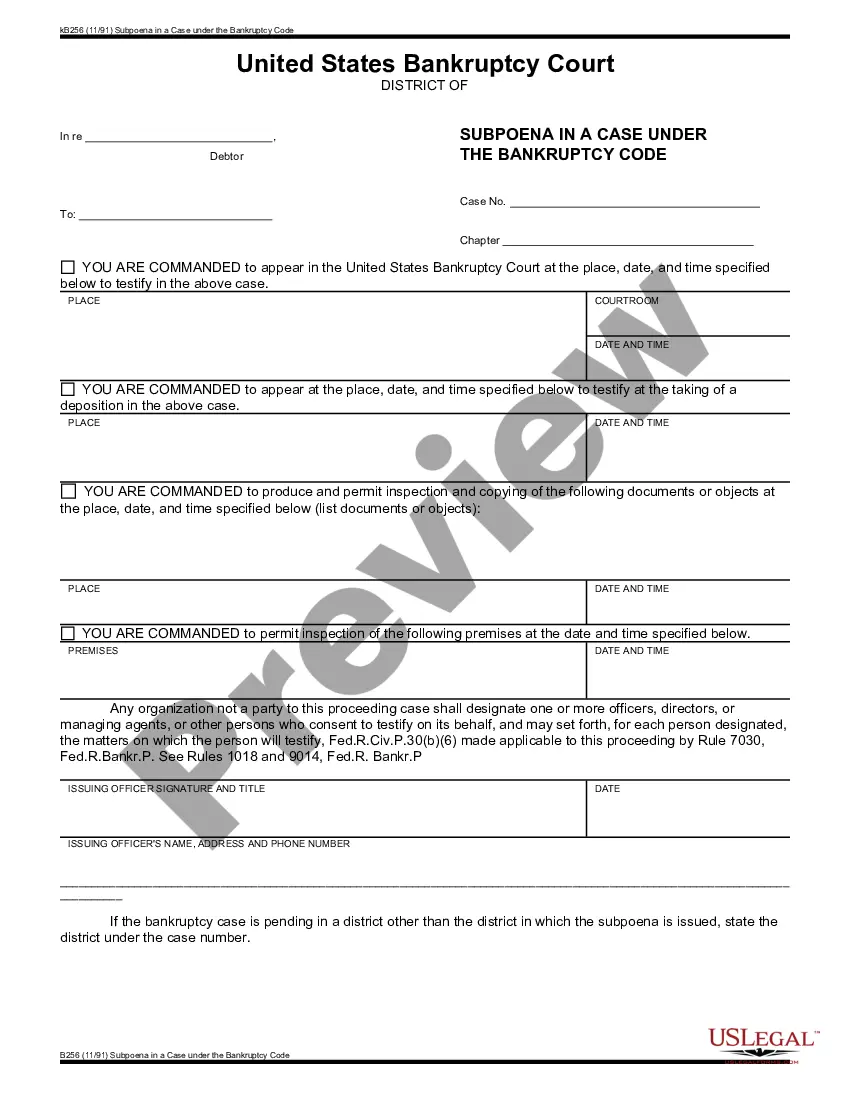
Kentucky Subpoena for Rule 2004 Examination - B 254
Description
How to fill out Subpoena For Rule 2004 Examination - B 254?
Choosing the best authorized document format can be quite a have a problem. Naturally, there are a variety of web templates available on the net, but how do you obtain the authorized develop you need? Use the US Legal Forms website. The services offers a huge number of web templates, like the Kentucky Subpoena for Rule 2004 Examination - B 254, that you can use for business and private needs. Each of the forms are inspected by experts and meet federal and state requirements.
Should you be presently authorized, log in to your bank account and click the Obtain option to have the Kentucky Subpoena for Rule 2004 Examination - B 254. Make use of your bank account to look from the authorized forms you may have acquired previously. Go to the My Forms tab of the bank account and obtain yet another copy from the document you need.
Should you be a fresh user of US Legal Forms, listed below are simple guidelines for you to comply with:
- Initially, make sure you have chosen the proper develop for your metropolis/area. You can examine the shape using the Preview option and read the shape explanation to guarantee this is the best for you.
- In the event the develop will not meet your expectations, make use of the Seach industry to get the proper develop.
- When you are positive that the shape is acceptable, click on the Purchase now option to have the develop.
- Opt for the costs program you want and enter in the needed information. Design your bank account and pay for your order making use of your PayPal bank account or charge card.
- Pick the data file formatting and down load the authorized document format to your product.
- Total, change and printing and signal the received Kentucky Subpoena for Rule 2004 Examination - B 254.
US Legal Forms may be the largest collection of authorized forms for which you can find numerous document web templates. Use the company to down load skillfully-produced documents that comply with condition requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
If the case has major errors, the Trustee may deny a discharge, need to convert from Chapter 7 to Chapter 13, or may file for a dismissal. For the worst-case scenarios, it may be sent to the AUSA (Assistant United States Attorney) for criminal prosecution. What Happens at a 2004 Examination Audit? Everything You Should Know bankruptcy-divorce.com ? what-happens-at-... bankruptcy-divorce.com ? what-happens-at-...
Authority to Take a Rule 2004 Exam: FRBP 2004 provides parties with the opportunity to conduct an examination of a person and/or documents, even though an adversary proceeding has not been filed. This is called a "Rule 2004 Examination".
Under Rule 2004, the bankruptcy court can order testimony or production of documents from anyone with relevant information about the filer's finances. Rule 2004 exams and Section 341 meetings do have some things in common. Both proceedings take place under oath and are recorded.
Bankruptcy Rule 2004 Examinations conducted pursuant to Rule 2004 have often been characterized as ?fishing expeditions? because the scope is far ranging with limited protection for defending parties. Colliers on Bankruptcy §2004.01 (16th Ed.
The purpose of Rule 2004 is to help a party in interest assess the nature and extent of the debtor's estate, reveal assets, examine transactions, and determine if wrongdoing, such as fraudulent conduct, may have occurred. Smart Code. The overall goal of a Rule 2004 examination is to benefit the estate. Rule 2004: Bankruptcy Discovery - Bloomberg Law bloomberglaw.com ? XCOIPIFC000000 ? b... bloomberglaw.com ? XCOIPIFC000000 ? b...
Authority to Take a Rule 2004 Exam: FRBP 2004 provides parties with the opportunity to conduct an examination of a person and/or documents, even though an adversary proceeding has not been filed. Rule 2004 Examination: Preliminary Discovery: Subpoena uscourts.gov ? the-central-guide ? rule-... uscourts.gov ? the-central-guide ? rule-...
It is similar to a deposition, sometimes requiring the production of documents. However, unlike a deposition, the witness who is the subject of a 2004 exam is not always entitled to attorney representation or cross-examination, and the right to object to questions is limited. What Is a 2004 Examination in Bankruptcy? - Nolo nolo.com ? legal-encyclopedia ? what-is-20... nolo.com ? legal-encyclopedia ? what-is-20...