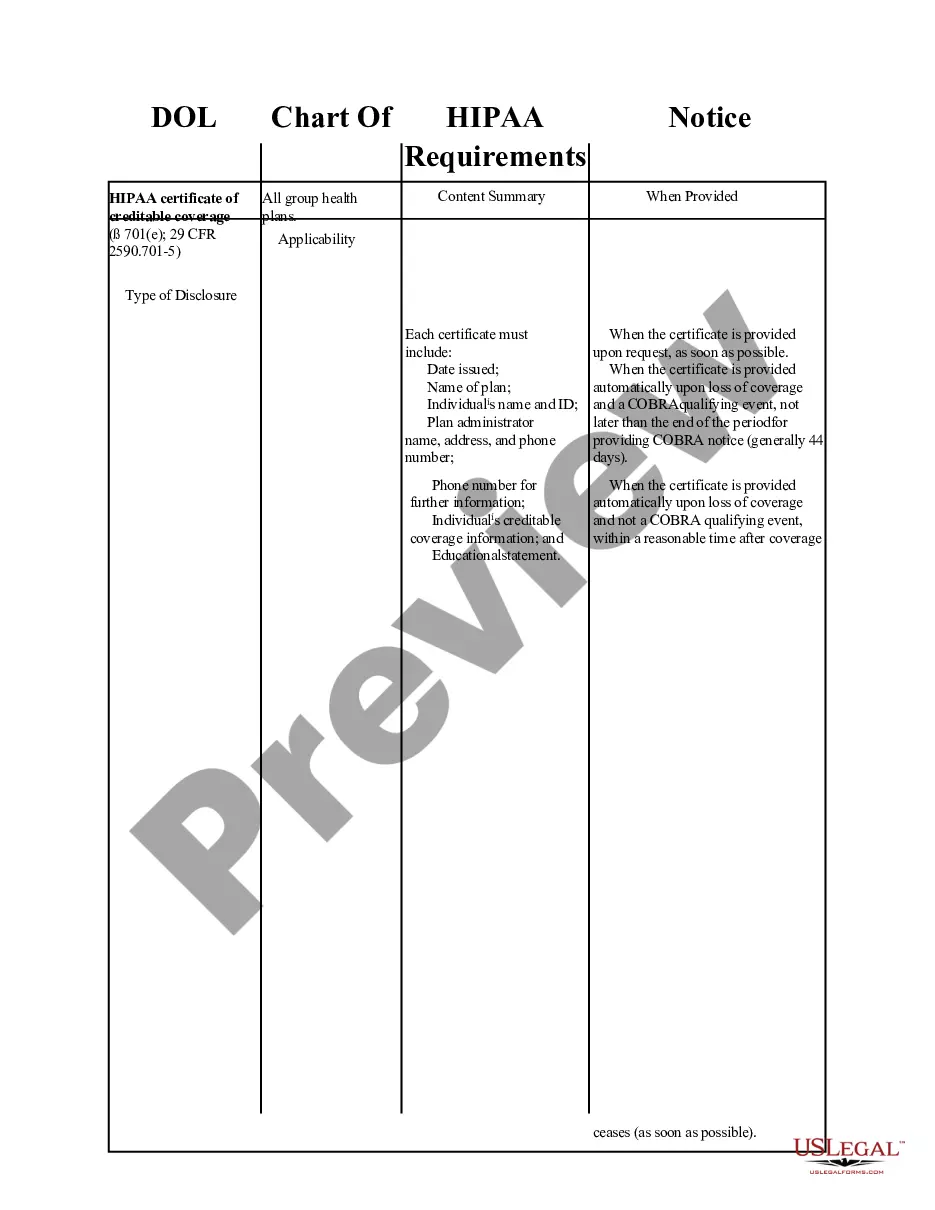
Kentucky HIPAA Certification Requirements
Description
How to fill out HIPAA Certification Requirements?
It is feasible to invest hours online searching for the legal document template that meets the federal and state stipulations you require.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal forms that are vetted by professionals.
It is easy to obtain or print the Kentucky HIPAA Certification Requirements from our platform.
If you want to find another version of the form, utilize the Search field to discover the template that fits your needs and requirements. After you locate the desired template, simply click Purchase now to proceed. Select the pricing plan you prefer, enter your details, and register an account on US Legal Forms. Complete the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to pay for the legal document. Choose the format of the document and download it to your device. Make modifications to your document if necessary. It is possible to fill out, edit, sign, and print the Kentucky HIPAA Certification Requirements. Acquire and print numerous document templates using the US Legal Forms website, which offers the largest collection of legal forms. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to address your business or personal needs.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and then click the Acquire button.
- Subsequently, you can fill out, edit, print, or sign the Kentucky HIPAA Certification Requirements.
- Every legal document template you purchase is yours indefinitely.
- To obtain another copy of any purchased form, navigate to the My documents section and click the appropriate button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms site for the first time, follow the straightforward instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for your chosen state/city.
- Check the form description to confirm you have selected the right form.
- If available, utilize the Preview button to review the document template as well.
Form popularity
FAQ
HIPAA only specifies that employees be retrained when the regulations change. However, the majority of employers do retraining on a yearly or 2 year basis. Our certificates are by default dated for 2 years so you would need to take a refresher training again after 2 years.
Organizations that do not have to follow the government's privacy rule known as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) include the following, according to the US Department of Health and Human Services: Life insurers. Employers. Workers' compensation carriers.
Covered entities (anyone providing treatment, payment, and operations in healthcare) and business associates (anyone who has access to patient information and provides support in treatment, payment, or operations) must meet HIPAA Compliance.
HIPAA requires that both covered entities and business associates provide HIPAA training to members of their workforce who handle PHI. This means that even small physician's offices need to train their personnel on HIPAA. Doctors need to be trained.
Introduction. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) required the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to develop regulations protecting the privacy and security of certain health information.
Hospitals, doctors, clinics, psychologists, dentists, chiropractors, nursing homes, and pharmacies are considered Healthcare Providers and need to be HIPAA compliant. Examples of Health Plans include health insurance companies, HMOs, company health plans, Medicare, and Medicaid.
Beyond the legal requirement to provide/undergo HIPAA training, HIPAA training is important because it demonstrates to members of the workforce how Covered Entities and Business Associates protect patient privacy and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI so members of the workforce can perform
HIPAA requires organizations to provide training for all employees, new workforce members, and periodic refresher training. The definition of periodic is not defined and can be left open to interpretation. However, most organizations train all employees on HIPAA annually. This is considered to be a best practice.
These training sessions should be periodic, which is accepted to be at least every two years, although the best practice adopted by many healthcare organizations is to provide annual refresher HIPAA training sessions.
HIPAA Compliance and Certification Services HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996) is United States legislation,which provides data privacy and security provisions to safeguard medical information.