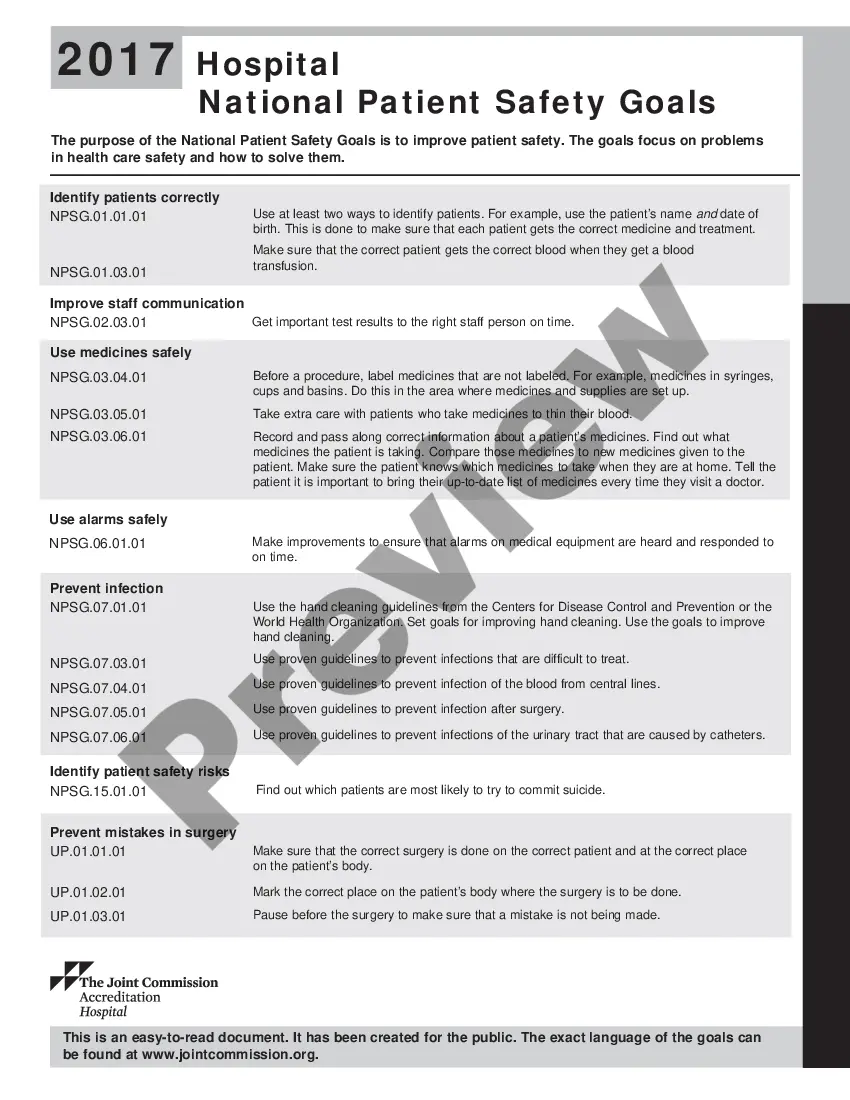
Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being and safety of patients receiving medical care in hospitals across the state. These goals are established by various healthcare organizations and regulatory bodies to improve patient outcomes and minimize potential risks and errors. The primary objective of the Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals is to standardize the delivery of healthcare services and address potential areas of concern in clinical practice. By implementing these goals, healthcare providers can identify and prioritize patient safety initiatives to enhance the overall quality of care. Some important keywords related to the Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals include: 1. Patient safety: Emphasizing the protection of patients from any harm or potential risks during their healthcare journey. 2. Standardization: Implementing uniform processes, protocols, and best practices across all healthcare facilities in Kentucky to ensure consistent and reliable patient care. 3. Quality improvement: Focusing on continuous enhancement of healthcare services through data analysis, risk assessment, and process optimization. 4. Medical errors: Identifying, preventing, and mitigating any preventable mistakes or adverse events that may occur during patient care. 5. Regulatory bodies: Organizations like the Kentucky Department for Public Health (KPH) and The Joint Commission (TJC) as key entities responsible for setting the patient safety goals. 6. Risk management: Developing strategies and protocols to identify potential hazards and mitigate risks related to patient care. 7. Communication: Promoting effective and clear communication among healthcare teams, patients, and family members to ensure appropriate care coordination and avoid misunderstandings. 8. Medication safety: Ensuring the safe and accurate administration, storage, and labeling of medications to prevent medication errors and adverse drug events. 9. Infection control: Implementing measures to prevent and control healthcare-associated infections within healthcare facilities. 10. Identifying patient correctly: Implementing protocols to verify the correct patient identity to prevent identification, wrong treatments, or procedures. 11. Fall prevention: Implementing strategies to reduce the risk of patient falls within hospitals and providing necessary support and interventions for those at high risk. 12. Care transitions: Ensuring safe and effective patient hand-offs during care transitions, such as admission, discharge, or transfer between healthcare facilities or personnel. 13. Alarm safety: Developing policies and protocols to manage and reduce alarm fatigue, ensuring that healthcare staff respond appropriately to alarms without becoming desensitized. 14. Access to information: Ensuring timely access to accurate patient information, diagnostic reports, and test results to facilitate informed decision-making by healthcare providers. It is important to note that the specific goals may vary depending on the healthcare organization or regulatory body. However, the overall aim remains consistent — to create a culture of patient safety and continuous improvement within Kentucky hospitals.
Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Finding the right authorized papers format can be a have a problem. Needless to say, there are a variety of templates available online, but how do you get the authorized develop you need? Make use of the US Legal Forms website. The support delivers a large number of templates, such as the Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, that you can use for company and personal demands. All the kinds are checked out by pros and meet up with state and federal specifications.
When you are presently registered, log in in your account and click on the Obtain option to have the Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Utilize your account to search with the authorized kinds you may have purchased earlier. Visit the My Forms tab of your respective account and obtain one more copy of your papers you need.
When you are a whole new user of US Legal Forms, listed here are straightforward directions that you should comply with:
- Initially, be sure you have chosen the proper develop for the metropolis/county. You may check out the shape using the Preview option and look at the shape explanation to ensure this is the right one for you.
- In the event the develop is not going to meet up with your preferences, use the Seach field to find the appropriate develop.
- Once you are positive that the shape is suitable, click on the Buy now option to have the develop.
- Opt for the costs prepare you need and type in the necessary details. Build your account and pay for an order using your PayPal account or credit card.
- Pick the document file format and acquire the authorized papers format in your device.
- Complete, modify and print out and indication the received Kentucky Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
US Legal Forms will be the greatest catalogue of authorized kinds in which you will find numerous papers templates. Make use of the company to acquire expertly-produced paperwork that comply with express specifications.